(function(root, factory){
//UMD
if ( typeof define === "function" && define.amd ) {
define(function() {
return factory();
});
} else if (typeof module === "object") {
module.exports = factory();
} else {
root.Tone = factory();
}
}(this, function(){
"use strict";
var Tone;
//constructs the main Tone object
function Main(func){
Tone = func();
}
//invokes each of the modules with the main Tone object as the argument
function Module(func){
func(Tone);
} /**
* Tone.js
* @author Yotam Mann
* @license http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT MIT License
* @copyright 2014-2017 Yotam Mann
*/
Main(function () {
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// WEB AUDIO CONTEXT
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
function isUndef(val) {
return typeof val === 'undefined';
}
function isFunction(val) {
return typeof val === 'function';
}
var audioContext;
//polyfill for AudioContext and OfflineAudioContext
if (isUndef(window.AudioContext)) {
window.AudioContext = window.webkitAudioContext;
}
if (isUndef(window.OfflineAudioContext)) {
window.OfflineAudioContext = window.webkitOfflineAudioContext;
}
if (!isUndef(AudioContext)) {
audioContext = new AudioContext();
} else {
throw new Error('Web Audio is not supported in this browser');
}
//SHIMS////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if (!isFunction(AudioContext.prototype.createGain)) {
AudioContext.prototype.createGain = AudioContext.prototype.createGainNode;
}
if (!isFunction(AudioContext.prototype.createDelay)) {
AudioContext.prototype.createDelay = AudioContext.prototype.createDelayNode;
}
if (!isFunction(AudioContext.prototype.createPeriodicWave)) {
AudioContext.prototype.createPeriodicWave = AudioContext.prototype.createWaveTable;
}
if (!isFunction(AudioBufferSourceNode.prototype.start)) {
AudioBufferSourceNode.prototype.start = AudioBufferSourceNode.prototype.noteGrainOn;
}
if (!isFunction(AudioBufferSourceNode.prototype.stop)) {
AudioBufferSourceNode.prototype.stop = AudioBufferSourceNode.prototype.noteOff;
}
if (!isFunction(OscillatorNode.prototype.start)) {
OscillatorNode.prototype.start = OscillatorNode.prototype.noteOn;
}
if (!isFunction(OscillatorNode.prototype.stop)) {
OscillatorNode.prototype.stop = OscillatorNode.prototype.noteOff;
}
if (!isFunction(OscillatorNode.prototype.setPeriodicWave)) {
OscillatorNode.prototype.setPeriodicWave = OscillatorNode.prototype.setWaveTable;
}
//extend the connect function to include Tones
if (isUndef(AudioNode.prototype._nativeConnect)) {
AudioNode.prototype._nativeConnect = AudioNode.prototype.connect;
AudioNode.prototype.connect = function (B, outNum, inNum) {
if (B.input) {
if (Array.isArray(B.input)) {
if (isUndef(inNum)) {
inNum = 0;
}
this.connect(B.input[inNum]);
} else {
this.connect(B.input, outNum, inNum);
}
} else {
try {
if (B instanceof AudioNode) {
this._nativeConnect(B, outNum, inNum);
} else {
this._nativeConnect(B, outNum);
}
} catch (e) {
throw new Error('error connecting to node: ' + B);
}
}
};
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TONE
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* @class Tone is the base class of all other classes. It provides
* a lot of methods and functionality to all classes that extend
* it.
*
* @constructor
* @alias Tone
* @param {number} [inputs=1] the number of input nodes
* @param {number} [outputs=1] the number of output nodes
*/
var Tone = function (inputs, outputs) {
/**
* the input node(s)
* @type {GainNode|Array}
*/
if (isUndef(inputs) || inputs === 1) {
this.input = this.context.createGain();
} else if (inputs > 1) {
this.input = new Array(inputs);
}
/**
* the output node(s)
* @type {GainNode|Array}
*/
if (isUndef(outputs) || outputs === 1) {
this.output = this.context.createGain();
} else if (outputs > 1) {
this.output = new Array(inputs);
}
};
/**
* Set the parameters at once. Either pass in an
* object mapping parameters to values, or to set a
* single parameter, by passing in a string and value.
* The last argument is an optional ramp time which
* will ramp any signal values to their destination value
* over the duration of the rampTime.
* @param {Object|string} params
* @param {number=} value
* @param {Time=} rampTime
* @returns {Tone} this
* @example
* //set values using an object
* filter.set({
* "frequency" : 300,
* "type" : highpass
* });
* @example
* filter.set("type", "highpass");
* @example
* //ramp to the value 220 over 3 seconds.
* oscillator.set({
* "frequency" : 220
* }, 3);
*/
Tone.prototype.set = function (params, value, rampTime) {
if (this.isObject(params)) {
rampTime = value;
} else if (this.isString(params)) {
var tmpObj = {};
tmpObj[params] = value;
params = tmpObj;
}
paramLoop:
for (var attr in params) {
value = params[attr];
var parent = this;
if (attr.indexOf('.') !== -1) {
var attrSplit = attr.split('.');
for (var i = 0; i < attrSplit.length - 1; i++) {
parent = parent[attrSplit[i]];
if (parent instanceof Tone) {
attrSplit.splice(0, i + 1);
var innerParam = attrSplit.join('.');
parent.set(innerParam, value);
continue paramLoop;
}
}
attr = attrSplit[attrSplit.length - 1];
}
var param = parent[attr];
if (isUndef(param)) {
continue;
}
if (Tone.Signal && param instanceof Tone.Signal || Tone.Param && param instanceof Tone.Param) {
if (param.value !== value) {
if (isUndef(rampTime)) {
param.value = value;
} else {
param.rampTo(value, rampTime);
}
}
} else if (param instanceof AudioParam) {
if (param.value !== value) {
param.value = value;
}
} else if (param instanceof Tone) {
param.set(value);
} else if (param !== value) {
parent[attr] = value;
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Get the object's attributes. Given no arguments get
* will return all available object properties and their corresponding
* values. Pass in a single attribute to retrieve or an array
* of attributes. The attribute strings can also include a "."
* to access deeper properties.
* @example
* osc.get();
* //returns {"type" : "sine", "frequency" : 440, ...etc}
* @example
* osc.get("type");
* //returns { "type" : "sine"}
* @example
* //use dot notation to access deep properties
* synth.get(["envelope.attack", "envelope.release"]);
* //returns {"envelope" : {"attack" : 0.2, "release" : 0.4}}
* @param {Array=|string|undefined} params the parameters to get, otherwise will return
* all available.
* @returns {Object}
*/
Tone.prototype.get = function (params) {
if (isUndef(params)) {
params = this._collectDefaults(this.constructor);
} else if (this.isString(params)) {
params = [params];
}
var ret = {};
for (var i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
var attr = params[i];
var parent = this;
var subRet = ret;
if (attr.indexOf('.') !== -1) {
var attrSplit = attr.split('.');
for (var j = 0; j < attrSplit.length - 1; j++) {
var subAttr = attrSplit[j];
subRet[subAttr] = subRet[subAttr] || {};
subRet = subRet[subAttr];
parent = parent[subAttr];
}
attr = attrSplit[attrSplit.length - 1];
}
var param = parent[attr];
if (this.isObject(params[attr])) {
subRet[attr] = param.get();
} else if (Tone.Signal && param instanceof Tone.Signal) {
subRet[attr] = param.value;
} else if (Tone.Param && param instanceof Tone.Param) {
subRet[attr] = param.value;
} else if (param instanceof AudioParam) {
subRet[attr] = param.value;
} else if (param instanceof Tone) {
subRet[attr] = param.get();
} else if (!isFunction(param) && !isUndef(param)) {
subRet[attr] = param;
}
}
return ret;
};
/**
* collect all of the default attributes in one
* @private
* @param {function} constr the constructor to find the defaults from
* @return {Array} all of the attributes which belong to the class
*/
Tone.prototype._collectDefaults = function (constr) {
var ret = [];
if (!isUndef(constr.defaults)) {
ret = Object.keys(constr.defaults);
}
if (!isUndef(constr._super)) {
var superDefs = this._collectDefaults(constr._super);
//filter out repeats
for (var i = 0; i < superDefs.length; i++) {
if (ret.indexOf(superDefs[i]) === -1) {
ret.push(superDefs[i]);
}
}
}
return ret;
};
/**
* @returns {string} returns the name of the class as a string
*/
Tone.prototype.toString = function () {
for (var className in Tone) {
var isLetter = className[0].match(/^[A-Z]$/);
var sameConstructor = Tone[className] === this.constructor;
if (isFunction(Tone[className]) && isLetter && sameConstructor) {
return className;
}
}
return 'Tone';
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CLASS VARS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* A static pointer to the audio context accessible as Tone.context.
* @type {AudioContext}
*/
Tone.context = audioContext;
/**
* The audio context.
* @type {AudioContext}
*/
Tone.prototype.context = Tone.context;
/**
* the default buffer size
* @type {number}
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.prototype.bufferSize = 2048;
/**
* The delay time of a single frame (128 samples according to the spec).
* @type {number}
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.prototype.blockTime = 128 / Tone.context.sampleRate;
/**
* The time of a single sample
* @type {number}
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.prototype.sampleTime = 1 / Tone.context.sampleRate;
/**
* The number of inputs feeding into the AudioNode.
* For source nodes, this will be 0.
* @memberOf Tone#
* @name numberOfInputs
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.prototype, 'numberOfInputs', {
get: function () {
if (this.input) {
if (this.isArray(this.input)) {
return this.input.length;
} else {
return 1;
}
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
/**
* The number of outputs coming out of the AudioNode.
* For source nodes, this will be 0.
* @memberOf Tone#
* @name numberOfInputs
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.prototype, 'numberOfOutputs', {
get: function () {
if (this.output) {
if (this.isArray(this.output)) {
return this.output.length;
} else {
return 1;
}
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CONNECTIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* disconnect and dispose
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.dispose = function () {
if (!this.isUndef(this.input)) {
if (this.input instanceof AudioNode) {
this.input.disconnect();
}
this.input = null;
}
if (!this.isUndef(this.output)) {
if (this.output instanceof AudioNode) {
this.output.disconnect();
}
this.output = null;
}
return this;
};
/**
* a silent connection to the DesinationNode
* which will ensure that anything connected to it
* will not be garbage collected
*
* @private
*/
var _silentNode = null;
/**
* makes a connection to ensure that the node will not be garbage collected
* until 'dispose' is explicitly called
*
* use carefully. circumvents JS and WebAudio's normal Garbage Collection behavior
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.noGC = function () {
this.output.connect(_silentNode);
return this;
};
AudioNode.prototype.noGC = function () {
this.connect(_silentNode);
return this;
};
/**
* connect the output of a ToneNode to an AudioParam, AudioNode, or ToneNode
* @param {Tone | AudioParam | AudioNode} unit
* @param {number} [outputNum=0] optionally which output to connect from
* @param {number} [inputNum=0] optionally which input to connect to
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.connect = function (unit, outputNum, inputNum) {
if (Array.isArray(this.output)) {
outputNum = this.defaultArg(outputNum, 0);
this.output[outputNum].connect(unit, 0, inputNum);
} else {
this.output.connect(unit, outputNum, inputNum);
}
return this;
};
/**
* disconnect the output
* @param {Number|AudioNode} output Either the output index to disconnect
* if the output is an array, or the
* node to disconnect from.
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.disconnect = function (output) {
if (Array.isArray(this.output)) {
output = this.defaultArg(output, 0);
this.output[output].disconnect();
} else if (!this.isUndef(output)) {
this.output.disconnect(output);
} else {
this.output.disconnect();
}
return this;
};
/**
* connect together all of the arguments in series
* @param {...AudioParam|Tone|AudioNode} nodes
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.connectSeries = function () {
if (arguments.length > 1) {
var currentUnit = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
var toUnit = arguments[i];
currentUnit.connect(toUnit);
currentUnit = toUnit;
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Connect the output of this node to the rest of the nodes in series.
* @example
* //connect a node to an effect, panVol and then to the master output
* node.chain(effect, panVol, Tone.Master);
* @param {...AudioParam|Tone|AudioNode} nodes
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.chain = function () {
if (arguments.length > 0) {
var currentUnit = this;
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
var toUnit = arguments[i];
currentUnit.connect(toUnit);
currentUnit = toUnit;
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* connect the output of this node to the rest of the nodes in parallel.
* @param {...AudioParam|Tone|AudioNode} nodes
* @returns {Tone} this
*/
Tone.prototype.fan = function () {
if (arguments.length > 0) {
for (var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
this.connect(arguments[i]);
}
}
return this;
};
//give native nodes chain and fan methods
AudioNode.prototype.chain = Tone.prototype.chain;
AudioNode.prototype.fan = Tone.prototype.fan;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// UTILITIES / HELPERS / MATHS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* If the `given` parameter is undefined, use the `fallback`.
* If both `given` and `fallback` are object literals, it will
* return a deep copy which includes all of the parameters from both
* objects. If a parameter is undefined in given, it will return
* the fallback property.
*
* WARNING: if object is self referential, it will go into an an
* infinite recursive loop.
*
* @param {*} given
* @param {*} fallback
* @return {*}
*/
Tone.prototype.defaultArg = function (given, fallback) {
if (this.isObject(given) && this.isObject(fallback)) {
var ret = {};
//make a deep copy of the given object
for (var givenProp in given) {
ret[givenProp] = this.defaultArg(fallback[givenProp], given[givenProp]);
}
for (var fallbackProp in fallback) {
ret[fallbackProp] = this.defaultArg(given[fallbackProp], fallback[fallbackProp]);
}
return ret;
} else {
return isUndef(given) ? fallback : given;
}
};
/**
* returns the args as an options object with given arguments
* mapped to the names provided.
*
* if the args given is an array containing only one object, it is assumed
* that that's already the options object and will just return it.
*
* @param {Array} values the 'arguments' object of the function
* @param {Array} keys the names of the arguments as they
* should appear in the options object
* @param {Object=} defaults optional defaults to mixin to the returned
* options object
* @return {Object} the options object with the names mapped to the arguments
*/
Tone.prototype.optionsObject = function (values, keys, defaults) {
var options = {};
if (values.length === 1 && this.isObject(values[0])) {
options = values[0];
} else {
for (var i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
options[keys[i]] = values[i];
}
}
if (!this.isUndef(defaults)) {
return this.defaultArg(options, defaults);
} else {
return options;
}
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TYPE CHECKING
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* test if the arg is undefined
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is undefined
* @function
*/
Tone.prototype.isUndef = isUndef;
/**
* test if the arg is a function
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is a function
* @function
*/
Tone.prototype.isFunction = isFunction;
/**
* Test if the argument is a number.
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is a number
*/
Tone.prototype.isNumber = function (arg) {
return typeof arg === 'number';
};
/**
* Test if the given argument is an object literal (i.e. `{}`);
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is an object literal.
*/
Tone.prototype.isObject = function (arg) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(arg) === '[object Object]' && arg.constructor === Object;
};
/**
* Test if the argument is a boolean.
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is a boolean
*/
Tone.prototype.isBoolean = function (arg) {
return typeof arg === 'boolean';
};
/**
* Test if the argument is an Array
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is an array
*/
Tone.prototype.isArray = function (arg) {
return Array.isArray(arg);
};
/**
* Test if the argument is a string.
* @param {*} arg the argument to test
* @returns {boolean} true if the arg is a string
*/
Tone.prototype.isString = function (arg) {
return typeof arg === 'string';
};
/**
* An empty function.
* @static
*/
Tone.noOp = function () {
};
/**
* Make the property not writable. Internal use only.
* @private
* @param {string} property the property to make not writable
*/
Tone.prototype._readOnly = function (property) {
if (Array.isArray(property)) {
for (var i = 0; i < property.length; i++) {
this._readOnly(property[i]);
}
} else {
Object.defineProperty(this, property, {
writable: false,
enumerable: true
});
}
};
/**
* Make an attribute writeable. Interal use only.
* @private
* @param {string} property the property to make writable
*/
Tone.prototype._writable = function (property) {
if (Array.isArray(property)) {
for (var i = 0; i < property.length; i++) {
this._writable(property[i]);
}
} else {
Object.defineProperty(this, property, { writable: true });
}
};
/**
* Possible play states.
* @enum {string}
*/
Tone.State = {
Started: 'started',
Stopped: 'stopped',
Paused: 'paused'
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// GAIN CONVERSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Equal power gain scale. Good for cross-fading.
* @param {NormalRange} percent (0-1)
* @return {Number} output gain (0-1)
*/
Tone.prototype.equalPowerScale = function (percent) {
var piFactor = 0.5 * Math.PI;
return Math.sin(percent * piFactor);
};
/**
* Convert decibels into gain.
* @param {Decibels} db
* @return {Number}
*/
Tone.prototype.dbToGain = function (db) {
return Math.pow(2, db / 6);
};
/**
* Convert gain to decibels.
* @param {Number} gain (0-1)
* @return {Decibels}
*/
Tone.prototype.gainToDb = function (gain) {
return 20 * (Math.log(gain) / Math.LN10);
};
/**
* Convert an interval (in semitones) to a frequency ratio.
* @param {Interval} interval the number of semitones above the base note
* @return {number} the frequency ratio
* @example
* tone.intervalToFrequencyRatio(0); // 1
* tone.intervalToFrequencyRatio(12); // 2
* tone.intervalToFrequencyRatio(-12); // 0.5
*/
Tone.prototype.intervalToFrequencyRatio = function (interval) {
return Math.pow(2, interval / 12);
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TIMING
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Return the current time of the AudioContext clock.
* @return {Number} the currentTime from the AudioContext
*/
Tone.prototype.now = function () {
return this.context.currentTime;
};
/**
* Return the current time of the AudioContext clock.
* @return {Number} the currentTime from the AudioContext
* @static
*/
Tone.now = function () {
return Tone.context.currentTime;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// INHERITANCE
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* have a child inherit all of Tone's (or a parent's) prototype
* to inherit the parent's properties, make sure to call
* Parent.call(this) in the child's constructor
*
* based on closure library's inherit function
*
* @static
* @param {function} child
* @param {function=} parent (optional) parent to inherit from
* if no parent is supplied, the child
* will inherit from Tone
*/
Tone.extend = function (child, parent) {
if (isUndef(parent)) {
parent = Tone;
}
function TempConstructor() {
}
TempConstructor.prototype = parent.prototype;
child.prototype = new TempConstructor();
/** @override */
child.prototype.constructor = child;
child._super = parent;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CONTEXT
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* array of callbacks to be invoked when a new context is added
* @private
* @private
*/
var newContextCallbacks = [];
/**
* invoke this callback when a new context is added
* will be invoked initially with the first context
* @private
* @static
* @param {function(AudioContext)} callback the callback to be invoked
* with the audio context
*/
Tone._initAudioContext = function (callback) {
//invoke the callback with the existing AudioContext
callback(Tone.context);
//add it to the array
newContextCallbacks.push(callback);
};
/**
* Tone automatically creates a context on init, but if you are working
* with other libraries which also create an AudioContext, it can be
* useful to set your own. If you are going to set your own context,
* be sure to do it at the start of your code, before creating any objects.
* @static
* @param {AudioContext} ctx The new audio context to set
*/
Tone.setContext = function (ctx) {
//set the prototypes
Tone.prototype.context = ctx;
Tone.context = ctx;
//invoke all the callbacks
for (var i = 0; i < newContextCallbacks.length; i++) {
newContextCallbacks[i](ctx);
}
};
//setup the context
Tone._initAudioContext(function (audioContext) {
//set the blockTime
Tone.prototype.blockTime = 128 / audioContext.sampleRate;
Tone.prototype.sampleTime = 1 / audioContext.sampleRate;
_silentNode = audioContext.createGain();
_silentNode.gain.value = 0;
_silentNode.connect(audioContext.destination);
});
Tone.version = 'r9';
// allow optional silencing of this log
if (!window.TONE_SILENCE_VERSION_LOGGING) {
console.log('%c * Tone.js ' + Tone.version + ' * ', 'background: #000; color: #fff');
}
return Tone;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Base class for all Signals. Used Internally.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.SignalBase = function () {
};
Tone.extend(Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* When signals connect to other signals or AudioParams,
* they take over the output value of that signal or AudioParam.
* For all other nodes, the behavior is the same as a default connect.
*
* @override
* @param {AudioParam|AudioNode|Tone.Signal|Tone} node
* @param {number} [outputNumber=0] The output number to connect from.
* @param {number} [inputNumber=0] The input number to connect to.
* @returns {Tone.SignalBase} this
*/
Tone.SignalBase.prototype.connect = function (node, outputNumber, inputNumber) {
//zero it out so that the signal can have full control
if (Tone.Signal && Tone.Signal === node.constructor || Tone.Param && Tone.Param === node.constructor || Tone.TimelineSignal && Tone.TimelineSignal === node.constructor) {
//cancel changes
node._param.cancelScheduledValues(0);
//reset the value
node._param.value = 0;
//mark the value as overridden
node.overridden = true;
} else if (node instanceof AudioParam) {
node.cancelScheduledValues(0);
node.value = 0;
}
Tone.prototype.connect.call(this, node, outputNumber, inputNumber);
return this;
};
return Tone.SignalBase;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Wraps the native Web Audio API
* [WaveShaperNode](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#the-waveshapernode-interface).
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @param {function|Array|Number} mapping The function used to define the values.
* The mapping function should take two arguments:
* the first is the value at the current position
* and the second is the array position.
* If the argument is an array, that array will be
* set as the wave shaping function. The input
* signal is an AudioRange [-1, 1] value and the output
* signal can take on any numerical values.
*
* @param {Number} [bufferLen=1024] The length of the WaveShaperNode buffer.
* @example
* var timesTwo = new Tone.WaveShaper(function(val){
* return val * 2;
* }, 2048);
* @example
* //a waveshaper can also be constructed with an array of values
* var invert = new Tone.WaveShaper([1, -1]);
*/
Tone.WaveShaper = function (mapping, bufferLen) {
/**
* the waveshaper
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._shaper = this.input = this.output = this.context.createWaveShaper();
/**
* the waveshapers curve
* @type {Float32Array}
* @private
*/
this._curve = null;
if (Array.isArray(mapping)) {
this.curve = mapping;
} else if (isFinite(mapping) || this.isUndef(mapping)) {
this._curve = new Float32Array(this.defaultArg(mapping, 1024));
} else if (this.isFunction(mapping)) {
this._curve = new Float32Array(this.defaultArg(bufferLen, 1024));
this.setMap(mapping);
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.WaveShaper, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* Uses a mapping function to set the value of the curve.
* @param {function} mapping The function used to define the values.
* The mapping function take two arguments:
* the first is the value at the current position
* which goes from -1 to 1 over the number of elements
* in the curve array. The second argument is the array position.
* @returns {Tone.WaveShaper} this
* @example
* //map the input signal from [-1, 1] to [0, 10]
* shaper.setMap(function(val, index){
* return (val + 1) * 5;
* })
*/
Tone.WaveShaper.prototype.setMap = function (mapping) {
for (var i = 0, len = this._curve.length; i < len; i++) {
var normalized = i / (len - 1) * 2 - 1;
this._curve[i] = mapping(normalized, i);
}
this._shaper.curve = this._curve;
return this;
};
/**
* The array to set as the waveshaper curve. For linear curves
* array length does not make much difference, but for complex curves
* longer arrays will provide smoother interpolation.
* @memberOf Tone.WaveShaper#
* @type {Array}
* @name curve
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.WaveShaper.prototype, 'curve', {
get: function () {
return this._shaper.curve;
},
set: function (mapping) {
this._curve = new Float32Array(mapping);
this._shaper.curve = this._curve;
}
});
/**
* Specifies what type of oversampling (if any) should be used when
* applying the shaping curve. Can either be "none", "2x" or "4x".
* @memberOf Tone.WaveShaper#
* @type {string}
* @name oversample
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.WaveShaper.prototype, 'oversample', {
get: function () {
return this._shaper.oversample;
},
set: function (oversampling) {
if ([
'none',
'2x',
'4x'
].indexOf(oversampling) !== -1) {
this._shaper.oversample = oversampling;
} else {
throw new RangeError('Tone.WaveShaper: oversampling must be either \'none\', \'2x\', or \'4x\'');
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.WaveShaper} this
*/
Tone.WaveShaper.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._shaper.disconnect();
this._shaper = null;
this._curve = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.WaveShaper;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.TimeBase is a flexible encoding of time
* which can be evaluated to and from a string.
* Parsing code modified from https://code.google.com/p/tapdigit/
* Copyright 2011 2012 Ariya Hidayat, New BSD License
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Time} val The time value as a number or string
* @param {String=} units Unit values
* @example
* Tone.TimeBase(4, "n")
* Tone.TimeBase(2, "t")
* Tone.TimeBase("2t").add("1m")
* Tone.TimeBase("2t + 1m");
*/
Tone.TimeBase = function (val, units) {
//allows it to be constructed with or without 'new'
if (this instanceof Tone.TimeBase) {
/**
* Any expressions parsed from the Time
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._expr = this._noOp;
if (val instanceof Tone.TimeBase) {
this.copy(val);
} else if (!this.isUndef(units) || this.isNumber(val)) {
//default units
units = this.defaultArg(units, this._defaultUnits);
var method = this._primaryExpressions[units].method;
this._expr = method.bind(this, val);
} else if (this.isString(val)) {
this.set(val);
} else if (this.isUndef(val)) {
//default expression
this._expr = this._defaultExpr();
}
} else {
return new Tone.TimeBase(val, units);
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.TimeBase);
/**
* Repalce the current time value with the value
* given by the expression string.
* @param {String} exprString
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} this
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.set = function (exprString) {
this._expr = this._parseExprString(exprString);
return this;
};
/**
* Return a clone of the TimeBase object.
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} The new cloned Tone.TimeBase
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.clone = function () {
var instance = new this.constructor();
instance.copy(this);
return instance;
};
/**
* Copies the value of time to this Time
* @param {Tone.TimeBase} time
* @return {TimeBase}
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.copy = function (time) {
var val = time._expr();
return this.set(val);
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// ABSTRACT SYNTAX TREE PARSER
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* All the primary expressions.
* @private
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._primaryExpressions = {
'n': {
regexp: /^(\d+)n/i,
method: function (value) {
value = parseInt(value);
if (value === 1) {
return this._beatsToUnits(this._timeSignature());
} else {
return this._beatsToUnits(4 / value);
}
}
},
't': {
regexp: /^(\d+)t/i,
method: function (value) {
value = parseInt(value);
return this._beatsToUnits(8 / (parseInt(value) * 3));
}
},
'm': {
regexp: /^(\d+)m/i,
method: function (value) {
return this._beatsToUnits(parseInt(value) * this._timeSignature());
}
},
'i': {
regexp: /^(\d+)i/i,
method: function (value) {
return this._ticksToUnits(parseInt(value));
}
},
'hz': {
regexp: /^(\d+(?:\.\d+)?)hz/i,
method: function (value) {
return this._frequencyToUnits(parseFloat(value));
}
},
'tr': {
regexp: /^(\d+(?:\.\d+)?):(\d+(?:\.\d+)?):?(\d+(?:\.\d+)?)?/,
method: function (m, q, s) {
var total = 0;
if (m && m !== '0') {
total += this._beatsToUnits(this._timeSignature() * parseFloat(m));
}
if (q && q !== '0') {
total += this._beatsToUnits(parseFloat(q));
}
if (s && s !== '0') {
total += this._beatsToUnits(parseFloat(s) / 4);
}
return total;
}
},
's': {
regexp: /^(\d+(?:\.\d+)?s)/,
method: function (value) {
return this._secondsToUnits(parseFloat(value));
}
},
'samples': {
regexp: /^(\d+)samples/,
method: function (value) {
return parseInt(value) / this.context.sampleRate;
}
},
'default': {
regexp: /^(\d+(?:\.\d+)?)/,
method: function (value) {
return this._primaryExpressions[this._defaultUnits].method.call(this, value);
}
}
};
/**
* All the binary expressions that TimeBase can accept.
* @private
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._binaryExpressions = {
'+': {
regexp: /^\+/,
precedence: 2,
method: function (lh, rh) {
return lh() + rh();
}
},
'-': {
regexp: /^\-/,
precedence: 2,
method: function (lh, rh) {
return lh() - rh();
}
},
'*': {
regexp: /^\*/,
precedence: 1,
method: function (lh, rh) {
return lh() * rh();
}
},
'/': {
regexp: /^\//,
precedence: 1,
method: function (lh, rh) {
return lh() / rh();
}
}
};
/**
* All the unary expressions.
* @private
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._unaryExpressions = {
'neg': {
regexp: /^\-/,
method: function (lh) {
return -lh();
}
}
};
/**
* Syntactic glue which holds expressions together
* @private
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._syntaxGlue = {
'(': { regexp: /^\(/ },
')': { regexp: /^\)/ }
};
/**
* tokenize the expression based on the Expressions object
* @param {string} expr
* @return {Object} returns two methods on the tokenized list, next and peek
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._tokenize = function (expr) {
var position = -1;
var tokens = [];
while (expr.length > 0) {
expr = expr.trim();
var token = getNextToken(expr, this);
tokens.push(token);
expr = expr.substr(token.value.length);
}
function getNextToken(expr, context) {
var expressions = [
'_binaryExpressions',
'_unaryExpressions',
'_primaryExpressions',
'_syntaxGlue'
];
for (var i = 0; i < expressions.length; i++) {
var group = context[expressions[i]];
for (var opName in group) {
var op = group[opName];
var reg = op.regexp;
var match = expr.match(reg);
if (match !== null) {
return {
method: op.method,
precedence: op.precedence,
regexp: op.regexp,
value: match[0]
};
}
}
}
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.TimeBase: Unexpected token ' + expr);
}
return {
next: function () {
return tokens[++position];
},
peek: function () {
return tokens[position + 1];
}
};
};
/**
* Given a token, find the value within the groupName
* @param {Object} token
* @param {String} groupName
* @param {Number} precedence
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._matchGroup = function (token, group, prec) {
var ret = false;
if (!this.isUndef(token)) {
for (var opName in group) {
var op = group[opName];
if (op.regexp.test(token.value)) {
if (!this.isUndef(prec)) {
if (op.precedence === prec) {
return op;
}
} else {
return op;
}
}
}
}
return ret;
};
/**
* Match a binary expression given the token and the precedence
* @param {Lexer} lexer
* @param {Number} precedence
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._parseBinary = function (lexer, precedence) {
if (this.isUndef(precedence)) {
precedence = 2;
}
var expr;
if (precedence < 0) {
expr = this._parseUnary(lexer);
} else {
expr = this._parseBinary(lexer, precedence - 1);
}
var token = lexer.peek();
while (token && this._matchGroup(token, this._binaryExpressions, precedence)) {
token = lexer.next();
expr = token.method.bind(this, expr, this._parseBinary(lexer, precedence - 1));
token = lexer.peek();
}
return expr;
};
/**
* Match a unary expression.
* @param {Lexer} lexer
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._parseUnary = function (lexer) {
var token, expr;
token = lexer.peek();
var op = this._matchGroup(token, this._unaryExpressions);
if (op) {
token = lexer.next();
expr = this._parseUnary(lexer);
return op.method.bind(this, expr);
}
return this._parsePrimary(lexer);
};
/**
* Match a primary expression (a value).
* @param {Lexer} lexer
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._parsePrimary = function (lexer) {
var token, expr;
token = lexer.peek();
if (this.isUndef(token)) {
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.TimeBase: Unexpected end of expression');
}
if (this._matchGroup(token, this._primaryExpressions)) {
token = lexer.next();
var matching = token.value.match(token.regexp);
return token.method.bind(this, matching[1], matching[2], matching[3]);
}
if (token && token.value === '(') {
lexer.next();
expr = this._parseBinary(lexer);
token = lexer.next();
if (!(token && token.value === ')')) {
throw new SyntaxError('Expected )');
}
return expr;
}
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.TimeBase: Cannot process token ' + token.value);
};
/**
* Recursively parse the string expression into a syntax tree.
* @param {string} expr
* @return {Function} the bound method to be evaluated later
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._parseExprString = function (exprString) {
if (!this.isString(exprString)) {
exprString = exprString.toString();
}
var lexer = this._tokenize(exprString);
var tree = this._parseBinary(lexer);
return tree;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// DEFAULTS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* The initial expression value
* @return {Number} The initial value 0
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._noOp = function () {
return 0;
};
/**
* The default expression value if no arguments are given
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._defaultExpr = function () {
return this._noOp;
};
/**
* The default units if none are given.
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._defaultUnits = 's';
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// UNIT CONVERSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Returns the value of a frequency in the current units
* @param {Frequency} freq
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._frequencyToUnits = function (freq) {
return 1 / freq;
};
/**
* Return the value of the beats in the current units
* @param {Number} beats
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._beatsToUnits = function (beats) {
return 60 / Tone.Transport.bpm.value * beats;
};
/**
* Returns the value of a second in the current units
* @param {Seconds} seconds
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._secondsToUnits = function (seconds) {
return seconds;
};
/**
* Returns the value of a tick in the current time units
* @param {Ticks} ticks
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._ticksToUnits = function (ticks) {
return ticks * (this._beatsToUnits(1) / Tone.Transport.PPQ);
};
/**
* Return the time signature.
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._timeSignature = function () {
return Tone.Transport.timeSignature;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// EXPRESSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Push an expression onto the expression list
* @param {Time} val
* @param {String} type
* @param {String} units
* @return {Tone.TimeBase}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype._pushExpr = function (val, name, units) {
//create the expression
if (!(val instanceof Tone.TimeBase)) {
val = new this.constructor(val, units);
}
this._expr = this._binaryExpressions[name].method.bind(this, this._expr, val._expr);
return this;
};
/**
* Add to the current value.
* @param {Time} val The value to add
* @param {String=} units Optional units to use with the value.
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} this
* @example
* Tone.TimeBase("2m").add("1m"); //"3m"
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.add = function (val, units) {
return this._pushExpr(val, '+', units);
};
/**
* Subtract the value from the current time.
* @param {Time} val The value to subtract
* @param {String=} units Optional units to use with the value.
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} this
* @example
* Tone.TimeBase("2m").sub("1m"); //"1m"
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.sub = function (val, units) {
return this._pushExpr(val, '-', units);
};
/**
* Multiply the current value by the given time.
* @param {Time} val The value to multiply
* @param {String=} units Optional units to use with the value.
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} this
* @example
* Tone.TimeBase("2m").mult("2"); //"4m"
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.mult = function (val, units) {
return this._pushExpr(val, '*', units);
};
/**
* Divide the current value by the given time.
* @param {Time} val The value to divide by
* @param {String=} units Optional units to use with the value.
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} this
* @example
* Tone.TimeBase("2m").div(2); //"1m"
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.div = function (val, units) {
return this._pushExpr(val, '/', units);
};
/**
* Evaluate the time value. Returns the time
* in seconds.
* @return {Seconds}
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.eval = function () {
return this._expr();
};
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.TimeBase} this
*/
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.dispose = function () {
this._expr = null;
};
return Tone.TimeBase;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Time is a primitive type for encoding Time values.
* Eventually all time values are evaluated to seconds
* using the `eval` method. Tone.Time can be constructed
* with or without the `new` keyword. Tone.Time can be passed
* into the parameter of any method which takes time as an argument.
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.TimeBase}
* @param {String|Number} val The time value.
* @param {String=} units The units of the value.
* @example
* var t = Tone.Time("4n");//encodes a quarter note
* t.mult(4); // multiply that value by 4
* t.toNotation(); //returns "1m"
*/
Tone.Time = function (val, units) {
if (this instanceof Tone.Time) {
/**
* If the current clock time should
* be added to the output
* @type {Boolean}
* @private
*/
this._plusNow = false;
Tone.TimeBase.call(this, val, units);
} else {
return new Tone.Time(val, units);
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Time, Tone.TimeBase);
//clone the expressions so that
//we can add more without modifying the original
Tone.Time.prototype._unaryExpressions = Object.create(Tone.TimeBase.prototype._unaryExpressions);
/*
* Adds an additional unary expression
* which quantizes values to the next subdivision
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Time.prototype._unaryExpressions.quantize = {
regexp: /^@/,
method: function (rh) {
return Tone.Transport.nextSubdivision(rh());
}
};
/*
* Adds an additional unary expression
* which adds the current clock time.
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Time.prototype._unaryExpressions.now = {
regexp: /^\+/,
method: function (lh) {
this._plusNow = true;
return lh();
}
};
/**
* Quantize the time by the given subdivision. Optionally add a
* percentage which will move the time value towards the ideal
* quantized value by that percentage.
* @param {Number|Time} val The subdivision to quantize to
* @param {NormalRange} [percent=1] Move the time value
* towards the quantized value by
* a percentage.
* @return {Tone.Time} this
* @example
* Tone.Time(21).quantize(2).eval() //returns 22
* Tone.Time(0.6).quantize("4n", 0.5).eval() //returns 0.55
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.quantize = function (subdiv, percent) {
percent = this.defaultArg(percent, 1);
this._expr = function (expr, subdivision, percent) {
expr = expr();
subdivision = subdivision.toSeconds();
var multiple = Math.round(expr / subdivision);
var ideal = multiple * subdivision;
var diff = ideal - expr;
return expr + diff * percent;
}.bind(this, this._expr, new this.constructor(subdiv), percent);
return this;
};
/**
* Adds the clock time to the time expression at the
* moment of evaluation.
* @return {Tone.Time} this
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.addNow = function () {
this._plusNow = true;
return this;
};
/**
* @override
* Override the default value return when no arguments are passed in.
* The default value is 'now'
* @private
*/
Tone.Time.prototype._defaultExpr = function () {
this._plusNow = true;
return this._noOp;
};
/**
* Copies the value of time to this Time
* @param {Tone.Time} time
* @return {Time}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.copy = function (time) {
Tone.TimeBase.prototype.copy.call(this, time);
this._plusNow = time._plusNow;
return this;
};
//CONVERSIONS//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Convert a Time to Notation. Values will be thresholded to the nearest 128th note.
* @return {Notation}
* @example
* //if the Transport is at 120bpm:
* Tone.Time(2).toNotation();//returns "1m"
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toNotation = function () {
var time = this.toSeconds();
var testNotations = [
'1m',
'2n',
'4n',
'8n',
'16n',
'32n',
'64n',
'128n'
];
var retNotation = this._toNotationHelper(time, testNotations);
//try the same thing but with tripelets
var testTripletNotations = [
'1m',
'2n',
'2t',
'4n',
'4t',
'8n',
'8t',
'16n',
'16t',
'32n',
'32t',
'64n',
'64t',
'128n'
];
var retTripletNotation = this._toNotationHelper(time, testTripletNotations);
//choose the simpler expression of the two
if (retTripletNotation.split('+').length < retNotation.split('+').length) {
return retTripletNotation;
} else {
return retNotation;
}
};
/**
* Helper method for Tone.toNotation
* @param {Number} units
* @param {Array} testNotations
* @return {String}
* @private
*/
Tone.Time.prototype._toNotationHelper = function (units, testNotations) {
//the threshold is the last value in the array
var threshold = this._notationToUnits(testNotations[testNotations.length - 1]);
var retNotation = '';
for (var i = 0; i < testNotations.length; i++) {
var notationTime = this._notationToUnits(testNotations[i]);
//account for floating point errors (i.e. round up if the value is 0.999999)
var multiple = units / notationTime;
var floatingPointError = 0.000001;
if (1 - multiple % 1 < floatingPointError) {
multiple += floatingPointError;
}
multiple = Math.floor(multiple);
if (multiple > 0) {
if (multiple === 1) {
retNotation += testNotations[i];
} else {
retNotation += multiple.toString() + '*' + testNotations[i];
}
units -= multiple * notationTime;
if (units < threshold) {
break;
} else {
retNotation += ' + ';
}
}
}
if (retNotation === '') {
retNotation = '0';
}
return retNotation;
};
/**
* Convert a notation value to the current units
* @param {Notation} notation
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Time.prototype._notationToUnits = function (notation) {
var primaryExprs = this._primaryExpressions;
var notationExprs = [
primaryExprs.n,
primaryExprs.t,
primaryExprs.m
];
for (var i = 0; i < notationExprs.length; i++) {
var expr = notationExprs[i];
var match = notation.match(expr.regexp);
if (match) {
return expr.method.call(this, match[1]);
}
}
};
/**
* Return the time encoded as Bars:Beats:Sixteenths.
* @return {BarsBeatsSixteenths}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toBarsBeatsSixteenths = function () {
var quarterTime = this._beatsToUnits(1);
var quarters = this.toSeconds() / quarterTime;
var measures = Math.floor(quarters / this._timeSignature());
var sixteenths = quarters % 1 * 4;
quarters = Math.floor(quarters) % this._timeSignature();
sixteenths = sixteenths.toString();
if (sixteenths.length > 3) {
sixteenths = parseFloat(sixteenths).toFixed(3);
}
var progress = [
measures,
quarters,
sixteenths
];
return progress.join(':');
};
/**
* Return the time in ticks.
* @return {Ticks}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toTicks = function () {
var quarterTime = this._beatsToUnits(1);
var quarters = this.eval() / quarterTime;
return Math.floor(quarters * Tone.Transport.PPQ);
};
/**
* Return the time in samples
* @return {Samples}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toSamples = function () {
return this.toSeconds() * this.context.sampleRate;
};
/**
* Return the time as a frequency value
* @return {Frequency}
* @example
* Tone.Time(2).toFrequency(); //0.5
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toFrequency = function () {
return 1 / this.toSeconds();
};
/**
* Return the time in seconds.
* @return {Seconds}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toSeconds = function () {
return this.eval();
};
/**
* Return the time in milliseconds.
* @return {Milliseconds}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.toMilliseconds = function () {
return this.toSeconds() * 1000;
};
/**
* Return the time in seconds.
* @return {Seconds}
*/
Tone.Time.prototype.eval = function () {
var val = this._expr();
return val + (this._plusNow ? this.now() : 0);
};
return Tone.Time;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Frequency is a primitive type for encoding Frequency values.
* Eventually all time values are evaluated to hertz
* using the `eval` method.
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.TimeBase}
* @param {String|Number} val The time value.
* @param {String=} units The units of the value.
* @example
* Tone.Frequency("C3").eval() // 261
* Tone.Frequency(38, "midi").eval() //
* Tone.Frequency("C3").transpose(4).eval();
*/
Tone.Frequency = function (val, units) {
if (this instanceof Tone.Frequency) {
Tone.TimeBase.call(this, val, units);
} else {
return new Tone.Frequency(val, units);
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Frequency, Tone.TimeBase);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AUGMENT BASE EXPRESSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//clone the expressions so that
//we can add more without modifying the original
Tone.Frequency.prototype._primaryExpressions = Object.create(Tone.TimeBase.prototype._primaryExpressions);
/*
* midi type primary expression
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._primaryExpressions.midi = {
regexp: /^(\d+(?:\.\d+)?midi)/,
method: function (value) {
return this.midiToFrequency(value);
}
};
/*
* note type primary expression
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._primaryExpressions.note = {
regexp: /^([a-g]{1}(?:b|#|x|bb)?)(-?[0-9]+)/i,
method: function (pitch, octave) {
var index = noteToScaleIndex[pitch.toLowerCase()];
var noteNumber = index + (parseInt(octave) + 1) * 12;
return this.midiToFrequency(noteNumber);
}
};
/*
* BeatsBarsSixteenths type primary expression
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._primaryExpressions.tr = {
regexp: /^(\d+(?:\.\d+)?):(\d+(?:\.\d+)?):?(\d+(?:\.\d+)?)?/,
method: function (m, q, s) {
var total = 1;
if (m && m !== '0') {
total *= this._beatsToUnits(this._timeSignature() * parseFloat(m));
}
if (q && q !== '0') {
total *= this._beatsToUnits(parseFloat(q));
}
if (s && s !== '0') {
total *= this._beatsToUnits(parseFloat(s) / 4);
}
return total;
}
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// EXPRESSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Transposes the frequency by the given number of semitones.
* @param {Interval} interval
* @return {Tone.Frequency} this
* @example
* Tone.Frequency("A4").transpose(3); //"C5"
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.transpose = function (interval) {
this._expr = function (expr, interval) {
var val = expr();
return val * this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(interval);
}.bind(this, this._expr, interval);
return this;
};
/**
* Takes an array of semitone intervals and returns
* an array of frequencies transposed by those intervals.
* @param {Array} intervals
* @return {Tone.Frequency} this
* @example
* Tone.Frequency("A4").harmonize([0, 3, 7]); //["A4", "C5", "E5"]
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.harmonize = function (intervals) {
this._expr = function (expr, intervals) {
var val = expr();
var ret = [];
for (var i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
ret[i] = val * this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(intervals[i]);
}
return ret;
}.bind(this, this._expr, intervals);
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// UNIT CONVERSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Return the value of the frequency as a MIDI note
* @return {MIDI}
* @example
* Tone.Frequency("C4").toMidi(); //60
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.toMidi = function () {
return this.frequencyToMidi(this.eval());
};
/**
* Return the value of the frequency in Scientific Pitch Notation
* @return {Note}
* @example
* Tone.Frequency(69, "midi").toNote(); //"A4"
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.toNote = function () {
var freq = this.eval();
var log = Math.log(freq / Tone.Frequency.A4) / Math.LN2;
var noteNumber = Math.round(12 * log) + 57;
var octave = Math.floor(noteNumber / 12);
if (octave < 0) {
noteNumber += -12 * octave;
}
var noteName = scaleIndexToNote[noteNumber % 12];
return noteName + octave.toString();
};
/**
* Return the duration of one cycle in seconds.
* @return {Seconds}
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.toSeconds = function () {
return 1 / this.eval();
};
/**
* Return the value in Hertz
* @return {Frequency}
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.toFrequency = function () {
return this.eval();
};
/**
* Return the duration of one cycle in ticks
* @return {Ticks}
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.toTicks = function () {
var quarterTime = this._beatsToUnits(1);
var quarters = this.eval() / quarterTime;
return Math.floor(quarters * Tone.Transport.PPQ);
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// UNIT CONVERSIONS HELPERS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Returns the value of a frequency in the current units
* @param {Frequency} freq
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._frequencyToUnits = function (freq) {
return freq;
};
/**
* Returns the value of a tick in the current time units
* @param {Ticks} ticks
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._ticksToUnits = function (ticks) {
return 1 / (ticks * 60 / (Tone.Transport.bpm.value * Tone.Transport.PPQ));
};
/**
* Return the value of the beats in the current units
* @param {Number} beats
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._beatsToUnits = function (beats) {
return 1 / Tone.TimeBase.prototype._beatsToUnits.call(this, beats);
};
/**
* Returns the value of a second in the current units
* @param {Seconds} seconds
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._secondsToUnits = function (seconds) {
return 1 / seconds;
};
/**
* The default units if none are given.
* @private
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype._defaultUnits = 'hz';
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// FREQUENCY CONVERSIONS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Note to scale index
* @type {Object}
*/
var noteToScaleIndex = {
'cbb': -2,
'cb': -1,
'c': 0,
'c#': 1,
'cx': 2,
'dbb': 0,
'db': 1,
'd': 2,
'd#': 3,
'dx': 4,
'ebb': 2,
'eb': 3,
'e': 4,
'e#': 5,
'ex': 6,
'fbb': 3,
'fb': 4,
'f': 5,
'f#': 6,
'fx': 7,
'gbb': 5,
'gb': 6,
'g': 7,
'g#': 8,
'gx': 9,
'abb': 7,
'ab': 8,
'a': 9,
'a#': 10,
'ax': 11,
'bbb': 9,
'bb': 10,
'b': 11,
'b#': 12,
'bx': 13
};
/**
* scale index to note (sharps)
* @type {Array}
*/
var scaleIndexToNote = [
'C',
'C#',
'D',
'D#',
'E',
'F',
'F#',
'G',
'G#',
'A',
'A#',
'B'
];
/**
* The [concert pitch](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concert_pitch)
* A4's values in Hertz.
* @type {Frequency}
* @static
*/
Tone.Frequency.A4 = 440;
/**
* Convert a MIDI note to frequency value.
* @param {MIDI} midi The midi number to convert.
* @return {Frequency} the corresponding frequency value
* @example
* tone.midiToFrequency(69); // returns 440
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.midiToFrequency = function (midi) {
return Tone.Frequency.A4 * Math.pow(2, (midi - 69) / 12);
};
/**
* Convert a frequency value to a MIDI note.
* @param {Frequency} frequency The value to frequency value to convert.
* @returns {MIDI}
* @example
* tone.midiToFrequency(440); // returns 69
*/
Tone.Frequency.prototype.frequencyToMidi = function (frequency) {
return 69 + 12 * Math.log(frequency / Tone.Frequency.A4) / Math.LN2;
};
return Tone.Frequency;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.TransportTime is a the time along the Transport's
* timeline. It is similar to Tone.Time, but instead of evaluating
* against the AudioContext's clock, it is evaluated against
* the Transport's position. See [TransportTime wiki](https://github.com/Tonejs/Tone.js/wiki/TransportTime).
* @constructor
* @param {Time} val The time value as a number or string
* @param {String=} units Unit values
* @extends {Tone.Time}
*/
Tone.TransportTime = function (val, units) {
if (this instanceof Tone.TransportTime) {
Tone.Time.call(this, val, units);
} else {
return new Tone.TransportTime(val, units);
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.TransportTime, Tone.Time);
//clone the expressions so that
//we can add more without modifying the original
Tone.TransportTime.prototype._unaryExpressions = Object.create(Tone.Time.prototype._unaryExpressions);
/**
* Adds an additional unary expression
* which quantizes values to the next subdivision
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.TransportTime.prototype._unaryExpressions.quantize = {
regexp: /^@/,
method: function (rh) {
var subdivision = this._secondsToTicks(rh());
var multiple = Math.ceil(Tone.Transport.ticks / subdivision);
return this._ticksToUnits(multiple * subdivision);
}
};
/**
* Convert seconds into ticks
* @param {Seconds} seconds
* @return {Ticks}
* @private
*/
Tone.TransportTime.prototype._secondsToTicks = function (seconds) {
var quarterTime = this._beatsToUnits(1);
var quarters = seconds / quarterTime;
return Math.round(quarters * Tone.Transport.PPQ);
};
/**
* Evaluate the time expression. Returns values in ticks
* @return {Ticks}
*/
Tone.TransportTime.prototype.eval = function () {
var val = this._secondsToTicks(this._expr());
return val + (this._plusNow ? Tone.Transport.ticks : 0);
};
/**
* Return the time in ticks.
* @return {Ticks}
*/
Tone.TransportTime.prototype.toTicks = function () {
return this.eval();
};
/**
* Return the time in seconds.
* @return {Seconds}
*/
Tone.TransportTime.prototype.toSeconds = function () {
var val = this._expr();
return val + (this._plusNow ? Tone.Transport.seconds : 0);
};
/**
* Return the time as a frequency value
* @return {Frequency}
*/
Tone.TransportTime.prototype.toFrequency = function () {
return 1 / this.toSeconds();
};
return Tone.TransportTime;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TYPES
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Units which a value can take on.
* @enum {String}
*/
Tone.Type = {
/**
* Default units
* @typedef {Default}
*/
Default: 'number',
/**
* Time can be described in a number of ways. Read more [Time](https://github.com/Tonejs/Tone.js/wiki/Time).
*
*
* - Numbers, which will be taken literally as the time (in seconds).
* - Notation, ("4n", "8t") describes time in BPM and time signature relative values.
* - TransportTime, ("4:3:2") will also provide tempo and time signature relative times
* in the form BARS:QUARTERS:SIXTEENTHS.
* - Frequency, ("8hz") is converted to the length of the cycle in seconds.
* - Now-Relative, ("+1") prefix any of the above with "+" and it will be interpreted as
* "the current time plus whatever expression follows".
* - Expressions, ("3:0 + 2 - (1m / 7)") any of the above can also be combined
* into a mathematical expression which will be evaluated to compute the desired time.
* - No Argument, for methods which accept time, no argument will be interpreted as
* "now" (i.e. the currentTime).
*
*
* @typedef {Time}
*/
Time: 'time',
/**
* Frequency can be described similar to time, except ultimately the
* values are converted to frequency instead of seconds. A number
* is taken literally as the value in hertz. Additionally any of the
* Time encodings can be used. Note names in the form
* of NOTE OCTAVE (i.e. C4) are also accepted and converted to their
* frequency value.
* @typedef {Frequency}
*/
Frequency: 'frequency',
/**
* TransportTime describes a position along the Transport's timeline. It is
* similar to Time in that it uses all the same encodings, but TransportTime specifically
* pertains to the Transport's timeline, which is startable, stoppable, loopable, and seekable.
* [Read more](https://github.com/Tonejs/Tone.js/wiki/TransportTime)
* @typedef {TransportTime}
*/
TransportTime: 'transportTime',
/**
* Ticks are the basic subunit of the Transport. They are
* the smallest unit of time that the Transport supports.
* @typedef {Ticks}
*/
Ticks: 'ticks',
/**
* Normal values are within the range [0, 1].
* @typedef {NormalRange}
*/
NormalRange: 'normalRange',
/**
* AudioRange values are between [-1, 1].
* @typedef {AudioRange}
*/
AudioRange: 'audioRange',
/**
* Decibels are a logarithmic unit of measurement which is useful for volume
* because of the logarithmic way that we perceive loudness. 0 decibels
* means no change in volume. -10db is approximately half as loud and 10db
* is twice is loud.
* @typedef {Decibels}
*/
Decibels: 'db',
/**
* Half-step note increments, i.e. 12 is an octave above the root. and 1 is a half-step up.
* @typedef {Interval}
*/
Interval: 'interval',
/**
* Beats per minute.
* @typedef {BPM}
*/
BPM: 'bpm',
/**
* The value must be greater than or equal to 0.
* @typedef {Positive}
*/
Positive: 'positive',
/**
* A cent is a hundredth of a semitone.
* @typedef {Cents}
*/
Cents: 'cents',
/**
* Angle between 0 and 360.
* @typedef {Degrees}
*/
Degrees: 'degrees',
/**
* A number representing a midi note.
* @typedef {MIDI}
*/
MIDI: 'midi',
/**
* A colon-separated representation of time in the form of
* Bars:Beats:Sixteenths.
* @typedef {BarsBeatsSixteenths}
*/
BarsBeatsSixteenths: 'barsBeatsSixteenths',
/**
* Sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal.
* Audio is typically sampled 44100 times per second.
* @typedef {Samples}
*/
Samples: 'samples',
/**
* Hertz are a frequency representation defined as one cycle per second.
* @typedef {Hertz}
*/
Hertz: 'hertz',
/**
* A frequency represented by a letter name,
* accidental and octave. This system is known as
* [Scientific Pitch Notation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientific_pitch_notation).
* @typedef {Note}
*/
Note: 'note',
/**
* One millisecond is a thousandth of a second.
* @typedef {Milliseconds}
*/
Milliseconds: 'milliseconds',
/**
* Seconds are the time unit of the AudioContext. In the end,
* all values need to be evaluated to seconds.
* @typedef {Seconds}
*/
Seconds: 'seconds',
/**
* A string representing a duration relative to a measure.
*
* - "4n" = quarter note
* - "2m" = two measures
* - "8t" = eighth-note triplet
*
* @typedef {Notation}
*/
Notation: 'notation'
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AUGMENT TONE's PROTOTYPE
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Convert Time into seconds.
*
* Unlike the method which it overrides, this takes into account
* transporttime and musical notation.
*
* Time : 1.40
* Notation: 4n|1m|2t
* Now Relative: +3n
* Math: 3n+16n or even complicated expressions ((3n*2)/6 + 1)
*
* @param {Time} time
* @return {Seconds}
*/
Tone.prototype.toSeconds = function (time) {
if (this.isNumber(time)) {
return time;
} else if (this.isUndef(time)) {
return this.now();
} else if (this.isString(time)) {
return new Tone.Time(time).toSeconds();
} else if (time instanceof Tone.TimeBase) {
return time.toSeconds();
}
};
/**
* Convert a frequency representation into a number.
* @param {Frequency} freq
* @return {Hertz} the frequency in hertz
*/
Tone.prototype.toFrequency = function (freq) {
if (this.isNumber(freq)) {
return freq;
} else if (this.isString(freq) || this.isUndef(freq)) {
return new Tone.Frequency(freq).eval();
} else if (freq instanceof Tone.TimeBase) {
return freq.toFrequency();
}
};
/**
* Convert a time representation into ticks.
* @param {Time} time
* @return {Ticks} the time in ticks
*/
Tone.prototype.toTicks = function (time) {
if (this.isNumber(time) || this.isString(time)) {
return new Tone.TransportTime(time).toTicks();
} else if (this.isUndef(time)) {
return Tone.Transport.ticks;
} else if (time instanceof Tone.TimeBase) {
return time.toTicks();
}
};
return Tone;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Param wraps the native Web Audio's AudioParam to provide
* additional unit conversion functionality. It also
* serves as a base-class for classes which have a single,
* automatable parameter.
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {AudioParam} param The parameter to wrap.
* @param {Tone.Type} units The units of the audio param.
* @param {Boolean} convert If the param should be converted.
*/
Tone.Param = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'param',
'units',
'convert'
], Tone.Param.defaults);
/**
* The native parameter to control
* @type {AudioParam}
* @private
*/
this._param = this.input = options.param;
/**
* The units of the parameter
* @type {Tone.Type}
*/
this.units = options.units;
/**
* If the value should be converted or not
* @type {Boolean}
*/
this.convert = options.convert;
/**
* True if the signal value is being overridden by
* a connected signal.
* @readOnly
* @type {boolean}
* @private
*/
this.overridden = false;
/**
* If there is an LFO, this is where it is held.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfo = null;
if (this.isObject(options.lfo)) {
this.value = options.lfo;
} else if (!this.isUndef(options.value)) {
this.value = options.value;
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Param);
/**
* Defaults
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.Param.defaults = {
'units': Tone.Type.Default,
'convert': true,
'param': undefined
};
/**
* The current value of the parameter.
* @memberOf Tone.Param#
* @type {Number}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Param.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
return this._toUnits(this._param.value);
},
set: function (value) {
if (this.isObject(value)) {
//throw an error if the LFO needs to be included
if (this.isUndef(Tone.LFO)) {
throw new Error('Include \'Tone.LFO\' to use an LFO as a Param value.');
}
//remove the old one
if (this._lfo) {
this._lfo.dispose();
}
this._lfo = new Tone.LFO(value).start();
this._lfo.connect(this.input);
} else {
var convertedVal = this._fromUnits(value);
this._param.cancelScheduledValues(0);
this._param.value = convertedVal;
}
}
});
/**
* Convert the given value from the type specified by Tone.Param.units
* into the destination value (such as Gain or Frequency).
* @private
* @param {*} val the value to convert
* @return {number} the number which the value should be set to
*/
Tone.Param.prototype._fromUnits = function (val) {
if (this.convert || this.isUndef(this.convert)) {
switch (this.units) {
case Tone.Type.Time:
return this.toSeconds(val);
case Tone.Type.Frequency:
return this.toFrequency(val);
case Tone.Type.Decibels:
return this.dbToGain(val);
case Tone.Type.NormalRange:
return Math.min(Math.max(val, 0), 1);
case Tone.Type.AudioRange:
return Math.min(Math.max(val, -1), 1);
case Tone.Type.Positive:
return Math.max(val, 0);
default:
return val;
}
} else {
return val;
}
};
/**
* Convert the parameters value into the units specified by Tone.Param.units.
* @private
* @param {number} val the value to convert
* @return {number}
*/
Tone.Param.prototype._toUnits = function (val) {
if (this.convert || this.isUndef(this.convert)) {
switch (this.units) {
case Tone.Type.Decibels:
return this.gainToDb(val);
default:
return val;
}
} else {
return val;
}
};
/**
* the minimum output value
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Param.prototype._minOutput = 0.00001;
/**
* Schedules a parameter value change at the given time.
* @param {*} value The value to set the signal.
* @param {Time} time The time when the change should occur.
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
* @example
* //set the frequency to "G4" in exactly 1 second from now.
* freq.setValueAtTime("G4", "+1");
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.setValueAtTime = function (value, time) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
time = this.toSeconds(time);
if (time <= this.now() + this.blockTime) {
this._param.value = value;
} else {
this._param.setValueAtTime(value, time);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Creates a schedule point with the current value at the current time.
* This is useful for creating an automation anchor point in order to
* schedule changes from the current value.
*
* @param {number=} now (Optionally) pass the now value in.
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.setRampPoint = function (now) {
now = this.defaultArg(now, this.now());
var currentVal = this._param.value;
// exponentialRampToValueAt cannot ever ramp from or to 0
// More info: https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1125600#c2
if (currentVal === 0) {
currentVal = this._minOutput;
}
this._param.setValueAtTime(currentVal, now);
return this;
};
/**
* Schedules a linear continuous change in parameter value from the
* previous scheduled parameter value to the given value.
*
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} endTime
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.linearRampToValueAtTime = function (value, endTime) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
this._param.linearRampToValueAtTime(value, this.toSeconds(endTime));
return this;
};
/**
* Schedules an exponential continuous change in parameter value from
* the previous scheduled parameter value to the given value.
*
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} endTime
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.exponentialRampToValueAtTime = function (value, endTime) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
value = Math.max(this._minOutput, value);
this._param.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(value, this.toSeconds(endTime));
return this;
};
/**
* Schedules an exponential continuous change in parameter value from
* the current time and current value to the given value over the
* duration of the rampTime.
*
* @param {number} value The value to ramp to.
* @param {Time} rampTime the time that it takes the
* value to ramp from it's current value
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the ramp should start.
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
* @example
* //exponentially ramp to the value 2 over 4 seconds.
* signal.exponentialRampToValue(2, 4);
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.exponentialRampToValue = function (value, rampTime, startTime) {
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
this.setRampPoint(startTime);
this.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(value, startTime + this.toSeconds(rampTime));
return this;
};
/**
* Schedules an linear continuous change in parameter value from
* the current time and current value to the given value over the
* duration of the rampTime.
*
* @param {number} value The value to ramp to.
* @param {Time} rampTime the time that it takes the
* value to ramp from it's current value
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the ramp should start.
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
* @example
* //linearly ramp to the value 4 over 3 seconds.
* signal.linearRampToValue(4, 3);
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.linearRampToValue = function (value, rampTime, startTime) {
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
this.setRampPoint(startTime);
this.linearRampToValueAtTime(value, startTime + this.toSeconds(rampTime));
return this;
};
/**
* Start exponentially approaching the target value at the given time with
* a rate having the given time constant.
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} startTime
* @param {number} timeConstant
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.setTargetAtTime = function (value, startTime, timeConstant) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
// The value will never be able to approach without timeConstant > 0.
// http://www.w3.org/TR/webaudio/#dfn-setTargetAtTime, where the equation
// is described. 0 results in a division by 0.
value = Math.max(this._minOutput, value);
timeConstant = Math.max(this._minOutput, timeConstant);
this._param.setTargetAtTime(value, this.toSeconds(startTime), timeConstant);
return this;
};
/**
* Sets an array of arbitrary parameter values starting at the given time
* for the given duration.
*
* @param {Array} values
* @param {Time} startTime
* @param {Time} duration
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.setValueCurveAtTime = function (values, startTime, duration) {
for (var i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
values[i] = this._fromUnits(values[i]);
}
this._param.setValueCurveAtTime(values, this.toSeconds(startTime), this.toSeconds(duration));
return this;
};
/**
* Cancels all scheduled parameter changes with times greater than or
* equal to startTime.
*
* @param {Time} startTime
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.cancelScheduledValues = function (startTime) {
this._param.cancelScheduledValues(this.toSeconds(startTime));
return this;
};
/**
* Ramps to the given value over the duration of the rampTime.
* Automatically selects the best ramp type (exponential or linear)
* depending on the `units` of the signal
*
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} rampTime The time that it takes the
* value to ramp from it's current value
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the ramp should start.
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
* @example
* //ramp to the value either linearly or exponentially
* //depending on the "units" value of the signal
* signal.rampTo(0, 10);
* @example
* //schedule it to ramp starting at a specific time
* signal.rampTo(0, 10, 5)
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.rampTo = function (value, rampTime, startTime) {
rampTime = this.defaultArg(rampTime, 0);
if (this.units === Tone.Type.Frequency || this.units === Tone.Type.BPM) {
this.exponentialRampToValue(value, rampTime, startTime);
} else {
this.linearRampToValue(value, rampTime, startTime);
}
return this;
};
/**
* The LFO created by the signal instance. If none
* was created, this is null.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.Param#
* @name lfo
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Param.prototype, 'lfo', {
get: function () {
return this._lfo;
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @returns {Tone.Param} this
*/
Tone.Param.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._param = null;
if (this._lfo) {
this._lfo.dispose();
this._lfo = null;
}
return this;
};
return Tone.Param;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A thin wrapper around the Native Web Audio GainNode.
* The GainNode is a basic building block of the Web Audio
* API and is useful for routing audio and adjusting gains.
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Number=} gain The initial gain of the GainNode
* @param {Tone.Type=} units The units of the gain parameter.
*/
Tone.Gain = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'gain',
'units'
], Tone.Gain.defaults);
/**
* The GainNode
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.input = this.output = this._gainNode = this.context.createGain();
/**
* The gain parameter of the gain node.
* @type {Tone.Param}
* @signal
*/
this.gain = new Tone.Param({
'param': this._gainNode.gain,
'units': options.units,
'value': options.gain,
'convert': options.convert
});
this._readOnly('gain');
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Gain);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Gain.defaults = {
'gain': 1,
'convert': true
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Gain} this
*/
Tone.Gain.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Param.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._gainNode.disconnect();
this._gainNode = null;
this._writable('gain');
this.gain.dispose();
this.gain = null;
};
//STATIC///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Create input and outputs for this object.
* @param {Number} input The number of inputs
* @param {Number=} outputs The number of outputs
* @return {Tone} this
* @internal
*/
Tone.prototype.createInsOuts = function (inputs, outputs) {
if (inputs === 1) {
this.input = new Tone.Gain();
} else if (inputs > 1) {
this.input = new Array(inputs);
}
if (outputs === 1) {
this.output = new Tone.Gain();
} else if (outputs > 1) {
this.output = new Array(inputs);
}
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
return Tone.Gain;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A signal is an audio-rate value. Tone.Signal is a core component of the library.
* Unlike a number, Signals can be scheduled with sample-level accuracy. Tone.Signal
* has all of the methods available to native Web Audio
* [AudioParam](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#the-audioparam-interface)
* as well as additional conveniences. Read more about working with signals
* [here](https://github.com/Tonejs/Tone.js/wiki/Signals).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Param}
* @param {Number|AudioParam} [value] Initial value of the signal. If an AudioParam
* is passed in, that parameter will be wrapped
* and controlled by the Signal.
* @param {string} [units=Number] unit The units the signal is in.
* @example
* var signal = new Tone.Signal(10);
*/
Tone.Signal = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'value',
'units'
], Tone.Signal.defaults);
/**
* The node where the constant signal value is scaled.
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.output = this._gain = this.context.createGain();
options.param = this._gain.gain;
Tone.Param.call(this, options);
/**
* The node where the value is set.
* @type {Tone.Param}
* @private
*/
this.input = this._param = this._gain.gain;
//connect the const output to the node output
Tone.Signal._constant.chain(this._gain);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Signal, Tone.Param);
/**
* The default values
* @type {Object}
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.Signal.defaults = {
'value': 0,
'units': Tone.Type.Default,
'convert': true
};
/**
* When signals connect to other signals or AudioParams,
* they take over the output value of that signal or AudioParam.
* For all other nodes, the behavior is the same as a default connect.
*
* @override
* @param {AudioParam|AudioNode|Tone.Signal|Tone} node
* @param {number} [outputNumber=0] The output number to connect from.
* @param {number} [inputNumber=0] The input number to connect to.
* @returns {Tone.SignalBase} this
* @method
*/
Tone.Signal.prototype.connect = Tone.SignalBase.prototype.connect;
/**
* dispose and disconnect
* @returns {Tone.Signal} this
*/
Tone.Signal.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Param.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._param = null;
this._gain.disconnect();
this._gain = null;
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// STATIC
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Generates a constant output of 1.
* @static
* @private
* @const
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
*/
Tone.Signal._constant = null;
/**
* initializer function
*/
Tone._initAudioContext(function (audioContext) {
var buffer = audioContext.createBuffer(1, 128, audioContext.sampleRate);
var arr = buffer.getChannelData(0);
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = 1;
}
Tone.Signal._constant = audioContext.createBufferSource();
Tone.Signal._constant.channelCount = 1;
Tone.Signal._constant.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
Tone.Signal._constant.buffer = buffer;
Tone.Signal._constant.loop = true;
Tone.Signal._constant.start(0);
Tone.Signal._constant.noGC();
});
return Tone.Signal;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A Timeline class for scheduling and maintaining state
* along a timeline. All events must have a "time" property.
* Internally, events are stored in time order for fast
* retrieval.
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Positive} [memory=Infinity] The number of previous events that are retained.
*/
Tone.Timeline = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['memory'], Tone.Timeline.defaults);
/**
* The array of scheduled timeline events
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._timeline = [];
/**
* An array of items to remove from the list.
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._toRemove = [];
/**
* Flag if the tieline is mid iteration
* @private
* @type {Boolean}
*/
this._iterating = false;
/**
* The memory of the timeline, i.e.
* how many events in the past it will retain
* @type {Positive}
*/
this.memory = options.memory;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Timeline);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.Timeline.defaults = { 'memory': Infinity };
/**
* The number of items in the timeline.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Timeline#
* @name length
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Timeline.prototype, 'length', {
get: function () {
return this._timeline.length;
}
});
/**
* Insert an event object onto the timeline. Events must have a "time" attribute.
* @param {Object} event The event object to insert into the
* timeline.
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.add = function (event) {
//the event needs to have a time attribute
if (this.isUndef(event.time)) {
throw new Error('Tone.Timeline: events must have a time attribute');
}
if (this._timeline.length) {
var index = this._search(event.time);
this._timeline.splice(index + 1, 0, event);
} else {
this._timeline.push(event);
}
//if the length is more than the memory, remove the previous ones
if (this.length > this.memory) {
var diff = this.length - this.memory;
this._timeline.splice(0, diff);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Remove an event from the timeline.
* @param {Object} event The event object to remove from the list.
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.remove = function (event) {
if (this._iterating) {
this._toRemove.push(event);
} else {
var index = this._timeline.indexOf(event);
if (index !== -1) {
this._timeline.splice(index, 1);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Get the nearest event whose time is less than or equal to the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @returns {Object} The event object set after that time.
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.get = function (time) {
var index = this._search(time);
if (index !== -1) {
return this._timeline[index];
} else {
return null;
}
};
/**
* Return the first event in the timeline without removing it
* @returns {Object} The first event object
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.peek = function () {
return this._timeline[0];
};
/**
* Return the first event in the timeline and remove it
* @returns {Object} The first event object
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.shift = function () {
return this._timeline.shift();
};
/**
* Get the event which is scheduled after the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @returns {Object} The event object after the given time
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.getAfter = function (time) {
var index = this._search(time);
if (index + 1 < this._timeline.length) {
return this._timeline[index + 1];
} else {
return null;
}
};
/**
* Get the event before the event at the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @returns {Object} The event object before the given time
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.getBefore = function (time) {
var len = this._timeline.length;
//if it's after the last item, return the last item
if (len > 0 && this._timeline[len - 1].time < time) {
return this._timeline[len - 1];
}
var index = this._search(time);
if (index - 1 >= 0) {
return this._timeline[index - 1];
} else {
return null;
}
};
/**
* Cancel events after the given time
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.cancel = function (after) {
if (this._timeline.length > 1) {
var index = this._search(after);
if (index >= 0) {
if (this._timeline[index].time === after) {
//get the first item with that time
for (var i = index; i >= 0; i--) {
if (this._timeline[i].time === after) {
index = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
this._timeline = this._timeline.slice(0, index);
} else {
this._timeline = this._timeline.slice(0, index + 1);
}
} else {
this._timeline = [];
}
} else if (this._timeline.length === 1) {
//the first item's time
if (this._timeline[0].time >= after) {
this._timeline = [];
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Cancel events before or equal to the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to cancel before.
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.cancelBefore = function (time) {
if (this._timeline.length) {
var index = this._search(time);
if (index >= 0) {
this._timeline = this._timeline.slice(index + 1);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Does a binary serach on the timeline array and returns the
* nearest event index whose time is after or equal to the given time.
* If a time is searched before the first index in the timeline, -1 is returned.
* If the time is after the end, the index of the last item is returned.
* @param {Number} time
* @return {Number} the index in the timeline array
* @private
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype._search = function (time) {
var beginning = 0;
var len = this._timeline.length;
var end = len;
if (len > 0 && this._timeline[len - 1].time <= time) {
return len - 1;
}
while (beginning < end) {
// calculate the midpoint for roughly equal partition
var midPoint = Math.floor(beginning + (end - beginning) / 2);
var event = this._timeline[midPoint];
var nextEvent = this._timeline[midPoint + 1];
if (event.time === time) {
//choose the last one that has the same time
for (var i = midPoint; i < this._timeline.length; i++) {
var testEvent = this._timeline[i];
if (testEvent.time === time) {
midPoint = i;
}
}
return midPoint;
} else if (event.time < time && nextEvent.time > time) {
return midPoint;
} else if (event.time > time) {
//search lower
end = midPoint;
} else if (event.time < time) {
//search upper
beginning = midPoint + 1;
}
}
return -1;
};
/**
* Internal iterator. Applies extra safety checks for
* removing items from the array.
* @param {Function} callback
* @param {Number=} lowerBound
* @param {Number=} upperBound
* @private
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype._iterate = function (callback, lowerBound, upperBound) {
this._iterating = true;
lowerBound = this.defaultArg(lowerBound, 0);
upperBound = this.defaultArg(upperBound, this._timeline.length - 1);
for (var i = lowerBound; i <= upperBound; i++) {
callback(this._timeline[i]);
}
this._iterating = false;
if (this._toRemove.length > 0) {
for (var j = 0; j < this._toRemove.length; j++) {
var index = this._timeline.indexOf(this._toRemove[j]);
if (index !== -1) {
this._timeline.splice(index, 1);
}
}
this._toRemove = [];
}
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.forEach = function (callback) {
this._iterate(callback);
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array at or before the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to check if items are before
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.forEachBefore = function (time, callback) {
//iterate over the items in reverse so that removing an item doesn't break things
var upperBound = this._search(time);
if (upperBound !== -1) {
this._iterate(callback, 0, upperBound);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array after the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to check if items are before
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.forEachAfter = function (time, callback) {
//iterate over the items in reverse so that removing an item doesn't break things
var lowerBound = this._search(time);
this._iterate(callback, lowerBound + 1);
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array at or after the given time. Similar to
* forEachAfter, but includes the item(s) at the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to check if items are before
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.forEachFrom = function (time, callback) {
//iterate over the items in reverse so that removing an item doesn't break things
var lowerBound = this._search(time);
//work backwards until the event time is less than time
while (lowerBound >= 0 && this._timeline[lowerBound].time >= time) {
lowerBound--;
}
this._iterate(callback, lowerBound + 1);
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array at the given time
* @param {Number} time The time to check if items are before
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.forEachAtTime = function (time, callback) {
//iterate over the items in reverse so that removing an item doesn't break things
var upperBound = this._search(time);
if (upperBound !== -1) {
this._iterate(function (event) {
if (event.time === time) {
callback(event);
}
}, 0, upperBound);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Timeline} this
*/
Tone.Timeline.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._timeline = null;
this._toRemove = null;
};
return Tone.Timeline;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A signal which adds the method getValueAtTime.
* Code and inspiration from https://github.com/jsantell/web-audio-automation-timeline
* @extends {Tone.Param}
* @param {Number=} value The initial value of the signal
* @param {String=} units The conversion units of the signal.
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'value',
'units'
], Tone.Signal.defaults);
/**
* The scheduled events
* @type {Tone.Timeline}
* @private
*/
this._events = new Tone.Timeline(10);
//constructors
Tone.Signal.apply(this, options);
options.param = this._param;
Tone.Param.call(this, options);
/**
* The initial scheduled value
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._initial = this._fromUnits(this._param.value);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.TimelineSignal, Tone.Param);
/**
* The event types of a schedulable signal.
* @enum {String}
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.Type = {
Linear: 'linear',
Exponential: 'exponential',
Target: 'target',
Curve: 'curve',
Set: 'set'
};
/**
* The current value of the signal.
* @memberOf Tone.TimelineSignal#
* @type {Number}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
var now = this.now();
var val = this.getValueAtTime(now);
return this._toUnits(val);
},
set: function (value) {
var convertedVal = this._fromUnits(value);
this._initial = convertedVal;
this.cancelScheduledValues();
this._param.value = convertedVal;
}
});
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SCHEDULING
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Schedules a parameter value change at the given time.
* @param {*} value The value to set the signal.
* @param {Time} time The time when the change should occur.
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
* @example
* //set the frequency to "G4" in exactly 1 second from now.
* freq.setValueAtTime("G4", "+1");
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.setValueAtTime = function (value, startTime) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
this._events.add({
'type': Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Set,
'value': value,
'time': startTime
});
//invoke the original event
this._param.setValueAtTime(value, startTime);
return this;
};
/**
* Schedules a linear continuous change in parameter value from the
* previous scheduled parameter value to the given value.
*
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} endTime
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.linearRampToValueAtTime = function (value, endTime) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
endTime = this.toSeconds(endTime);
this._events.add({
'type': Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Linear,
'value': value,
'time': endTime
});
this._param.linearRampToValueAtTime(value, endTime);
return this;
};
/**
* Schedules an exponential continuous change in parameter value from
* the previous scheduled parameter value to the given value.
*
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} endTime
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.exponentialRampToValueAtTime = function (value, endTime) {
//get the previous event and make sure it's not starting from 0
endTime = this.toSeconds(endTime);
var beforeEvent = this._searchBefore(endTime);
if (beforeEvent && beforeEvent.value === 0) {
//reschedule that event
this.setValueAtTime(this._minOutput, beforeEvent.time);
}
value = this._fromUnits(value);
var setValue = Math.max(value, this._minOutput);
this._events.add({
'type': Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Exponential,
'value': setValue,
'time': endTime
});
//if the ramped to value is 0, make it go to the min output, and then set to 0.
if (value < this._minOutput) {
this._param.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(this._minOutput, endTime - this.sampleTime);
this.setValueAtTime(0, endTime);
} else {
this._param.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(value, endTime);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Start exponentially approaching the target value at the given time with
* a rate having the given time constant.
* @param {number} value
* @param {Time} startTime
* @param {number} timeConstant
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.setTargetAtTime = function (value, startTime, timeConstant) {
value = this._fromUnits(value);
value = Math.max(this._minOutput, value);
timeConstant = Math.max(this._minOutput, timeConstant);
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
this._events.add({
'type': Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Target,
'value': value,
'time': startTime,
'constant': timeConstant
});
this._param.setTargetAtTime(value, startTime, timeConstant);
return this;
};
/**
* Set an array of arbitrary values starting at the given time for the given duration.
* @param {Float32Array} values
* @param {Time} startTime
* @param {Time} duration
* @param {NormalRange} [scaling=1] If the values in the curve should be scaled by some value
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.setValueCurveAtTime = function (values, startTime, duration, scaling) {
scaling = this.defaultArg(scaling, 1);
//copy the array
var floats = new Array(values.length);
for (var i = 0; i < floats.length; i++) {
floats[i] = this._fromUnits(values[i]) * scaling;
}
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this._events.add({
'type': Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Curve,
'value': floats,
'time': startTime,
'duration': duration
});
//set the first value
this._param.setValueAtTime(floats[0], startTime);
//schedule a lienar ramp for each of the segments
for (var j = 1; j < floats.length; j++) {
var segmentTime = startTime + j / (floats.length - 1) * duration;
this._param.linearRampToValueAtTime(floats[j], segmentTime);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Cancels all scheduled parameter changes with times greater than or
* equal to startTime.
*
* @param {Time} startTime
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.cancelScheduledValues = function (after) {
after = this.toSeconds(after);
this._events.cancel(after);
this._param.cancelScheduledValues(after);
return this;
};
/**
* Sets the computed value at the given time. This provides
* a point from which a linear or exponential curve
* can be scheduled after. Will cancel events after
* the given time and shorten the currently scheduled
* linear or exponential ramp so that it ends at `time` .
* This is to avoid discontinuities and clicks in envelopes.
* @param {Time} time When to set the ramp point
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.setRampPoint = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//get the value at the given time
var val = this._toUnits(this.getValueAtTime(time));
//if there is an event at the given time
//and that even is not a "set"
var before = this._searchBefore(time);
if (before && before.time === time) {
//remove everything after
this.cancelScheduledValues(time + this.sampleTime);
} else if (before && before.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Curve && before.time + before.duration > time) {
//if the curve is still playing
//cancel the curve
this.cancelScheduledValues(time);
this.linearRampToValueAtTime(val, time);
} else {
//reschedule the next event to end at the given time
var after = this._searchAfter(time);
if (after) {
//cancel the next event(s)
this.cancelScheduledValues(time);
if (after.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Linear) {
this.linearRampToValueAtTime(val, time);
} else if (after.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Exponential) {
this.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(val, time);
}
}
this.setValueAtTime(val, time);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Do a linear ramp to the given value between the start and finish times.
* @param {Number} value The value to ramp to.
* @param {Time} start The beginning anchor point to do the linear ramp
* @param {Time} finish The ending anchor point by which the value of
* the signal will equal the given value.
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.linearRampToValueBetween = function (value, start, finish) {
this.setRampPoint(start);
this.linearRampToValueAtTime(value, finish);
return this;
};
/**
* Do a exponential ramp to the given value between the start and finish times.
* @param {Number} value The value to ramp to.
* @param {Time} start The beginning anchor point to do the exponential ramp
* @param {Time} finish The ending anchor point by which the value of
* the signal will equal the given value.
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.exponentialRampToValueBetween = function (value, start, finish) {
this.setRampPoint(start);
this.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(value, finish);
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// GETTING SCHEDULED VALUES
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Returns the value before or equal to the given time
* @param {Number} time The time to query
* @return {Object} The event at or before the given time.
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype._searchBefore = function (time) {
return this._events.get(time);
};
/**
* The event after the given time
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @return {Object} The next event after the given time
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype._searchAfter = function (time) {
return this._events.getAfter(time);
};
/**
* Get the scheduled value at the given time. This will
* return the unconverted (raw) value.
* @param {Number} time The time in seconds.
* @return {Number} The scheduled value at the given time.
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.getValueAtTime = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var after = this._searchAfter(time);
var before = this._searchBefore(time);
var value = this._initial;
//if it was set by
if (before === null) {
value = this._initial;
} else if (before.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Target) {
var previous = this._events.getBefore(before.time);
var previouVal;
if (previous === null) {
previouVal = this._initial;
} else {
previouVal = previous.value;
}
value = this._exponentialApproach(before.time, previouVal, before.value, before.constant, time);
} else if (before.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Curve) {
value = this._curveInterpolate(before.time, before.value, before.duration, time);
} else if (after === null) {
value = before.value;
} else if (after.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Linear) {
value = this._linearInterpolate(before.time, before.value, after.time, after.value, time);
} else if (after.type === Tone.TimelineSignal.Type.Exponential) {
value = this._exponentialInterpolate(before.time, before.value, after.time, after.value, time);
} else {
value = before.value;
}
return value;
};
/**
* When signals connect to other signals or AudioParams,
* they take over the output value of that signal or AudioParam.
* For all other nodes, the behavior is the same as a default connect.
*
* @override
* @param {AudioParam|AudioNode|Tone.Signal|Tone} node
* @param {number} [outputNumber=0] The output number to connect from.
* @param {number} [inputNumber=0] The input number to connect to.
* @returns {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
* @method
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.connect = Tone.SignalBase.prototype.connect;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AUTOMATION CURVE CALCULATIONS
// MIT License, copyright (c) 2014 Jordan Santell
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Calculates the the value along the curve produced by setTargetAtTime
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype._exponentialApproach = function (t0, v0, v1, timeConstant, t) {
return v1 + (v0 - v1) * Math.exp(-(t - t0) / timeConstant);
};
/**
* Calculates the the value along the curve produced by linearRampToValueAtTime
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype._linearInterpolate = function (t0, v0, t1, v1, t) {
return v0 + (v1 - v0) * ((t - t0) / (t1 - t0));
};
/**
* Calculates the the value along the curve produced by exponentialRampToValueAtTime
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype._exponentialInterpolate = function (t0, v0, t1, v1, t) {
v0 = Math.max(this._minOutput, v0);
return v0 * Math.pow(v1 / v0, (t - t0) / (t1 - t0));
};
/**
* Calculates the the value along the curve produced by setValueCurveAtTime
* @private
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype._curveInterpolate = function (start, curve, duration, time) {
var len = curve.length;
// If time is after duration, return the last curve value
if (time >= start + duration) {
return curve[len - 1];
} else if (time <= start) {
return curve[0];
} else {
var progress = (time - start) / duration;
var lowerIndex = Math.floor((len - 1) * progress);
var upperIndex = Math.ceil((len - 1) * progress);
var lowerVal = curve[lowerIndex];
var upperVal = curve[upperIndex];
if (upperIndex === lowerIndex) {
return lowerVal;
} else {
return this._linearInterpolate(lowerIndex, lowerVal, upperIndex, upperVal, progress * (len - 1));
}
}
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.TimelineSignal} this
*/
Tone.TimelineSignal.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Signal.prototype.dispose.call(this);
Tone.Param.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._events.dispose();
this._events = null;
};
return Tone.TimelineSignal;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Pow applies an exponent to the incoming signal. The incoming signal
* must be AudioRange.
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @param {Positive} exp The exponent to apply to the incoming signal, must be at least 2.
* @example
* var pow = new Tone.Pow(2);
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(0.5).connect(pow);
* //output of pow is 0.25.
*/
Tone.Pow = function (exp) {
/**
* the exponent
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._exp = this.defaultArg(exp, 1);
/**
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._expScaler = this.input = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(this._expFunc(this._exp), 8192);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Pow, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* The value of the exponent.
* @memberOf Tone.Pow#
* @type {number}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Pow.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
return this._exp;
},
set: function (exp) {
this._exp = exp;
this._expScaler.setMap(this._expFunc(this._exp));
}
});
/**
* the function which maps the waveshaper
* @param {number} exp
* @return {function}
* @private
*/
Tone.Pow.prototype._expFunc = function (exp) {
return function (val) {
return Math.pow(Math.abs(val), exp);
};
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Pow} this
*/
Tone.Pow.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._expScaler.dispose();
this._expScaler = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Pow;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Envelope is an [ADSR](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synthesizer#ADSR_envelope)
* envelope generator. Tone.Envelope outputs a signal which
* can be connected to an AudioParam or Tone.Signal.
*  *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Time} [attack] The amount of time it takes for the envelope to go from
* 0 to it's maximum value.
* @param {Time} [decay] The period of time after the attack that it takes for the envelope
* to fall to the sustain value.
* @param {NormalRange} [sustain] The percent of the maximum value that the envelope rests at until
* the release is triggered.
* @param {Time} [release] The amount of time after the release is triggered it takes to reach 0.
* @example
* //an amplitude envelope
* var gainNode = Tone.context.createGain();
* var env = new Tone.Envelope({
* "attack" : 0.1,
* "decay" : 0.2,
* "sustain" : 1,
* "release" : 0.8,
* });
* env.connect(gainNode.gain);
*/
Tone.Envelope = function () {
//get all of the defaults
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'attack',
'decay',
'sustain',
'release'
], Tone.Envelope.defaults);
/**
* When triggerAttack is called, the attack time is the amount of
* time it takes for the envelope to reach it's maximum value.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.attack = options.attack;
/**
* After the attack portion of the envelope, the value will fall
* over the duration of the decay time to it's sustain value.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.decay = options.decay;
/**
* The sustain value is the value
* which the envelope rests at after triggerAttack is
* called, but before triggerRelease is invoked.
* @type {NormalRange}
*/
this.sustain = options.sustain;
/**
* After triggerRelease is called, the envelope's
* value will fall to it's miminum value over the
* duration of the release time.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.release = options.release;
/**
* the next time the envelope is at standby
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._attackCurve = 'linear';
/**
* the next time the envelope is at standby
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._releaseCurve = 'exponential';
/**
* the signal
* @type {Tone.TimelineSignal}
* @private
*/
this._sig = this.output = new Tone.TimelineSignal();
this._sig.setValueAtTime(0, 0);
//set the attackCurve initially
this.attackCurve = options.attackCurve;
this.releaseCurve = options.releaseCurve;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Envelope);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.Envelope.defaults = {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0.5,
'release': 1,
'attackCurve': 'linear',
'releaseCurve': 'exponential'
};
/**
* Read the current value of the envelope. Useful for
* syncronizing visual output to the envelope.
* @memberOf Tone.Envelope#
* @type {Number}
* @name value
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Envelope.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
return this.getValueAtTime(this.now());
}
});
/**
* The shape of the attack.
* Can be any of these strings:
*
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Time} [attack] The amount of time it takes for the envelope to go from
* 0 to it's maximum value.
* @param {Time} [decay] The period of time after the attack that it takes for the envelope
* to fall to the sustain value.
* @param {NormalRange} [sustain] The percent of the maximum value that the envelope rests at until
* the release is triggered.
* @param {Time} [release] The amount of time after the release is triggered it takes to reach 0.
* @example
* //an amplitude envelope
* var gainNode = Tone.context.createGain();
* var env = new Tone.Envelope({
* "attack" : 0.1,
* "decay" : 0.2,
* "sustain" : 1,
* "release" : 0.8,
* });
* env.connect(gainNode.gain);
*/
Tone.Envelope = function () {
//get all of the defaults
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'attack',
'decay',
'sustain',
'release'
], Tone.Envelope.defaults);
/**
* When triggerAttack is called, the attack time is the amount of
* time it takes for the envelope to reach it's maximum value.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.attack = options.attack;
/**
* After the attack portion of the envelope, the value will fall
* over the duration of the decay time to it's sustain value.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.decay = options.decay;
/**
* The sustain value is the value
* which the envelope rests at after triggerAttack is
* called, but before triggerRelease is invoked.
* @type {NormalRange}
*/
this.sustain = options.sustain;
/**
* After triggerRelease is called, the envelope's
* value will fall to it's miminum value over the
* duration of the release time.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.release = options.release;
/**
* the next time the envelope is at standby
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._attackCurve = 'linear';
/**
* the next time the envelope is at standby
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._releaseCurve = 'exponential';
/**
* the signal
* @type {Tone.TimelineSignal}
* @private
*/
this._sig = this.output = new Tone.TimelineSignal();
this._sig.setValueAtTime(0, 0);
//set the attackCurve initially
this.attackCurve = options.attackCurve;
this.releaseCurve = options.releaseCurve;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Envelope);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.Envelope.defaults = {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0.5,
'release': 1,
'attackCurve': 'linear',
'releaseCurve': 'exponential'
};
/**
* Read the current value of the envelope. Useful for
* syncronizing visual output to the envelope.
* @memberOf Tone.Envelope#
* @type {Number}
* @name value
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Envelope.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
return this.getValueAtTime(this.now());
}
});
/**
* The shape of the attack.
* Can be any of these strings:
*
* - linear
* - exponential
* - sine
* - cosine
* - bounce
* - ripple
* - step
*
* Can also be an array which describes the curve. Values
* in the array are evenly subdivided and linearly
* interpolated over the duration of the attack.
* @memberOf Tone.Envelope#
* @type {String|Array}
* @name attackCurve
* @example
* env.attackCurve = "linear";
* @example
* //can also be an array
* env.attackCurve = [0, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 1]
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Envelope.prototype, 'attackCurve', {
get: function () {
if (this.isString(this._attackCurve)) {
return this._attackCurve;
} else if (this.isArray(this._attackCurve)) {
//look up the name in the curves array
for (var type in Tone.Envelope.Type) {
if (Tone.Envelope.Type[type].In === this._attackCurve) {
return type;
}
}
//otherwise just return the array
return this._attackCurve;
}
},
set: function (curve) {
//check if it's a valid type
if (Tone.Envelope.Type.hasOwnProperty(curve)) {
var curveDef = Tone.Envelope.Type[curve];
if (this.isObject(curveDef)) {
this._attackCurve = curveDef.In;
} else {
this._attackCurve = curveDef;
}
} else if (this.isArray(curve)) {
this._attackCurve = curve;
} else {
throw new Error('Tone.Envelope: invalid curve: ' + curve);
}
}
});
/**
* The shape of the release. See the attack curve types.
* @memberOf Tone.Envelope#
* @type {String|Array}
* @name releaseCurve
* @example
* env.releaseCurve = "linear";
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Envelope.prototype, 'releaseCurve', {
get: function () {
if (this.isString(this._releaseCurve)) {
return this._releaseCurve;
} else if (this.isArray(this._releaseCurve)) {
//look up the name in the curves array
for (var type in Tone.Envelope.Type) {
if (Tone.Envelope.Type[type].Out === this._releaseCurve) {
return type;
}
}
//otherwise just return the array
return this._releaseCurve;
}
},
set: function (curve) {
//check if it's a valid type
if (Tone.Envelope.Type.hasOwnProperty(curve)) {
var curveDef = Tone.Envelope.Type[curve];
if (this.isObject(curveDef)) {
this._releaseCurve = curveDef.Out;
} else {
this._releaseCurve = curveDef;
}
} else if (this.isArray(curve)) {
this._releaseCurve = curve;
} else {
throw new Error('Tone.Envelope: invalid curve: ' + curve);
}
}
});
/**
* Trigger the attack/decay portion of the ADSR envelope.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the attack should start.
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] The velocity of the envelope scales the vales.
* number between 0-1
* @returns {Tone.Envelope} this
* @example
* //trigger the attack 0.5 seconds from now with a velocity of 0.2
* env.triggerAttack("+0.5", 0.2);
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.triggerAttack = function (time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var originalAttack = this.toSeconds(this.attack);
var attack = originalAttack;
var decay = this.toSeconds(this.decay);
velocity = this.defaultArg(velocity, 1);
//check if it's not a complete attack
var currentValue = this.getValueAtTime(time);
if (currentValue > 0) {
//subtract the current value from the attack time
var attackRate = 1 / attack;
var remainingDistance = 1 - currentValue;
//the attack is now the remaining time
attack = remainingDistance / attackRate;
}
//attack
if (this._attackCurve === 'linear') {
this._sig.linearRampToValue(velocity, attack, time);
} else if (this._attackCurve === 'exponential') {
this._sig.exponentialRampToValue(velocity, attack, time);
} else if (attack > 0) {
this._sig.setRampPoint(time);
var curve = this._attackCurve;
//take only a portion of the curve
if (attack < originalAttack) {
var percentComplete = 1 - attack / originalAttack;
var sliceIndex = Math.floor(percentComplete * this._attackCurve.length);
curve = this._attackCurve.slice(sliceIndex);
//the first index is the current value
curve[0] = currentValue;
}
this._sig.setValueCurveAtTime(curve, time, attack, velocity);
}
//decay
this._sig.exponentialRampToValue(velocity * this.sustain, decay, attack + time);
return this;
};
/**
* Triggers the release of the envelope.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the release portion of the envelope should start.
* @returns {Tone.Envelope} this
* @example
* //trigger release immediately
* env.triggerRelease();
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var currentValue = this.getValueAtTime(time);
if (currentValue > 0) {
var release = this.toSeconds(this.release);
if (this._releaseCurve === 'linear') {
this._sig.linearRampToValue(0, release, time);
} else if (this._releaseCurve === 'exponential') {
this._sig.exponentialRampToValue(0, release, time);
} else {
var curve = this._releaseCurve;
if (this.isArray(curve)) {
this._sig.setRampPoint(time);
this._sig.setValueCurveAtTime(curve, time, release, currentValue);
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Get the scheduled value at the given time. This will
* return the unconverted (raw) value.
* @param {Number} time The time in seconds.
* @return {Number} The scheduled value at the given time.
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.getValueAtTime = function (time) {
return this._sig.getValueAtTime(time);
};
/**
* triggerAttackRelease is shorthand for triggerAttack, then waiting
* some duration, then triggerRelease.
* @param {Time} duration The duration of the sustain.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the attack should be triggered.
* @param {number} [velocity=1] The velocity of the envelope.
* @returns {Tone.Envelope} this
* @example
* //trigger the attack and then the release after 0.6 seconds.
* env.triggerAttackRelease(0.6);
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (duration, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.triggerRelease(time + this.toSeconds(duration));
return this;
};
/**
* Cancels all scheduled envelope changes after the given time.
* @param {Time} after
* @returns {Tone.Envelope} this
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.cancel = function (after) {
this._sig.cancelScheduledValues(after);
return this;
};
/**
* Borrows the connect method from Tone.Signal.
* @function
* @private
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.connect = Tone.Signal.prototype.connect;
/**
* Generate some complex envelope curves.
*/
(function _createCurves() {
var curveLen = 128;
var i, k;
//cosine curve
var cosineCurve = [];
for (i = 0; i < curveLen; i++) {
cosineCurve[i] = Math.sin(i / (curveLen - 1) * (Math.PI / 2));
}
//ripple curve
var rippleCurve = [];
var rippleCurveFreq = 6.4;
for (i = 0; i < curveLen - 1; i++) {
k = i / (curveLen - 1);
var sineWave = Math.sin(k * (Math.PI * 2) * rippleCurveFreq - Math.PI / 2) + 1;
rippleCurve[i] = sineWave / 10 + k * 0.83;
}
rippleCurve[curveLen - 1] = 1;
//stairs curve
var stairsCurve = [];
var steps = 5;
for (i = 0; i < curveLen; i++) {
stairsCurve[i] = Math.ceil(i / (curveLen - 1) * steps) / steps;
}
//in-out easing curve
var sineCurve = [];
for (i = 0; i < curveLen; i++) {
k = i / (curveLen - 1);
sineCurve[i] = 0.5 * (1 - Math.cos(Math.PI * k));
}
//a bounce curve
var bounceCurve = [];
for (i = 0; i < curveLen; i++) {
k = i / (curveLen - 1);
var freq = Math.pow(k, 3) * 4 + 0.2;
var val = Math.cos(freq * Math.PI * 2 * k);
bounceCurve[i] = Math.abs(val * (1 - k));
}
/**
* Invert a value curve to make it work for the release
* @private
*/
function invertCurve(curve) {
var out = new Array(curve.length);
for (var j = 0; j < curve.length; j++) {
out[j] = 1 - curve[j];
}
return out;
}
/**
* reverse the curve
* @private
*/
function reverseCurve(curve) {
return curve.slice(0).reverse();
}
/**
* attack and release curve arrays
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Envelope.Type = {
'linear': 'linear',
'exponential': 'exponential',
'bounce': {
In: invertCurve(bounceCurve),
Out: bounceCurve
},
'cosine': {
In: cosineCurve,
Out: reverseCurve(cosineCurve)
},
'step': {
In: stairsCurve,
Out: invertCurve(stairsCurve)
},
'ripple': {
In: rippleCurve,
Out: invertCurve(rippleCurve)
},
'sine': {
In: sineCurve,
Out: invertCurve(sineCurve)
}
};
}());
/**
* Disconnect and dispose.
* @returns {Tone.Envelope} this
*/
Tone.Envelope.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._sig.dispose();
this._sig = null;
this._attackCurve = null;
this._releaseCurve = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Envelope;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope is a Tone.Envelope connected to a gain node.
* Unlike Tone.Envelope, which outputs the envelope's value, Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope accepts
* an audio signal as the input and will apply the envelope to the amplitude
* of the signal. Read more about ADSR Envelopes on [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synthesizer#ADSR_envelope).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Envelope}
* @param {Time|Object} [attack] The amount of time it takes for the envelope to go from
* 0 to it's maximum value.
* @param {Time} [decay] The period of time after the attack that it takes for the envelope
* to fall to the sustain value.
* @param {NormalRange} [sustain] The percent of the maximum value that the envelope rests at until
* the release is triggered.
* @param {Time} [release] The amount of time after the release is triggered it takes to reach 0.
* @example
* var ampEnv = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope({
* "attack": 0.1,
* "decay": 0.2,
* "sustain": 1.0,
* "release": 0.8
* }).toMaster();
* //create an oscillator and connect it
* var osc = new Tone.Oscillator().connect(ampEnv).start();
* //trigger the envelopes attack and release "8t" apart
* ampEnv.triggerAttackRelease("8t");
*/
Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope = function () {
Tone.Envelope.apply(this, arguments);
/**
* the input node
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.input = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
this._sig.connect(this.output.gain);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope, Tone.Envelope);
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope} this
*/
Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.input.dispose();
this.input = null;
Tone.Envelope.prototype.dispose.call(this);
return this;
};
return Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Wrapper around the native Web Audio's
* [AnalyserNode](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#idl-def-AnalyserNode).
* Extracts FFT or Waveform data from the incoming signal.
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {String=} type The return type of the analysis, either "fft", or "waveform".
* @param {Number=} size The size of the FFT. Value must be a power of
* two in the range 32 to 32768.
*/
Tone.Analyser = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'type',
'size'
], Tone.Analyser.defaults);
/**
* The analyser node.
* @private
* @type {AnalyserNode}
*/
this._analyser = this.input = this.output = this.context.createAnalyser();
/**
* The analysis type
* @type {String}
* @private
*/
this._type = options.type;
/**
* The return type of the analysis
* @type {String}
* @private
*/
this._returnType = options.returnType;
/**
* The buffer that the FFT data is written to
* @type {TypedArray}
* @private
*/
this._buffer = null;
//set the values initially
this.size = options.size;
this.type = options.type;
this.returnType = options.returnType;
this.minDecibels = options.minDecibels;
this.maxDecibels = options.maxDecibels;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Analyser);
/**
* The default values.
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.Analyser.defaults = {
'size': 1024,
'returnType': 'byte',
'type': 'fft',
'smoothing': 0.8,
'maxDecibels': -30,
'minDecibels': -100
};
/**
* Possible return types of Tone.Analyser.analyse()
* @enum {String}
*/
Tone.Analyser.Type = {
Waveform: 'waveform',
FFT: 'fft'
};
/**
* Possible return types of Tone.Analyser.analyse().
* byte values are between [0,255]. float values are between
* [-1, 1] when the type is set to "waveform" and between
* [minDecibels,maxDecibels] when the type is "fft".
* @enum {String}
*/
Tone.Analyser.ReturnType = {
Byte: 'byte',
Float: 'float'
};
/**
* Run the analysis given the current settings and return the
* result as a TypedArray.
* @returns {TypedArray}
*/
Tone.Analyser.prototype.analyse = function () {
if (this._type === Tone.Analyser.Type.FFT) {
if (this._returnType === Tone.Analyser.ReturnType.Byte) {
this._analyser.getByteFrequencyData(this._buffer);
} else {
this._analyser.getFloatFrequencyData(this._buffer);
}
} else if (this._type === Tone.Analyser.Type.Waveform) {
if (this._returnType === Tone.Analyser.ReturnType.Byte) {
this._analyser.getByteTimeDomainData(this._buffer);
} else {
if (this.isFunction(AnalyserNode.prototype.getFloatTimeDomainData)) {
this._analyser.getFloatTimeDomainData(this._buffer);
} else {
var uint8 = new Uint8Array(this._buffer.length);
this._analyser.getByteTimeDomainData(uint8);
//referenced https://github.com/mohayonao/get-float-time-domain-data
// POLYFILL
for (var i = 0; i < uint8.length; i++) {
this._buffer[i] = (uint8[i] - 128) * 0.0078125;
}
}
}
}
return this._buffer;
};
/**
* The size of analysis. This must be a power of two in the range 32 to 32768.
* @memberOf Tone.Analyser#
* @type {Number}
* @name size
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Analyser.prototype, 'size', {
get: function () {
return this._analyser.frequencyBinCount;
},
set: function (size) {
this._analyser.fftSize = size * 2;
this.type = this._type;
}
});
/**
* The return type of Tone.Analyser.analyse(), either "byte" or "float".
* When the type is set to "byte" the range of values returned in the array
* are between 0-255. "float" values are between
* [-1, 1] when the type is set to "waveform" and between
* [minDecibels,maxDecibels] when the type is "fft".
* @memberOf Tone.Analyser#
* @type {String}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Analyser.prototype, 'returnType', {
get: function () {
return this._returnType;
},
set: function (type) {
if (type === Tone.Analyser.ReturnType.Byte) {
this._buffer = new Uint8Array(this._analyser.frequencyBinCount);
} else if (type === Tone.Analyser.ReturnType.Float) {
this._buffer = new Float32Array(this._analyser.frequencyBinCount);
} else {
throw new TypeError('Tone.Analayser: invalid return type: ' + type);
}
this._returnType = type;
}
});
/**
* The analysis function returned by Tone.Analyser.analyse(), either "fft" or "waveform".
* @memberOf Tone.Analyser#
* @type {String}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Analyser.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._type;
},
set: function (type) {
if (type !== Tone.Analyser.Type.Waveform && type !== Tone.Analyser.Type.FFT) {
throw new TypeError('Tone.Analyser: invalid type: ' + type);
}
this._type = type;
}
});
/**
* 0 represents no time averaging with the last analysis frame.
* @memberOf Tone.Analyser#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name smoothing
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Analyser.prototype, 'smoothing', {
get: function () {
return this._analyser.smoothingTimeConstant;
},
set: function (val) {
this._analyser.smoothingTimeConstant = val;
}
});
/**
* The smallest decibel value which is analysed by the FFT.
* @memberOf Tone.Analyser#
* @type {Decibels}
* @name minDecibels
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Analyser.prototype, 'minDecibels', {
get: function () {
return this._analyser.minDecibels;
},
set: function (val) {
this._analyser.minDecibels = val;
}
});
/**
* The largest decibel value which is analysed by the FFT.
* @memberOf Tone.Analyser#
* @type {Decibels}
* @name maxDecibels
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Analyser.prototype, 'maxDecibels', {
get: function () {
return this._analyser.maxDecibels;
},
set: function (val) {
this._analyser.maxDecibels = val;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Analyser} this
*/
Tone.Analyser.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._analyser.disconnect();
this._analyser = null;
this._buffer = null;
};
return Tone.Analyser;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Compressor is a thin wrapper around the Web Audio
* [DynamicsCompressorNode](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#the-dynamicscompressornode-interface).
* Compression reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds
* by narrowing or "compressing" an audio signal's dynamic range.
* Read more on [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynamic_range_compression).
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {Decibels|Object} [threshold] The value above which the compression starts to be applied.
* @param {Positive} [ratio] The gain reduction ratio.
* @example
* var comp = new Tone.Compressor(-30, 3);
*/
Tone.Compressor = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'threshold',
'ratio'
], Tone.Compressor.defaults);
/**
* the compressor node
* @type {DynamicsCompressorNode}
* @private
*/
this._compressor = this.input = this.output = this.context.createDynamicsCompressor();
/**
* the threshold vaue
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.threshold = new Tone.Param({
'param': this._compressor.threshold,
'units': Tone.Type.Decibels,
'convert': false
});
/**
* The attack parameter
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.attack = new Tone.Param(this._compressor.attack, Tone.Type.Time);
/**
* The release parameter
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.release = new Tone.Param(this._compressor.release, Tone.Type.Time);
/**
* The knee parameter
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.knee = new Tone.Param({
'param': this._compressor.knee,
'units': Tone.Type.Decibels,
'convert': false
});
/**
* The ratio value
* @type {Number}
* @signal
*/
this.ratio = new Tone.Param({
'param': this._compressor.ratio,
'convert': false
});
//set the defaults
this._readOnly([
'knee',
'release',
'attack',
'ratio',
'threshold'
]);
this.set(options);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Compressor);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Compressor.defaults = {
'ratio': 12,
'threshold': -24,
'release': 0.25,
'attack': 0.003,
'knee': 30
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Compressor} this
*/
Tone.Compressor.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'knee',
'release',
'attack',
'ratio',
'threshold'
]);
this._compressor.disconnect();
this._compressor = null;
this.attack.dispose();
this.attack = null;
this.release.dispose();
this.release = null;
this.threshold.dispose();
this.threshold = null;
this.ratio.dispose();
this.ratio = null;
this.knee.dispose();
this.knee = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Compressor;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Add a signal and a number or two signals. When no value is
* passed into the constructor, Tone.Add will sum input[0]
* and input[1]. If a value is passed into the constructor,
* the it will be added to the input.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Signal}
* @param {number=} value If no value is provided, Tone.Add will sum the first
* and second inputs.
* @example
* var signal = new Tone.Signal(2);
* var add = new Tone.Add(2);
* signal.connect(add);
* //the output of add equals 4
* @example
* //if constructed with no arguments
* //it will add the first and second inputs
* var add = new Tone.Add();
* var sig0 = new Tone.Signal(3).connect(add, 0, 0);
* var sig1 = new Tone.Signal(4).connect(add, 0, 1);
* //the output of add equals 7.
*/
Tone.Add = function (value) {
this.createInsOuts(2, 0);
/**
* the summing node
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this._sum = this.input[0] = this.input[1] = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* @private
* @type {Tone.Signal}
*/
this._param = this.input[1] = new Tone.Signal(value);
this._param.connect(this._sum);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Add, Tone.Signal);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Add} this
*/
Tone.Add.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._sum.dispose();
this._sum = null;
this._param.dispose();
this._param = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Add;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Multiply two incoming signals. Or, if a number is given in the constructor,
* multiplies the incoming signal by that value.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Signal}
* @param {number=} value Constant value to multiple. If no value is provided,
* it will return the product of the first and second inputs
* @example
* var mult = new Tone.Multiply();
* var sigA = new Tone.Signal(3);
* var sigB = new Tone.Signal(4);
* sigA.connect(mult, 0, 0);
* sigB.connect(mult, 0, 1);
* //output of mult is 12.
* @example
* var mult = new Tone.Multiply(10);
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(2).connect(mult);
* //the output of mult is 20.
*/
Tone.Multiply = function (value) {
this.createInsOuts(2, 0);
/**
* the input node is the same as the output node
* it is also the GainNode which handles the scaling of incoming signal
*
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this._mult = this.input[0] = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the scaling parameter
* @type {AudioParam}
* @private
*/
this._param = this.input[1] = this.output.gain;
this._param.value = this.defaultArg(value, 0);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Multiply, Tone.Signal);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Multiply} this
*/
Tone.Multiply.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._mult.dispose();
this._mult = null;
this._param = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Multiply;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Negate the incoming signal. i.e. an input signal of 10 will output -10
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @example
* var neg = new Tone.Negate();
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(-2).connect(neg);
* //output of neg is positive 2.
*/
Tone.Negate = function () {
/**
* negation is done by multiplying by -1
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._multiply = this.input = this.output = new Tone.Multiply(-1);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Negate, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Negate} this
*/
Tone.Negate.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._multiply.dispose();
this._multiply = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Negate;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Subtract the signal connected to input[1] from the signal connected
* to input[0]. If an argument is provided in the constructor, the
* signals .value will be subtracted from the incoming signal.
*
* @extends {Tone.Signal}
* @constructor
* @param {number=} value The value to subtract from the incoming signal. If the value
* is omitted, it will subtract the second signal from the first.
* @example
* var sub = new Tone.Subtract(1);
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(4).connect(sub);
* //the output of sub is 3.
* @example
* var sub = new Tone.Subtract();
* var sigA = new Tone.Signal(10);
* var sigB = new Tone.Signal(2.5);
* sigA.connect(sub, 0, 0);
* sigB.connect(sub, 0, 1);
* //output of sub is 7.5
*/
Tone.Subtract = function (value) {
this.createInsOuts(2, 0);
/**
* the summing node
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this._sum = this.input[0] = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* negate the input of the second input before connecting it
* to the summing node.
* @type {Tone.Negate}
* @private
*/
this._neg = new Tone.Negate();
/**
* the node where the value is set
* @private
* @type {Tone.Signal}
*/
this._param = this.input[1] = new Tone.Signal(value);
this._param.chain(this._neg, this._sum);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Subtract, Tone.Signal);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.SignalBase} this
*/
Tone.Subtract.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._neg.dispose();
this._neg = null;
this._sum.disconnect();
this._sum = null;
this._param.dispose();
this._param = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Subtract;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class GreaterThanZero outputs 1 when the input is strictly greater than zero
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @example
* var gt0 = new Tone.GreaterThanZero();
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(0.01).connect(gt0);
* //the output of gt0 is 1.
* sig.value = 0;
* //the output of gt0 is 0.
*/
Tone.GreaterThanZero = function () {
/**
* @type {Tone.WaveShaper}
* @private
*/
this._thresh = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (val) {
if (val <= 0) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}, 127);
/**
* scale the first thresholded signal by a large value.
* this will help with values which are very close to 0
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._scale = this.input = new Tone.Multiply(10000);
//connections
this._scale.connect(this._thresh);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.GreaterThanZero, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* dispose method
* @returns {Tone.GreaterThanZero} this
*/
Tone.GreaterThanZero.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._scale.dispose();
this._scale = null;
this._thresh.dispose();
this._thresh = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.GreaterThanZero;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Output 1 if the signal is greater than the value, otherwise outputs 0.
* can compare two signals or a signal and a number.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Signal}
* @param {number} [value=0] the value to compare to the incoming signal
* @example
* var gt = new Tone.GreaterThan(2);
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(4).connect(gt);
* //output of gt is equal 1.
*/
Tone.GreaterThan = function (value) {
this.createInsOuts(2, 0);
/**
* subtract the amount from the incoming signal
* @type {Tone.Subtract}
* @private
*/
this._param = this.input[0] = new Tone.Subtract(value);
this.input[1] = this._param.input[1];
/**
* compare that amount to zero
* @type {Tone.GreaterThanZero}
* @private
*/
this._gtz = this.output = new Tone.GreaterThanZero();
//connect
this._param.connect(this._gtz);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.GreaterThan, Tone.Signal);
/**
* dispose method
* @returns {Tone.GreaterThan} this
*/
Tone.GreaterThan.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._param.dispose();
this._param = null;
this._gtz.dispose();
this._gtz = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.GreaterThan;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Return the absolute value of an incoming signal.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @example
* var signal = new Tone.Signal(-1);
* var abs = new Tone.Abs();
* signal.connect(abs);
* //the output of abs is 1.
*/
Tone.Abs = function () {
/**
* @type {Tone.LessThan}
* @private
*/
this._abs = this.input = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (val) {
if (val === 0) {
return 0;
} else {
return Math.abs(val);
}
}, 127);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Abs, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* dispose method
* @returns {Tone.Abs} this
*/
Tone.Abs.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._abs.dispose();
this._abs = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Abs;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Signal-rate modulo operator. Only works in AudioRange [-1, 1] and for modulus
* values in the NormalRange.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @param {NormalRange} modulus The modulus to apply.
* @example
* var mod = new Tone.Modulo(0.2)
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(0.5).connect(mod);
* //mod outputs 0.1
*/
Tone.Modulo = function (modulus) {
this.createInsOuts(1, 0);
/**
* A waveshaper gets the integer multiple of
* the input signal and the modulus.
* @private
* @type {Tone.WaveShaper}
*/
this._shaper = new Tone.WaveShaper(Math.pow(2, 16));
/**
* the integer multiple is multiplied by the modulus
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._multiply = new Tone.Multiply();
/**
* and subtracted from the input signal
* @type {Tone.Subtract}
* @private
*/
this._subtract = this.output = new Tone.Subtract();
/**
* the modulus signal
* @type {Tone.Signal}
* @private
*/
this._modSignal = new Tone.Signal(modulus);
//connections
this.input.fan(this._shaper, this._subtract);
this._modSignal.connect(this._multiply, 0, 0);
this._shaper.connect(this._multiply, 0, 1);
this._multiply.connect(this._subtract, 0, 1);
this._setWaveShaper(modulus);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Modulo, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* @param {number} mod the modulus to apply
* @private
*/
Tone.Modulo.prototype._setWaveShaper = function (mod) {
this._shaper.setMap(function (val) {
var multiple = Math.floor((val + 0.0001) / mod);
return multiple;
});
};
/**
* The modulus value.
* @memberOf Tone.Modulo#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Modulo.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
return this._modSignal.value;
},
set: function (mod) {
this._modSignal.value = mod;
this._setWaveShaper(mod);
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Modulo} this
*/
Tone.Modulo.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._shaper.dispose();
this._shaper = null;
this._multiply.dispose();
this._multiply = null;
this._subtract.dispose();
this._subtract = null;
this._modSignal.dispose();
this._modSignal = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Modulo;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class AudioToGain converts an input in AudioRange [-1,1] to NormalRange [0,1].
* See Tone.GainToAudio.
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @example
* var a2g = new Tone.AudioToGain();
*/
Tone.AudioToGain = function () {
/**
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._norm = this.input = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (x) {
return (x + 1) / 2;
});
};
Tone.extend(Tone.AudioToGain, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.AudioToGain} this
*/
Tone.AudioToGain.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._norm.dispose();
this._norm = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AudioToGain;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Evaluate an expression at audio rate.
* Parsing code modified from https://code.google.com/p/tapdigit/
* Copyright 2011 2012 Ariya Hidayat, New BSD License
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @param {string} expr the expression to generate
* @example
* //adds the signals from input[0] and input[1].
* var expr = new Tone.Expr("$0 + $1");
*/
Tone.Expr = function () {
var expr = this._replacements(Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments));
var inputCount = this._parseInputs(expr);
/**
* hold onto all of the nodes for disposal
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._nodes = [];
/**
* The inputs. The length is determined by the expression.
* @type {Array}
*/
this.input = new Array(inputCount);
//create a gain for each input
for (var i = 0; i < inputCount; i++) {
this.input[i] = this.context.createGain();
}
//parse the syntax tree
var tree = this._parseTree(expr);
//evaluate the results
var result;
try {
result = this._eval(tree);
} catch (e) {
this._disposeNodes();
throw new Error('Tone.Expr: Could evaluate expression: ' + expr);
}
/**
* The output node is the result of the expression
* @type {Tone}
*/
this.output = result;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Expr, Tone.SignalBase);
//some helpers to cut down the amount of code
function applyBinary(Constructor, args, self) {
var op = new Constructor();
self._eval(args[0]).connect(op, 0, 0);
self._eval(args[1]).connect(op, 0, 1);
return op;
}
function applyUnary(Constructor, args, self) {
var op = new Constructor();
self._eval(args[0]).connect(op, 0, 0);
return op;
}
function getNumber(arg) {
return arg ? parseFloat(arg) : undefined;
}
function literalNumber(arg) {
return arg && arg.args ? parseFloat(arg.args) : undefined;
}
/*
* the Expressions that Tone.Expr can parse.
*
* each expression belongs to a group and contains a regexp
* for selecting the operator as well as that operators method
*
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr._Expressions = {
//values
'value': {
'signal': {
regexp: /^\d+\.\d+|^\d+/,
method: function (arg) {
var sig = new Tone.Signal(getNumber(arg));
return sig;
}
},
'input': {
regexp: /^\$\d/,
method: function (arg, self) {
return self.input[getNumber(arg.substr(1))];
}
}
},
//syntactic glue
'glue': {
'(': { regexp: /^\(/ },
')': { regexp: /^\)/ },
',': { regexp: /^,/ }
},
//functions
'func': {
'abs': {
regexp: /^abs/,
method: applyUnary.bind(this, Tone.Abs)
},
'mod': {
regexp: /^mod/,
method: function (args, self) {
var modulus = literalNumber(args[1]);
var op = new Tone.Modulo(modulus);
self._eval(args[0]).connect(op);
return op;
}
},
'pow': {
regexp: /^pow/,
method: function (args, self) {
var exp = literalNumber(args[1]);
var op = new Tone.Pow(exp);
self._eval(args[0]).connect(op);
return op;
}
},
'a2g': {
regexp: /^a2g/,
method: function (args, self) {
var op = new Tone.AudioToGain();
self._eval(args[0]).connect(op);
return op;
}
}
},
//binary expressions
'binary': {
'+': {
regexp: /^\+/,
precedence: 1,
method: applyBinary.bind(this, Tone.Add)
},
'-': {
regexp: /^\-/,
precedence: 1,
method: function (args, self) {
//both unary and binary op
if (args.length === 1) {
return applyUnary(Tone.Negate, args, self);
} else {
return applyBinary(Tone.Subtract, args, self);
}
}
},
'*': {
regexp: /^\*/,
precedence: 0,
method: applyBinary.bind(this, Tone.Multiply)
}
},
//unary expressions
'unary': {
'-': {
regexp: /^\-/,
method: applyUnary.bind(this, Tone.Negate)
},
'!': {
regexp: /^\!/,
method: applyUnary.bind(this, Tone.NOT)
}
}
};
/**
* @param {string} expr the expression string
* @return {number} the input count
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype._parseInputs = function (expr) {
var inputArray = expr.match(/\$\d/g);
var inputMax = 0;
if (inputArray !== null) {
for (var i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i++) {
var inputNum = parseInt(inputArray[i].substr(1)) + 1;
inputMax = Math.max(inputMax, inputNum);
}
}
return inputMax;
};
/**
* @param {Array} args an array of arguments
* @return {string} the results of the replacements being replaced
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype._replacements = function (args) {
var expr = args.shift();
for (var i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
expr = expr.replace(/\%/i, args[i]);
}
return expr;
};
/**
* tokenize the expression based on the Expressions object
* @param {string} expr
* @return {Object} returns two methods on the tokenized list, next and peek
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype._tokenize = function (expr) {
var position = -1;
var tokens = [];
while (expr.length > 0) {
expr = expr.trim();
var token = getNextToken(expr);
tokens.push(token);
expr = expr.substr(token.value.length);
}
function getNextToken(expr) {
for (var type in Tone.Expr._Expressions) {
var group = Tone.Expr._Expressions[type];
for (var opName in group) {
var op = group[opName];
var reg = op.regexp;
var match = expr.match(reg);
if (match !== null) {
return {
type: type,
value: match[0],
method: op.method
};
}
}
}
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.Expr: Unexpected token ' + expr);
}
return {
next: function () {
return tokens[++position];
},
peek: function () {
return tokens[position + 1];
}
};
};
/**
* recursively parse the string expression into a syntax tree
*
* @param {string} expr
* @return {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype._parseTree = function (expr) {
var lexer = this._tokenize(expr);
var isUndef = this.isUndef.bind(this);
function matchSyntax(token, syn) {
return !isUndef(token) && token.type === 'glue' && token.value === syn;
}
function matchGroup(token, groupName, prec) {
var ret = false;
var group = Tone.Expr._Expressions[groupName];
if (!isUndef(token)) {
for (var opName in group) {
var op = group[opName];
if (op.regexp.test(token.value)) {
if (!isUndef(prec)) {
if (op.precedence === prec) {
return true;
}
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return ret;
}
function parseExpression(precedence) {
if (isUndef(precedence)) {
precedence = 5;
}
var expr;
if (precedence < 0) {
expr = parseUnary();
} else {
expr = parseExpression(precedence - 1);
}
var token = lexer.peek();
while (matchGroup(token, 'binary', precedence)) {
token = lexer.next();
expr = {
operator: token.value,
method: token.method,
args: [
expr,
parseExpression(precedence - 1)
]
};
token = lexer.peek();
}
return expr;
}
function parseUnary() {
var token, expr;
token = lexer.peek();
if (matchGroup(token, 'unary')) {
token = lexer.next();
expr = parseUnary();
return {
operator: token.value,
method: token.method,
args: [expr]
};
}
return parsePrimary();
}
function parsePrimary() {
var token, expr;
token = lexer.peek();
if (isUndef(token)) {
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.Expr: Unexpected termination of expression');
}
if (token.type === 'func') {
token = lexer.next();
return parseFunctionCall(token);
}
if (token.type === 'value') {
token = lexer.next();
return {
method: token.method,
args: token.value
};
}
if (matchSyntax(token, '(')) {
lexer.next();
expr = parseExpression();
token = lexer.next();
if (!matchSyntax(token, ')')) {
throw new SyntaxError('Expected )');
}
return expr;
}
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.Expr: Parse error, cannot process token ' + token.value);
}
function parseFunctionCall(func) {
var token, args = [];
token = lexer.next();
if (!matchSyntax(token, '(')) {
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.Expr: Expected ( in a function call "' + func.value + '"');
}
token = lexer.peek();
if (!matchSyntax(token, ')')) {
args = parseArgumentList();
}
token = lexer.next();
if (!matchSyntax(token, ')')) {
throw new SyntaxError('Tone.Expr: Expected ) in a function call "' + func.value + '"');
}
return {
method: func.method,
args: args,
name: name
};
}
function parseArgumentList() {
var token, expr, args = [];
while (true) {
expr = parseExpression();
if (isUndef(expr)) {
// TODO maybe throw exception?
break;
}
args.push(expr);
token = lexer.peek();
if (!matchSyntax(token, ',')) {
break;
}
lexer.next();
}
return args;
}
return parseExpression();
};
/**
* recursively evaluate the expression tree
* @param {Object} tree
* @return {AudioNode} the resulting audio node from the expression
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype._eval = function (tree) {
if (!this.isUndef(tree)) {
var node = tree.method(tree.args, this);
this._nodes.push(node);
return node;
}
};
/**
* dispose all the nodes
* @private
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype._disposeNodes = function () {
for (var i = 0; i < this._nodes.length; i++) {
var node = this._nodes[i];
if (this.isFunction(node.dispose)) {
node.dispose();
} else if (this.isFunction(node.disconnect)) {
node.disconnect();
}
node = null;
this._nodes[i] = null;
}
this._nodes = null;
};
/**
* clean up
*/
Tone.Expr.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._disposeNodes();
};
return Tone.Expr;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Convert an incoming signal between 0, 1 to an equal power gain scale.
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @example
* var eqPowGain = new Tone.EqualPowerGain();
*/
Tone.EqualPowerGain = function () {
/**
* @type {Tone.WaveShaper}
* @private
*/
this._eqPower = this.input = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (val) {
if (Math.abs(val) < 0.001) {
//should output 0 when input is 0
return 0;
} else {
return this.equalPowerScale(val);
}
}.bind(this), 4096);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.EqualPowerGain, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.EqualPowerGain} this
*/
Tone.EqualPowerGain.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._eqPower.dispose();
this._eqPower = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.EqualPowerGain;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Crossfade provides equal power fading between two inputs.
* More on crossfading technique [here](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fade_(audio_engineering)#Crossfading).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {NormalRange} [initialFade=0.5]
* @example
* var crossFade = new Tone.CrossFade(0.5);
* //connect effect A to crossfade from
* //effect output 0 to crossfade input 0
* effectA.connect(crossFade, 0, 0);
* //connect effect B to crossfade from
* //effect output 0 to crossfade input 1
* effectB.connect(crossFade, 0, 1);
* crossFade.fade.value = 0;
* // ^ only effectA is output
* crossFade.fade.value = 1;
* // ^ only effectB is output
* crossFade.fade.value = 0.5;
* // ^ the two signals are mixed equally.
*/
Tone.CrossFade = function (initialFade) {
this.createInsOuts(2, 1);
/**
* Alias for input[0].
* @type {Tone.Gain}
*/
this.a = this.input[0] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* Alias for input[1].
* @type {Tone.Gain}
*/
this.b = this.input[1] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* The mix between the two inputs. A fade value of 0
* will output 100% input[0] and
* a value of 1 will output 100% input[1].
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.fade = new Tone.Signal(this.defaultArg(initialFade, 0.5), Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* equal power gain cross fade
* @private
* @type {Tone.EqualPowerGain}
*/
this._equalPowerA = new Tone.EqualPowerGain();
/**
* equal power gain cross fade
* @private
* @type {Tone.EqualPowerGain}
*/
this._equalPowerB = new Tone.EqualPowerGain();
/**
* invert the incoming signal
* @private
* @type {Tone}
*/
this._invert = new Tone.Expr('1 - $0');
//connections
this.a.connect(this.output);
this.b.connect(this.output);
this.fade.chain(this._equalPowerB, this.b.gain);
this.fade.chain(this._invert, this._equalPowerA, this.a.gain);
this._readOnly('fade');
};
Tone.extend(Tone.CrossFade);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.CrossFade} this
*/
Tone.CrossFade.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable('fade');
this._equalPowerA.dispose();
this._equalPowerA = null;
this._equalPowerB.dispose();
this._equalPowerB = null;
this.fade.dispose();
this.fade = null;
this._invert.dispose();
this._invert = null;
this.a.dispose();
this.a = null;
this.b.dispose();
this.b = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.CrossFade;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Filter is a filter which allows for all of the same native methods
* as the [BiquadFilterNode](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#the-biquadfilternode-interface).
* Tone.Filter has the added ability to set the filter rolloff at -12
* (default), -24 and -48.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Frequency|Object} [frequency] The cutoff frequency of the filter.
* @param {string=} type The type of filter.
* @param {number=} rolloff The drop in decibels per octave after the cutoff frequency.
* 3 choices: -12, -24, and -48
* @example
* var filter = new Tone.Filter(200, "highpass");
*/
Tone.Filter = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'type',
'rolloff'
], Tone.Filter.defaults);
/**
* the filter(s)
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._filters = [];
/**
* The cutoff frequency of the filter.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune parameter
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(0, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* The gain of the filter, only used in certain filter types
* @type {Number}
* @signal
*/
this.gain = new Tone.Signal({
'value': options.gain,
'convert': false
});
/**
* The Q or Quality of the filter
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.Q = new Tone.Signal(options.Q);
/**
* the type of the filter
* @type {string}
* @private
*/
this._type = options.type;
/**
* the rolloff value of the filter
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._rolloff = options.rolloff;
//set the rolloff;
this.rolloff = options.rolloff;
this._readOnly([
'detune',
'frequency',
'gain',
'Q'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Filter);
/**
* the default parameters
*
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Filter.defaults = {
'type': 'lowpass',
'frequency': 350,
'rolloff': -12,
'Q': 1,
'gain': 0
};
/**
* The type of the filter. Types: "lowpass", "highpass",
* "bandpass", "lowshelf", "highshelf", "notch", "allpass", or "peaking".
* @memberOf Tone.Filter#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Filter.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._type;
},
set: function (type) {
var types = [
'lowpass',
'highpass',
'bandpass',
'lowshelf',
'highshelf',
'notch',
'allpass',
'peaking'
];
if (types.indexOf(type) === -1) {
throw new TypeError('Tone.Filter: invalid type ' + type);
}
this._type = type;
for (var i = 0; i < this._filters.length; i++) {
this._filters[i].type = type;
}
}
});
/**
* The rolloff of the filter which is the drop in db
* per octave. Implemented internally by cascading filters.
* Only accepts the values -12, -24, -48 and -96.
* @memberOf Tone.Filter#
* @type {number}
* @name rolloff
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Filter.prototype, 'rolloff', {
get: function () {
return this._rolloff;
},
set: function (rolloff) {
rolloff = parseInt(rolloff, 10);
var possibilities = [
-12,
-24,
-48,
-96
];
var cascadingCount = possibilities.indexOf(rolloff);
//check the rolloff is valid
if (cascadingCount === -1) {
throw new RangeError('Tone.Filter: rolloff can only be -12, -24, -48 or -96');
}
cascadingCount += 1;
this._rolloff = rolloff;
//first disconnect the filters and throw them away
this.input.disconnect();
for (var i = 0; i < this._filters.length; i++) {
this._filters[i].disconnect();
this._filters[i] = null;
}
this._filters = new Array(cascadingCount);
for (var count = 0; count < cascadingCount; count++) {
var filter = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
filter.type = this._type;
this.frequency.connect(filter.frequency);
this.detune.connect(filter.detune);
this.Q.connect(filter.Q);
this.gain.connect(filter.gain);
this._filters[count] = filter;
}
//connect them up
var connectionChain = [this.input].concat(this._filters).concat([this.output]);
this.connectSeries.apply(this, connectionChain);
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Filter} this
*/
Tone.Filter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
for (var i = 0; i < this._filters.length; i++) {
this._filters[i].disconnect();
this._filters[i] = null;
}
this._filters = null;
this._writable([
'detune',
'frequency',
'gain',
'Q'
]);
this.frequency.dispose();
this.Q.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.Q = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.gain.dispose();
this.gain = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Filter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Split the incoming signal into three bands (low, mid, high)
* with two crossover frequency controls.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency|Object} [lowFrequency] the low/mid crossover frequency
* @param {Frequency} [highFrequency] the mid/high crossover frequency
*/
Tone.MultibandSplit = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'lowFrequency',
'highFrequency'
], Tone.MultibandSplit.defaults);
/**
* the input
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this.input = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the outputs
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this.output = new Array(3);
/**
* The low band. Alias for output[0]
* @type {Tone.Filter}
*/
this.low = this.output[0] = new Tone.Filter(0, 'lowpass');
/**
* the lower filter of the mid band
* @type {Tone.Filter}
* @private
*/
this._lowMidFilter = new Tone.Filter(0, 'highpass');
/**
* The mid band output. Alias for output[1]
* @type {Tone.Filter}
*/
this.mid = this.output[1] = new Tone.Filter(0, 'lowpass');
/**
* The high band output. Alias for output[2]
* @type {Tone.Filter}
*/
this.high = this.output[2] = new Tone.Filter(0, 'highpass');
/**
* The low/mid crossover frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.lowFrequency = new Tone.Signal(options.lowFrequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The mid/high crossover frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.highFrequency = new Tone.Signal(options.highFrequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The quality of all the filters
* @type {Number}
* @signal
*/
this.Q = new Tone.Signal(options.Q);
this.input.fan(this.low, this.high);
this.input.chain(this._lowMidFilter, this.mid);
//the frequency control signal
this.lowFrequency.connect(this.low.frequency);
this.lowFrequency.connect(this._lowMidFilter.frequency);
this.highFrequency.connect(this.mid.frequency);
this.highFrequency.connect(this.high.frequency);
//the Q value
this.Q.connect(this.low.Q);
this.Q.connect(this._lowMidFilter.Q);
this.Q.connect(this.mid.Q);
this.Q.connect(this.high.Q);
this._readOnly([
'high',
'mid',
'low',
'highFrequency',
'lowFrequency'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MultibandSplit);
/**
* @private
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MultibandSplit.defaults = {
'lowFrequency': 400,
'highFrequency': 2500,
'Q': 1
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.MultibandSplit} this
*/
Tone.MultibandSplit.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'high',
'mid',
'low',
'highFrequency',
'lowFrequency'
]);
this.low.dispose();
this.low = null;
this._lowMidFilter.dispose();
this._lowMidFilter = null;
this.mid.dispose();
this.mid = null;
this.high.dispose();
this.high = null;
this.lowFrequency.dispose();
this.lowFrequency = null;
this.highFrequency.dispose();
this.highFrequency = null;
this.Q.dispose();
this.Q = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MultibandSplit;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.EQ3 is a three band EQ with control over low, mid, and high gain as
* well as the low and high crossover frequencies.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
*
* @param {Decibels|Object} [lowLevel] The gain applied to the lows.
* @param {Decibels} [midLevel] The gain applied to the mid.
* @param {Decibels} [highLevel] The gain applied to the high.
* @example
* var eq = new Tone.EQ3(-10, 3, -20);
*/
Tone.EQ3 = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'low',
'mid',
'high'
], Tone.EQ3.defaults);
/**
* the output node
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the multiband split
* @type {Tone.MultibandSplit}
* @private
*/
this._multibandSplit = this.input = new Tone.MultibandSplit({
'lowFrequency': options.lowFrequency,
'highFrequency': options.highFrequency
});
/**
* The gain for the lower signals
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._lowGain = new Tone.Gain(options.low, Tone.Type.Decibels);
/**
* The gain for the mid signals
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._midGain = new Tone.Gain(options.mid, Tone.Type.Decibels);
/**
* The gain in decibels of the high part
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._highGain = new Tone.Gain(options.high, Tone.Type.Decibels);
/**
* The gain in decibels of the low part
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.low = this._lowGain.gain;
/**
* The gain in decibels of the mid part
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.mid = this._midGain.gain;
/**
* The gain in decibels of the high part
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.high = this._highGain.gain;
/**
* The Q value for all of the filters.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.Q = this._multibandSplit.Q;
/**
* The low/mid crossover frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.lowFrequency = this._multibandSplit.lowFrequency;
/**
* The mid/high crossover frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.highFrequency = this._multibandSplit.highFrequency;
//the frequency bands
this._multibandSplit.low.chain(this._lowGain, this.output);
this._multibandSplit.mid.chain(this._midGain, this.output);
this._multibandSplit.high.chain(this._highGain, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'low',
'mid',
'high',
'lowFrequency',
'highFrequency'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.EQ3);
/**
* the default values
*/
Tone.EQ3.defaults = {
'low': 0,
'mid': 0,
'high': 0,
'lowFrequency': 400,
'highFrequency': 2500
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.EQ3} this
*/
Tone.EQ3.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'low',
'mid',
'high',
'lowFrequency',
'highFrequency'
]);
this._multibandSplit.dispose();
this._multibandSplit = null;
this.lowFrequency = null;
this.highFrequency = null;
this._lowGain.dispose();
this._lowGain = null;
this._midGain.dispose();
this._midGain = null;
this._highGain.dispose();
this._highGain = null;
this.low = null;
this.mid = null;
this.high = null;
this.Q = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.EQ3;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Performs a linear scaling on an input signal.
* Scales a NormalRange input to between
* outputMin and outputMax.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @param {number} [outputMin=0] The output value when the input is 0.
* @param {number} [outputMax=1] The output value when the input is 1.
* @example
* var scale = new Tone.Scale(50, 100);
* var signal = new Tone.Signal(0.5).connect(scale);
* //the output of scale equals 75
*/
Tone.Scale = function (outputMin, outputMax) {
/**
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._outputMin = this.defaultArg(outputMin, 0);
/**
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._outputMax = this.defaultArg(outputMax, 1);
/**
* @private
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._scale = this.input = new Tone.Multiply(1);
/**
* @private
* @type {Tone.Add}
* @private
*/
this._add = this.output = new Tone.Add(0);
this._scale.connect(this._add);
this._setRange();
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Scale, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* The minimum output value. This number is output when
* the value input value is 0.
* @memberOf Tone.Scale#
* @type {number}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Scale.prototype, 'min', {
get: function () {
return this._outputMin;
},
set: function (min) {
this._outputMin = min;
this._setRange();
}
});
/**
* The maximum output value. This number is output when
* the value input value is 1.
* @memberOf Tone.Scale#
* @type {number}
* @name max
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Scale.prototype, 'max', {
get: function () {
return this._outputMax;
},
set: function (max) {
this._outputMax = max;
this._setRange();
}
});
/**
* set the values
* @private
*/
Tone.Scale.prototype._setRange = function () {
this._add.value = this._outputMin;
this._scale.value = this._outputMax - this._outputMin;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Scale} this
*/
Tone.Scale.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._add.dispose();
this._add = null;
this._scale.dispose();
this._scale = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Scale;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Performs an exponential scaling on an input signal.
* Scales a NormalRange value [0,1] exponentially
* to the output range of outputMin to outputMax.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @param {number} [outputMin=0] The output value when the input is 0.
* @param {number} [outputMax=1] The output value when the input is 1.
* @param {number} [exponent=2] The exponent which scales the incoming signal.
* @example
* var scaleExp = new Tone.ScaleExp(0, 100, 2);
* var signal = new Tone.Signal(0.5).connect(scaleExp);
*/
Tone.ScaleExp = function (outputMin, outputMax, exponent) {
/**
* scale the input to the output range
* @type {Tone.Scale}
* @private
*/
this._scale = this.output = new Tone.Scale(outputMin, outputMax);
/**
* @private
* @type {Tone.Pow}
* @private
*/
this._exp = this.input = new Tone.Pow(this.defaultArg(exponent, 2));
this._exp.connect(this._scale);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.ScaleExp, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* Instead of interpolating linearly between the min and
* max values, setting the exponent will interpolate between
* the two values with an exponential curve.
* @memberOf Tone.ScaleExp#
* @type {number}
* @name exponent
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.ScaleExp.prototype, 'exponent', {
get: function () {
return this._exp.value;
},
set: function (exp) {
this._exp.value = exp;
}
});
/**
* The minimum output value. This number is output when
* the value input value is 0.
* @memberOf Tone.ScaleExp#
* @type {number}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.ScaleExp.prototype, 'min', {
get: function () {
return this._scale.min;
},
set: function (min) {
this._scale.min = min;
}
});
/**
* The maximum output value. This number is output when
* the value input value is 1.
* @memberOf Tone.ScaleExp#
* @type {number}
* @name max
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.ScaleExp.prototype, 'max', {
get: function () {
return this._scale.max;
},
set: function (max) {
this._scale.max = max;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.ScaleExp} this
*/
Tone.ScaleExp.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._scale.dispose();
this._scale = null;
this._exp.dispose();
this._exp = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.ScaleExp;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Wrapper around Web Audio's native [DelayNode](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#the-delaynode-interface).
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Time=} delayTime The delay applied to the incoming signal.
* @param {Time=} maxDelay The maximum delay time.
*/
Tone.Delay = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'delayTime',
'maxDelay'
], Tone.Delay.defaults);
/**
* The native delay node
* @type {DelayNode}
* @private
*/
this._delayNode = this.input = this.output = this.context.createDelay(this.toSeconds(options.maxDelay));
/**
* The amount of time the incoming signal is
* delayed.
* @type {Tone.Param}
* @signal
*/
this.delayTime = new Tone.Param({
'param': this._delayNode.delayTime,
'units': Tone.Type.Time,
'value': options.delayTime
});
this._readOnly('delayTime');
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Delay);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Delay.defaults = {
'maxDelay': 1,
'delayTime': 0
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Delay} this
*/
Tone.Delay.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Param.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._delayNode.disconnect();
this._delayNode = null;
this._writable('delayTime');
this.delayTime = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Delay;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Comb filters are basic building blocks for physical modeling. Read more
* about comb filters on [CCRMA's website](https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/pasp/Feedback_Comb_Filters.html).
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {Time|Object} [delayTime] The delay time of the filter.
* @param {NormalRange=} resonance The amount of feedback the filter has.
*/
Tone.FeedbackCombFilter = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'delayTime',
'resonance'
], Tone.FeedbackCombFilter.defaults);
/**
* the delay node
* @type {DelayNode}
* @private
*/
this._delay = this.input = this.output = new Tone.Delay(options.delayTime);
/**
* The amount of delay of the comb filter.
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.delayTime = this._delay.delayTime;
/**
* the feedback node
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this._feedback = new Tone.Gain(options.resonance, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* The amount of feedback of the delayed signal.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.resonance = this._feedback.gain;
this._delay.chain(this._feedback, this._delay);
this._readOnly([
'resonance',
'delayTime'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FeedbackCombFilter);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.FeedbackCombFilter.defaults = {
'delayTime': 0.1,
'resonance': 0.5
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.FeedbackCombFilter} this
*/
Tone.FeedbackCombFilter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'resonance',
'delayTime'
]);
this._delay.dispose();
this._delay = null;
this.delayTime = null;
this._feedback.dispose();
this._feedback = null;
this.resonance = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FeedbackCombFilter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Follower is a crude envelope follower which will follow
* the amplitude of an incoming signal.
* Take care with small (< 0.02) attack or decay values
* as follower has some ripple which is exaggerated
* at these values. Read more about envelope followers (also known
* as envelope detectors) on [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Envelope_detector).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Time|Object} [attack] The rate at which the follower rises.
* @param {Time=} release The rate at which the folower falls.
* @example
* var follower = new Tone.Follower(0.2, 0.4);
*/
Tone.Follower = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'attack',
'release'
], Tone.Follower.defaults);
/**
* @type {Tone.Abs}
* @private
*/
this._abs = new Tone.Abs();
/**
* the lowpass filter which smooths the input
* @type {BiquadFilterNode}
* @private
*/
this._filter = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
this._filter.type = 'lowpass';
this._filter.frequency.value = 0;
this._filter.Q.value = -100;
/**
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._frequencyValues = new Tone.WaveShaper();
/**
* @type {Tone.Subtract}
* @private
*/
this._sub = new Tone.Subtract();
/**
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._delay = new Tone.Delay(this.blockTime);
/**
* this keeps it far from 0, even for very small differences
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._mult = new Tone.Multiply(10000);
/**
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._attack = options.attack;
/**
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._release = options.release;
//the smoothed signal to get the values
this.input.chain(this._abs, this._filter, this.output);
//the difference path
this._abs.connect(this._sub, 0, 1);
this._filter.chain(this._delay, this._sub);
//threshold the difference and use the thresh to set the frequency
this._sub.chain(this._mult, this._frequencyValues, this._filter.frequency);
//set the attack and release values in the table
this._setAttackRelease(this._attack, this._release);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Follower);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Follower.defaults = {
'attack': 0.05,
'release': 0.5
};
/**
* sets the attack and release times in the wave shaper
* @param {Time} attack
* @param {Time} release
* @private
*/
Tone.Follower.prototype._setAttackRelease = function (attack, release) {
var minTime = this.blockTime;
attack = Tone.Time(attack).toFrequency();
release = Tone.Time(release).toFrequency();
attack = Math.max(attack, minTime);
release = Math.max(release, minTime);
this._frequencyValues.setMap(function (val) {
if (val <= 0) {
return attack;
} else {
return release;
}
});
};
/**
* The attack time.
* @memberOf Tone.Follower#
* @type {Time}
* @name attack
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Follower.prototype, 'attack', {
get: function () {
return this._attack;
},
set: function (attack) {
this._attack = attack;
this._setAttackRelease(this._attack, this._release);
}
});
/**
* The release time.
* @memberOf Tone.Follower#
* @type {Time}
* @name release
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Follower.prototype, 'release', {
get: function () {
return this._release;
},
set: function (release) {
this._release = release;
this._setAttackRelease(this._attack, this._release);
}
});
/**
* Borrows the connect method from Signal so that the output can be used
* as a Tone.Signal control signal.
* @function
*/
Tone.Follower.prototype.connect = Tone.Signal.prototype.connect;
/**
* dispose
* @returns {Tone.Follower} this
*/
Tone.Follower.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._filter.disconnect();
this._filter = null;
this._frequencyValues.disconnect();
this._frequencyValues = null;
this._delay.dispose();
this._delay = null;
this._sub.disconnect();
this._sub = null;
this._abs.dispose();
this._abs = null;
this._mult.dispose();
this._mult = null;
this._curve = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Follower;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.ScaledEnvelop is an envelope which can be scaled
* to any range. It's useful for applying an envelope
* to a frequency or any other non-NormalRange signal
* parameter.
*
* @extends {Tone.Envelope}
* @constructor
* @param {Time|Object} [attack] the attack time in seconds
* @param {Time} [decay] the decay time in seconds
* @param {number} [sustain] a percentage (0-1) of the full amplitude
* @param {Time} [release] the release time in seconds
* @example
* var scaledEnv = new Tone.ScaledEnvelope({
* "attack" : 0.2,
* "min" : 200,
* "max" : 2000
* });
* scaledEnv.connect(oscillator.frequency);
*/
Tone.ScaledEnvelope = function () {
//get all of the defaults
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'attack',
'decay',
'sustain',
'release'
], Tone.Envelope.defaults);
Tone.Envelope.call(this, options);
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.ScaledEnvelope.defaults);
/**
* scale the incoming signal by an exponent
* @type {Tone.Pow}
* @private
*/
this._exp = this.output = new Tone.Pow(options.exponent);
/**
* scale the signal to the desired range
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._scale = this.output = new Tone.Scale(options.min, options.max);
this._sig.chain(this._exp, this._scale);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.ScaledEnvelope, Tone.Envelope);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
*/
Tone.ScaledEnvelope.defaults = {
'min': 0,
'max': 1,
'exponent': 1
};
/**
* The envelope's min output value. This is the value which it
* starts at.
* @memberOf Tone.ScaledEnvelope#
* @type {number}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.ScaledEnvelope.prototype, 'min', {
get: function () {
return this._scale.min;
},
set: function (min) {
this._scale.min = min;
}
});
/**
* The envelope's max output value. In other words, the value
* at the peak of the attack portion of the envelope.
* @memberOf Tone.ScaledEnvelope#
* @type {number}
* @name max
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.ScaledEnvelope.prototype, 'max', {
get: function () {
return this._scale.max;
},
set: function (max) {
this._scale.max = max;
}
});
/**
* The envelope's exponent value.
* @memberOf Tone.ScaledEnvelope#
* @type {number}
* @name exponent
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.ScaledEnvelope.prototype, 'exponent', {
get: function () {
return this._exp.value;
},
set: function (exp) {
this._exp.value = exp;
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.ScaledEnvelope} this
*/
Tone.ScaledEnvelope.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Envelope.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._scale.dispose();
this._scale = null;
this._exp.dispose();
this._exp = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.ScaledEnvelope;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.FrequencyEnvelope is a Tone.ScaledEnvelope, but instead of `min` and `max`
* it's got a `baseFrequency` and `octaves` parameter.
*
* @extends {Tone.Envelope}
* @constructor
* @param {Time|Object} [attack] the attack time in seconds
* @param {Time} [decay] the decay time in seconds
* @param {number} [sustain] a percentage (0-1) of the full amplitude
* @param {Time} [release] the release time in seconds
* @example
* var env = new Tone.FrequencyEnvelope({
* "attack" : 0.2,
* "baseFrequency" : "C2",
* "octaves" : 4
* });
* scaledEnv.connect(oscillator.frequency);
*/
Tone.FrequencyEnvelope = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'attack',
'decay',
'sustain',
'release'
], Tone.Envelope.defaults);
Tone.ScaledEnvelope.call(this, options);
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.FrequencyEnvelope.defaults);
/**
* Stores the octave value
* @type {Positive}
* @private
*/
this._octaves = options.octaves;
//setup
this.baseFrequency = options.baseFrequency;
this.octaves = options.octaves;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FrequencyEnvelope, Tone.Envelope);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
*/
Tone.FrequencyEnvelope.defaults = {
'baseFrequency': 200,
'octaves': 4,
'exponent': 2
};
/**
* The envelope's mininum output value. This is the value which it
* starts at.
* @memberOf Tone.FrequencyEnvelope#
* @type {Frequency}
* @name baseFrequency
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FrequencyEnvelope.prototype, 'baseFrequency', {
get: function () {
return this._scale.min;
},
set: function (min) {
this._scale.min = this.toFrequency(min);
//also update the octaves
this.octaves = this._octaves;
}
});
/**
* The number of octaves above the baseFrequency that the
* envelope will scale to.
* @memberOf Tone.FrequencyEnvelope#
* @type {Positive}
* @name octaves
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FrequencyEnvelope.prototype, 'octaves', {
get: function () {
return this._octaves;
},
set: function (octaves) {
this._octaves = octaves;
this._scale.max = this.baseFrequency * Math.pow(2, octaves);
}
});
/**
* The envelope's exponent value.
* @memberOf Tone.FrequencyEnvelope#
* @type {number}
* @name exponent
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FrequencyEnvelope.prototype, 'exponent', {
get: function () {
return this._exp.value;
},
set: function (exp) {
this._exp.value = exp;
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.FrequencyEnvelope} this
*/
Tone.FrequencyEnvelope.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.ScaledEnvelope.prototype.dispose.call(this);
return this;
};
return Tone.FrequencyEnvelope;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Gate only passes a signal through when the incoming
* signal exceeds a specified threshold. To do this, Gate uses
* a Tone.Follower to follow the amplitude of the incoming signal.
* A common implementation of this class is a [Noise Gate](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Noise_gate).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Decibels|Object} [threshold] The threshold above which the gate will open.
* @param {Time=} attack The follower's attack time
* @param {Time=} release The follower's release time
* @example
* var gate = new Tone.Gate(-30, 0.2, 0.3).toMaster();
* var mic = new Tone.UserMedia().connect(gate);
* //the gate will only pass through the incoming
* //signal when it's louder than -30db
*/
Tone.Gate = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'threshold',
'attack',
'release'
], Tone.Gate.defaults);
/**
* @type {Tone.Follower}
* @private
*/
this._follower = new Tone.Follower(options.attack, options.release);
/**
* @type {Tone.GreaterThan}
* @private
*/
this._gt = new Tone.GreaterThan(this.dbToGain(options.threshold));
//the connections
this.input.connect(this.output);
//the control signal
this.input.chain(this._gt, this._follower, this.output.gain);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Gate);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Gate.defaults = {
'attack': 0.1,
'release': 0.1,
'threshold': -40
};
/**
* The threshold of the gate in decibels
* @memberOf Tone.Gate#
* @type {Decibels}
* @name threshold
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Gate.prototype, 'threshold', {
get: function () {
return this.gainToDb(this._gt.value);
},
set: function (thresh) {
this._gt.value = this.dbToGain(thresh);
}
});
/**
* The attack speed of the gate
* @memberOf Tone.Gate#
* @type {Time}
* @name attack
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Gate.prototype, 'attack', {
get: function () {
return this._follower.attack;
},
set: function (attackTime) {
this._follower.attack = attackTime;
}
});
/**
* The release speed of the gate
* @memberOf Tone.Gate#
* @type {Time}
* @name release
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Gate.prototype, 'release', {
get: function () {
return this._follower.release;
},
set: function (releaseTime) {
this._follower.release = releaseTime;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Gate} this
*/
Tone.Gate.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._follower.dispose();
this._gt.dispose();
this._follower = null;
this._gt = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Gate;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A Timeline State. Provides the methods: setStateAtTime("state", time)
* and getValueAtTime(time).
*
* @extends {Tone.Timeline}
* @param {String} initial The initial state of the TimelineState.
* Defaults to undefined
*/
Tone.TimelineState = function (initial) {
Tone.Timeline.call(this);
/**
* The initial state
* @private
* @type {String}
*/
this._initial = initial;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.TimelineState, Tone.Timeline);
/**
* Returns the scheduled state scheduled before or at
* the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @return {String} The name of the state input in setStateAtTime.
*/
Tone.TimelineState.prototype.getValueAtTime = function (time) {
var event = this.get(time);
if (event !== null) {
return event.state;
} else {
return this._initial;
}
};
/**
* Returns the scheduled state scheduled before or at
* the given time.
* @param {String} state The name of the state to set.
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
*/
Tone.TimelineState.prototype.setStateAtTime = function (state, time) {
this.add({
'state': state,
'time': time
});
};
return Tone.TimelineState;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Emitter gives classes which extend it
* the ability to listen for and emit events.
* Inspiration and reference from Jerome Etienne's [MicroEvent](https://github.com/jeromeetienne/microevent.js).
* MIT (c) 2011 Jerome Etienne.
*
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.Emitter = function () {
/**
* Contains all of the events.
* @private
* @type {Object}
*/
this._events = {};
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Emitter);
/**
* Bind a callback to a specific event.
* @param {String} event The name of the event to listen for.
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke when the
* event is emitted
* @return {Tone.Emitter} this
*/
Tone.Emitter.prototype.on = function (event, callback) {
//split the event
var events = event.split(/\W+/);
for (var i = 0; i < events.length; i++) {
var eventName = events[i];
if (!this._events.hasOwnProperty(eventName)) {
this._events[eventName] = [];
}
this._events[eventName].push(callback);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Remove the event listener.
* @param {String} event The event to stop listening to.
* @param {Function=} callback The callback which was bound to
* the event with Tone.Emitter.on.
* If no callback is given, all callbacks
* events are removed.
* @return {Tone.Emitter} this
*/
Tone.Emitter.prototype.off = function (event, callback) {
var events = event.split(/\W+/);
for (var ev = 0; ev < events.length; ev++) {
event = events[ev];
if (this._events.hasOwnProperty(event)) {
if (Tone.prototype.isUndef(callback)) {
this._events[event] = [];
} else {
var eventList = this._events[event];
for (var i = 0; i < eventList.length; i++) {
if (eventList[i] === callback) {
eventList.splice(i, 1);
}
}
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Invoke all of the callbacks bound to the event
* with any arguments passed in.
* @param {String} event The name of the event.
* @param {*...} args The arguments to pass to the functions listening.
* @return {Tone.Emitter} this
*/
Tone.Emitter.prototype.emit = function (event) {
if (this._events) {
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
if (this._events.hasOwnProperty(event)) {
var eventList = this._events[event];
for (var i = 0, len = eventList.length; i < len; i++) {
eventList[i].apply(this, args);
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Add Emitter functions (on/off/emit) to the object
* @param {Object|Function} object The object or class to extend.
*/
Tone.Emitter.mixin = function (object) {
var functions = [
'on',
'off',
'emit'
];
object._events = {};
for (var i = 0; i < functions.length; i++) {
var func = functions[i];
var emitterFunc = Tone.Emitter.prototype[func];
object[func] = emitterFunc;
}
};
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.Emitter} this
*/
Tone.Emitter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._events = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Emitter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A sample accurate clock which provides a callback at the given rate.
* While the callback is not sample-accurate (it is still susceptible to
* loose JS timing), the time passed in as the argument to the callback
* is precise. For most applications, it is better to use Tone.Transport
* instead of the Clock by itself since you can synchronize multiple callbacks.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Emitter}
* @param {function} callback The callback to be invoked with the time of the audio event
* @param {Frequency} frequency The rate of the callback
* @example
* //the callback will be invoked approximately once a second
* //and will print the time exactly once a second apart.
* var clock = new Tone.Clock(function(time){
* console.log(time);
* }, 1);
*/
Tone.Clock = function () {
Tone.Emitter.call(this);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'callback',
'frequency'
], Tone.Clock.defaults);
/**
* The callback function to invoke at the scheduled tick.
* @type {Function}
*/
this.callback = options.callback;
/**
* The next time the callback is scheduled.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._nextTick = 0;
/**
* The last state of the clock.
* @type {State}
* @private
*/
this._lastState = Tone.State.Stopped;
/**
* The rate the callback function should be invoked.
* @type {BPM}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.TimelineSignal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
this._readOnly('frequency');
/**
* The number of times the callback was invoked. Starts counting at 0
* and increments after the callback was invoked.
* @type {Ticks}
* @readOnly
*/
this.ticks = 0;
/**
* The state timeline
* @type {Tone.TimelineState}
* @private
*/
this._state = new Tone.TimelineState(Tone.State.Stopped);
/**
* The loop function bound to its context.
* This is necessary to remove the event in the end.
* @type {Function}
* @private
*/
this._boundLoop = this._loop.bind(this);
//bind a callback to the worker thread
Tone.Clock._worker.addEventListener('message', this._boundLoop);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Clock, Tone.Emitter);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Clock.defaults = {
'callback': Tone.noOp,
'frequency': 1,
'lookAhead': 'auto'
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, either "started", "stopped" or "paused".
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.Clock#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Clock.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._state.getValueAtTime(this.now());
}
});
/**
* Start the clock at the given time. Optionally pass in an offset
* of where to start the tick counter from.
* @param {Time} time The time the clock should start
* @param {Ticks=} offset Where the tick counter starts counting from.
* @return {Tone.Clock} this
*/
Tone.Clock.prototype.start = function (time, offset) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(time) !== Tone.State.Started) {
this._state.add({
'state': Tone.State.Started,
'time': time,
'offset': offset
});
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the clock. Stopping the clock resets the tick counter to 0.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the clock should stop.
* @returns {Tone.Clock} this
* @example
* clock.stop();
*/
Tone.Clock.prototype.stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._state.cancel(time);
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, time);
return this;
};
/**
* Pause the clock. Pausing does not reset the tick counter.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the clock should stop.
* @returns {Tone.Clock} this
*/
Tone.Clock.prototype.pause = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(time) === Tone.State.Started) {
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Paused, time);
}
return this;
};
/**
* The scheduling loop.
* @param {Number} time The current page time starting from 0
* when the page was loaded.
* @private
*/
Tone.Clock.prototype._loop = function () {
//get the frequency value to compute the value of the next loop
var now = this.now();
//if it's started
var lookAhead = Tone.Clock.lookAhead;
var updateInterval = Tone.Clock.updateInterval;
var lagCompensation = Tone.Clock.lag * 2;
var loopInterval = now + lookAhead + updateInterval + lagCompensation;
while (loopInterval > this._nextTick && this._state) {
var currentState = this._state.getValueAtTime(this._nextTick);
if (currentState !== this._lastState) {
this._lastState = currentState;
var event = this._state.get(this._nextTick);
// emit an event
if (currentState === Tone.State.Started) {
//correct the time
this._nextTick = event.time;
if (!this.isUndef(event.offset)) {
this.ticks = event.offset;
}
this.emit('start', event.time, this.ticks);
} else if (currentState === Tone.State.Stopped) {
this.ticks = 0;
this.emit('stop', event.time);
} else if (currentState === Tone.State.Paused) {
this.emit('pause', event.time);
}
}
var tickTime = this._nextTick;
if (this.frequency) {
this._nextTick += 1 / this.frequency.getValueAtTime(this._nextTick);
if (currentState === Tone.State.Started) {
this.callback(tickTime);
this.ticks++;
}
}
}
};
/**
* Returns the scheduled state at the given time.
* @param {Time} time The time to query.
* @return {String} The name of the state input in setStateAtTime.
* @example
* clock.start("+0.1");
* clock.getStateAtTime("+0.1"); //returns "started"
*/
Tone.Clock.prototype.getStateAtTime = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
return this._state.getValueAtTime(time);
};
/**
* Clean up
* @returns {Tone.Clock} this
*/
Tone.Clock.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Emitter.prototype.dispose.call(this);
Tone.Clock._worker.removeEventListener('message', this._boundLoop);
this._writable('frequency');
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this._boundLoop = null;
this._nextTick = Infinity;
this.callback = null;
this._state.dispose();
this._state = null;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// WORKER
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//URL Shim
window.URL = window.URL || window.webkitURL;
/**
* The minimum amount of time events are
* scheduled in advance.
* @private
* @type {Number}
*/
Tone.Clock._lookAhead = 0.1;
/**
* How often the worker ticks
* @type {Seconds}
* @private
*/
Tone.Clock._updateInterval = Tone.Clock._lookAhead / 3;
/**
* The script which runs in a web worker
* @type {Blob}
* @private
*/
var blob = new Blob([//the initial timeout time
'var timeoutTime = ' + Tone.Clock._updateInterval * 1000 + ';' + //onmessage callback
'self.onmessage = function(msg){' + '\ttimeoutTime = parseInt(msg.data);' + '};' + //the tick function which posts a message
//and schedules a new tick
'function tick(){' + '\tsetTimeout(tick, timeoutTime);' + '\tself.postMessage(\'tick\');' + '}' + //call tick initially
'tick();']);
/**
* Create a blob url from the Blob
* @type {URL}
* @private
*/
var blobUrl = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
/**
* The Worker which generates a regular callback
* @type {Worker}
* @private
* @static
*/
Tone.Clock._worker = new Worker(blobUrl);
/**
* @private
* @type {Number}
* The time of the last update
*/
var lastUpdate = -1;
/**
* The current computed update rate of the clock.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
var computedUpdateInterval = 0;
//listen for message events and update the global clock lookahead
Tone.Clock._worker.addEventListener('message', function () {
var now = Tone.now();
if (lastUpdate !== -1) {
var diff = now - lastUpdate;
computedUpdateInterval = Math.max(diff, computedUpdateInterval * 0.97);
}
lastUpdate = now;
});
/**
* This is the time that the clock is falling behind
* the scheduled update interval. The Clock automatically
* adjusts for the lag and schedules further in advance.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Clock
* @name lag
* @static
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Clock, 'lag', {
get: function () {
var diff = computedUpdateInterval - Tone.Clock._updateInterval;
diff = Math.max(diff, 0);
return diff;
}
});
/**
* The amount of time in advance that events are scheduled.
* The lookAhead will adjust slightly in response to the
* measured update time to try to avoid clicks.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Clock
* @name lookAhead
* @static
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Clock, 'lookAhead', {
get: function () {
return Tone.Clock._lookAhead;
},
set: function (lA) {
Tone.Clock._lookAhead = lA;
}
});
/**
* How often the Web Worker callback is invoked.
* This number corresponds to how responsive the scheduling
* can be. Clock.updateInterval + Clock.lookAhead gives you the
* total latency between scheduling an event and hearing it.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Clock
* @name updateInterval
* @static
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Clock, 'updateInterval', {
get: function () {
return Tone.Clock._updateInterval;
},
set: function (interval) {
Tone.Clock._updateInterval = Math.max(interval, 0.01);
Tone.Clock._worker.postMessage(interval * 1000);
}
});
/**
* The latency hint
* @private
* @type {String|Number}
*/
var latencyHint = 'interactive';
/**
* The type of playback, which affects tradeoffs between audio
* output latency and responsiveness.
*
* In addition to setting the value in seconds, the latencyHint also
* accepts the strings "interactive" (prioritizes low latency),
* "playback" (prioritizes sustained playback), "balanced" (balances
* latency and performance), and "fastest" (lowest latency, might glitch more often).
* @type {String|Seconds}
* @memberOf Tone.Clock#
* @name latencyHint
* @static
* @example
* //set the lookAhead to 0.3 seconds
* Tone.Clock.latencyHint = 0.3;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Clock, 'latencyHint', {
get: function () {
return latencyHint;
},
set: function (hint) {
var lookAhead = hint;
latencyHint = hint;
if (Tone.prototype.isString(hint)) {
switch (hint) {
case 'interactive':
lookAhead = 0.1;
Tone.context.latencyHint = hint;
break;
case 'playback':
lookAhead = 0.8;
Tone.context.latencyHint = hint;
break;
case 'balanced':
lookAhead = 0.25;
Tone.context.latencyHint = hint;
break;
case 'fastest':
lookAhead = 0.01;
break;
}
}
Tone.Clock.lookAhead = lookAhead;
Tone.Clock.updateInterval = lookAhead / 3;
}
});
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
lastUpdate = -1;
computedUpdateInterval = 0;
});
return Tone.Clock;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Similar to Tone.Timeline, but all events represent
* intervals with both "time" and "duration" times. The
* events are placed in a tree structure optimized
* for querying an intersection point with the timeline
* events. Internally uses an [Interval Tree](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interval_tree)
* to represent the data.
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline = function () {
/**
* The root node of the inteval tree
* @type {IntervalNode}
* @private
*/
this._root = null;
/**
* Keep track of the length of the timeline.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._length = 0;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.IntervalTimeline);
/**
* The event to add to the timeline. All events must
* have a time and duration value
* @param {Object} event The event to add to the timeline
* @return {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.add = function (event) {
if (this.isUndef(event.time) || this.isUndef(event.duration)) {
throw new Error('Tone.IntervalTimeline: events must have time and duration parameters');
}
var node = new IntervalNode(event.time, event.time + event.duration, event);
if (this._root === null) {
this._root = node;
} else {
this._root.insert(node);
}
this._length++;
// Restructure tree to be balanced
while (node !== null) {
node.updateHeight();
node.updateMax();
this._rebalance(node);
node = node.parent;
}
return this;
};
/**
* Remove an event from the timeline.
* @param {Object} event The event to remove from the timeline
* @return {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.remove = function (event) {
if (this._root !== null) {
var results = [];
this._root.search(event.time, results);
for (var i = 0; i < results.length; i++) {
var node = results[i];
if (node.event === event) {
this._removeNode(node);
this._length--;
break;
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* The number of items in the timeline.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.IntervalTimeline#
* @name length
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype, 'length', {
get: function () {
return this._length;
}
});
/**
* Remove events whose time time is after the given time
* @param {Number} time The time to query.
* @returns {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.cancel = function (after) {
this.forEachAfter(after, function (event) {
this.remove(event);
}.bind(this));
return this;
};
/**
* Set the root node as the given node
* @param {IntervalNode} node
* @private
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype._setRoot = function (node) {
this._root = node;
if (this._root !== null) {
this._root.parent = null;
}
};
/**
* Replace the references to the node in the node's parent
* with the replacement node.
* @param {IntervalNode} node
* @param {IntervalNode} replacement
* @private
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype._replaceNodeInParent = function (node, replacement) {
if (node.parent !== null) {
if (node.isLeftChild()) {
node.parent.left = replacement;
} else {
node.parent.right = replacement;
}
this._rebalance(node.parent);
} else {
this._setRoot(replacement);
}
};
/**
* Remove the node from the tree and replace it with
* a successor which follows the schema.
* @param {IntervalNode} node
* @private
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype._removeNode = function (node) {
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
this._replaceNodeInParent(node, null);
} else if (node.right === null) {
this._replaceNodeInParent(node, node.left);
} else if (node.left === null) {
this._replaceNodeInParent(node, node.right);
} else {
var balance = node.getBalance();
var replacement, temp;
if (balance > 0) {
if (node.left.right === null) {
replacement = node.left;
replacement.right = node.right;
temp = replacement;
} else {
replacement = node.left.right;
while (replacement.right !== null) {
replacement = replacement.right;
}
replacement.parent.right = replacement.left;
temp = replacement.parent;
replacement.left = node.left;
replacement.right = node.right;
}
} else {
if (node.right.left === null) {
replacement = node.right;
replacement.left = node.left;
temp = replacement;
} else {
replacement = node.right.left;
while (replacement.left !== null) {
replacement = replacement.left;
}
replacement.parent = replacement.parent;
replacement.parent.left = replacement.right;
temp = replacement.parent;
replacement.left = node.left;
replacement.right = node.right;
}
}
if (node.parent !== null) {
if (node.isLeftChild()) {
node.parent.left = replacement;
} else {
node.parent.right = replacement;
}
} else {
this._setRoot(replacement);
}
// this._replaceNodeInParent(node, replacement);
this._rebalance(temp);
}
node.dispose();
};
/**
* Rotate the tree to the left
* @param {IntervalNode} node
* @private
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype._rotateLeft = function (node) {
var parent = node.parent;
var isLeftChild = node.isLeftChild();
// Make node.right the new root of this sub tree (instead of node)
var pivotNode = node.right;
node.right = pivotNode.left;
pivotNode.left = node;
if (parent !== null) {
if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = pivotNode;
} else {
parent.right = pivotNode;
}
} else {
this._setRoot(pivotNode);
}
};
/**
* Rotate the tree to the right
* @param {IntervalNode} node
* @private
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype._rotateRight = function (node) {
var parent = node.parent;
var isLeftChild = node.isLeftChild();
// Make node.left the new root of this sub tree (instead of node)
var pivotNode = node.left;
node.left = pivotNode.right;
pivotNode.right = node;
if (parent !== null) {
if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = pivotNode;
} else {
parent.right = pivotNode;
}
} else {
this._setRoot(pivotNode);
}
};
/**
* Balance the BST
* @param {IntervalNode} node
* @private
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype._rebalance = function (node) {
var balance = node.getBalance();
if (balance > 1) {
if (node.left.getBalance() < 0) {
this._rotateLeft(node.left);
} else {
this._rotateRight(node);
}
} else if (balance < -1) {
if (node.right.getBalance() > 0) {
this._rotateRight(node.right);
} else {
this._rotateLeft(node);
}
}
};
/**
* Get an event whose time and duration span the give time. Will
* return the match whose "time" value is closest to the given time.
* @param {Object} event The event to add to the timeline
* @return {Object} The event which spans the desired time
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.get = function (time) {
if (this._root !== null) {
var results = [];
this._root.search(time, results);
if (results.length > 0) {
var max = results[0];
for (var i = 1; i < results.length; i++) {
if (results[i].low > max.low) {
max = results[i];
}
}
return max.event;
}
}
return null;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the timeline.
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.forEach = function (callback) {
if (this._root !== null) {
var allNodes = [];
if (this._root !== null) {
this._root.traverse(function (node) {
allNodes.push(node);
});
}
for (var i = 0; i < allNodes.length; i++) {
var ev = allNodes[i].event;
if (ev) {
callback(ev);
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array in which the given time
* overlaps with the time and duration time of the event.
* @param {Number} time The time to check if items are overlapping
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.forEachAtTime = function (time, callback) {
if (this._root !== null) {
var results = [];
this._root.search(time, results);
for (var i = results.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var ev = results[i].event;
if (ev) {
callback(ev);
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over everything in the array in which the time is greater
* than the given time.
* @param {Number} time The time to check if items are before
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every item
* @returns {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.forEachAfter = function (time, callback) {
if (this._root !== null) {
var results = [];
this._root.searchAfter(time, results);
for (var i = results.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var ev = results[i].event;
if (ev) {
callback(ev);
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.IntervalTimeline} this
*/
Tone.IntervalTimeline.prototype.dispose = function () {
var allNodes = [];
if (this._root !== null) {
this._root.traverse(function (node) {
allNodes.push(node);
});
}
for (var i = 0; i < allNodes.length; i++) {
allNodes[i].dispose();
}
allNodes = null;
this._root = null;
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// INTERVAL NODE HELPER
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Represents a node in the binary search tree, with the addition
* of a "high" value which keeps track of the highest value of
* its children.
* References:
* https://brooknovak.wordpress.com/2013/12/07/augmented-interval-tree-in-c/
* http://www.mif.vu.lt/~valdas/ALGORITMAI/LITERATURA/Cormen/Cormen.pdf
* @param {Number} low
* @param {Number} high
* @private
*/
var IntervalNode = function (low, high, event) {
//the event container
this.event = event;
//the low value
this.low = low;
//the high value
this.high = high;
//the high value for this and all child nodes
this.max = this.high;
//the nodes to the left
this._left = null;
//the nodes to the right
this._right = null;
//the parent node
this.parent = null;
//the number of child nodes
this.height = 0;
};
/**
* Insert a node into the correct spot in the tree
* @param {IntervalNode} node
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.insert = function (node) {
if (node.low <= this.low) {
if (this.left === null) {
this.left = node;
} else {
this.left.insert(node);
}
} else {
if (this.right === null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
this.right.insert(node);
}
}
};
/**
* Search the tree for nodes which overlap
* with the given point
* @param {Number} point The point to query
* @param {Array} results The array to put the results
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.search = function (point, results) {
// If p is to the right of the rightmost point of any interval
// in this node and all children, there won't be any matches.
if (point > this.max) {
return;
}
// Search left children
if (this.left !== null) {
this.left.search(point, results);
}
// Check this node
if (this.low <= point && this.high > point) {
results.push(this);
}
// If p is to the left of the time of this interval,
// then it can't be in any child to the right.
if (this.low > point) {
return;
}
// Search right children
if (this.right !== null) {
this.right.search(point, results);
}
};
/**
* Search the tree for nodes which are less
* than the given point
* @param {Number} point The point to query
* @param {Array} results The array to put the results
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.searchAfter = function (point, results) {
// Check this node
if (this.low >= point) {
results.push(this);
if (this.left !== null) {
this.left.searchAfter(point, results);
}
}
// search the right side
if (this.right !== null) {
this.right.searchAfter(point, results);
}
};
/**
* Invoke the callback on this element and both it's branches
* @param {Function} callback
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.traverse = function (callback) {
callback(this);
if (this.left !== null) {
this.left.traverse(callback);
}
if (this.right !== null) {
this.right.traverse(callback);
}
};
/**
* Update the height of the node
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.updateHeight = function () {
if (this.left !== null && this.right !== null) {
this.height = Math.max(this.left.height, this.right.height) + 1;
} else if (this.right !== null) {
this.height = this.right.height + 1;
} else if (this.left !== null) {
this.height = this.left.height + 1;
} else {
this.height = 0;
}
};
/**
* Update the height of the node
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.updateMax = function () {
this.max = this.high;
if (this.left !== null) {
this.max = Math.max(this.max, this.left.max);
}
if (this.right !== null) {
this.max = Math.max(this.max, this.right.max);
}
};
/**
* The balance is how the leafs are distributed on the node
* @return {Number} Negative numbers are balanced to the right
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.getBalance = function () {
var balance = 0;
if (this.left !== null && this.right !== null) {
balance = this.left.height - this.right.height;
} else if (this.left !== null) {
balance = this.left.height + 1;
} else if (this.right !== null) {
balance = -(this.right.height + 1);
}
return balance;
};
/**
* @returns {Boolean} true if this node is the left child
* of its parent
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.isLeftChild = function () {
return this.parent !== null && this.parent.left === this;
};
/**
* get/set the left node
* @type {IntervalNode}
*/
Object.defineProperty(IntervalNode.prototype, 'left', {
get: function () {
return this._left;
},
set: function (node) {
this._left = node;
if (node !== null) {
node.parent = this;
}
this.updateHeight();
this.updateMax();
}
});
/**
* get/set the right node
* @type {IntervalNode}
*/
Object.defineProperty(IntervalNode.prototype, 'right', {
get: function () {
return this._right;
},
set: function (node) {
this._right = node;
if (node !== null) {
node.parent = this;
}
this.updateHeight();
this.updateMax();
}
});
/**
* null out references.
*/
IntervalNode.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.parent = null;
this._left = null;
this._right = null;
this.event = null;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// END INTERVAL NODE HELPER
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
return Tone.IntervalTimeline;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Transport for timing musical events.
* Supports tempo curves and time changes. Unlike browser-based timing (setInterval, requestAnimationFrame)
* Tone.Transport timing events pass in the exact time of the scheduled event
* in the argument of the callback function. Pass that time value to the object
* you're scheduling.
* A single transport is created for you when the library is initialized.
*
* The transport emits the events: "start", "stop", "pause", and "loop" which are
* called with the time of that event as the argument.
*
* @extends {Tone.Emitter}
* @singleton
* @example
* //repeated event every 8th note
* Tone.Transport.scheduleRepeat(function(time){
* //do something with the time
* }, "8n");
* @example
* //schedule an event on the 16th measure
* Tone.Transport.schedule(function(time){
* //do something with the time
* }, "16:0:0");
*/
Tone.Transport = function () {
Tone.Emitter.call(this);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// LOOPING
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* If the transport loops or not.
* @type {boolean}
*/
this.loop = false;
/**
* The loop start position in ticks
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = 0;
/**
* The loop end position in ticks
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = 0;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CLOCK/TEMPO
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Pulses per quarter is the number of ticks per quarter note.
* @private
* @type {Number}
*/
this._ppq = TransportConstructor.defaults.PPQ;
/**
* watches the main oscillator for timing ticks
* initially starts at 120bpm
* @private
* @type {Tone.Clock}
*/
this._clock = new Tone.Clock({
'callback': this._processTick.bind(this),
'frequency': 0
});
this._bindClockEvents();
/**
* The Beats Per Minute of the Transport.
* @type {BPM}
* @signal
* @example
* Tone.Transport.bpm.value = 80;
* //ramp the bpm to 120 over 10 seconds
* Tone.Transport.bpm.rampTo(120, 10);
*/
this.bpm = this._clock.frequency;
this.bpm._toUnits = this._toUnits.bind(this);
this.bpm._fromUnits = this._fromUnits.bind(this);
this.bpm.units = Tone.Type.BPM;
this.bpm.value = TransportConstructor.defaults.bpm;
this._readOnly('bpm');
/**
* The time signature, or more accurately the numerator
* of the time signature over a denominator of 4.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._timeSignature = TransportConstructor.defaults.timeSignature;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TIMELINE EVENTS
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* All the events in an object to keep track by ID
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
this._scheduledEvents = {};
/**
* The event ID counter
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._eventID = 0;
/**
* The scheduled events.
* @type {Tone.Timeline}
* @private
*/
this._timeline = new Tone.Timeline();
/**
* Repeated events
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._repeatedEvents = new Tone.IntervalTimeline();
/**
* Events that occur once
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._onceEvents = new Tone.Timeline();
/**
* All of the synced Signals
* @private
* @type {Array}
*/
this._syncedSignals = [];
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SWING
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* The subdivision of the swing
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._swingTicks = TransportConstructor.defaults.PPQ / 2;
//8n
/**
* The swing amount
* @type {NormalRange}
* @private
*/
this._swingAmount = 0;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Transport, Tone.Emitter);
/**
* the defaults
* @type {Object}
* @const
* @static
*/
Tone.Transport.defaults = {
'bpm': 120,
'swing': 0,
'swingSubdivision': '8n',
'timeSignature': 4,
'loopStart': 0,
'loopEnd': '4m',
'PPQ': 192
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TICKS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* called on every tick
* @param {number} tickTime clock relative tick time
* @private
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype._processTick = function (tickTime) {
var ticks = this._clock.ticks;
//handle swing
if (this._swingAmount > 0 && ticks % this._ppq !== 0 && //not on a downbeat
ticks % (this._swingTicks * 2) !== 0) {
//add some swing
var progress = ticks % (this._swingTicks * 2) / (this._swingTicks * 2);
var amount = Math.sin(progress * Math.PI) * this._swingAmount;
tickTime += Tone.Time(this._swingTicks * 2 / 3, 'i').eval() * amount;
}
//do the loop test
if (this.loop) {
if (ticks === this._loopEnd) {
this.emit('loopEnd', tickTime);
this._clock.ticks = this._loopStart;
ticks = this._loopStart;
this.emit('loopStart', tickTime, this.seconds);
this.emit('loop', tickTime);
}
}
//process the single occurrence events
this._onceEvents.forEachBefore(ticks, function (event) {
event.callback(tickTime);
//remove the event
delete this._scheduledEvents[event.id.toString()];
}.bind(this));
//and clear the single occurrence timeline
this._onceEvents.cancelBefore(ticks);
//fire the next tick events if their time has come
this._timeline.forEachAtTime(ticks, function (event) {
event.callback(tickTime);
});
//process the repeated events
this._repeatedEvents.forEachAtTime(ticks, function (event) {
if ((ticks - event.time) % event.interval === 0) {
event.callback(tickTime);
}
});
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SCHEDULABLE EVENTS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Schedule an event along the timeline.
* @param {Function} callback The callback to be invoked at the time.
* @param {TransportTime} time The time to invoke the callback at.
* @return {Number} The id of the event which can be used for canceling the event.
* @example
* //trigger the callback when the Transport reaches the desired time
* Tone.Transport.schedule(function(time){
* envelope.triggerAttack(time);
* }, "128i");
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.schedule = function (callback, time) {
var event = {
'time': this.toTicks(time),
'callback': callback
};
var id = this._eventID++;
this._scheduledEvents[id.toString()] = {
'event': event,
'timeline': this._timeline
};
this._timeline.add(event);
return id;
};
/**
* Schedule a repeated event along the timeline. The event will fire
* at the `interval` starting at the `startTime` and for the specified
* `duration`.
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke.
* @param {Time} interval The duration between successive
* callbacks.
* @param {TimelinePosition=} startTime When along the timeline the events should
* start being invoked.
* @param {Time} [duration=Infinity] How long the event should repeat.
* @return {Number} The ID of the scheduled event. Use this to cancel
* the event.
* @example
* //a callback invoked every eighth note after the first measure
* Tone.Transport.scheduleRepeat(callback, "8n", "1m");
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.scheduleRepeat = function (callback, interval, startTime, duration) {
if (interval <= 0) {
throw new Error('Tone.Transport: repeat events must have an interval larger than 0');
}
var event = {
'time': this.toTicks(startTime),
'duration': this.toTicks(this.defaultArg(duration, Infinity)),
'interval': this.toTicks(interval),
'callback': callback
};
var id = this._eventID++;
this._scheduledEvents[id.toString()] = {
'event': event,
'timeline': this._repeatedEvents
};
this._repeatedEvents.add(event);
return id;
};
/**
* Schedule an event that will be removed after it is invoked.
* Note that if the given time is less than the current transport time,
* the event will be invoked immediately.
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke once.
* @param {TransportTime} time The time the callback should be invoked.
* @returns {Number} The ID of the scheduled event.
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.scheduleOnce = function (callback, time) {
var id = this._eventID++;
var event = {
'time': this.toTicks(time),
'callback': callback,
'id': id
};
this._scheduledEvents[id.toString()] = {
'event': event,
'timeline': this._onceEvents
};
this._onceEvents.add(event);
return id;
};
/**
* Clear the passed in event id from the timeline
* @param {Number} eventId The id of the event.
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.clear = function (eventId) {
if (this._scheduledEvents.hasOwnProperty(eventId)) {
var item = this._scheduledEvents[eventId.toString()];
item.timeline.remove(item.event);
delete this._scheduledEvents[eventId.toString()];
}
return this;
};
/**
* Remove scheduled events from the timeline after
* the given time. Repeated events will be removed
* if their startTime is after the given time
* @param {TransportTime} [after=0] Clear all events after
* this time.
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.cancel = function (after) {
after = this.defaultArg(after, 0);
after = this.toTicks(after);
this._timeline.cancel(after);
this._onceEvents.cancel(after);
this._repeatedEvents.cancel(after);
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// START/STOP/PAUSE
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Bind start/stop/pause events from the clock and emit them.
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype._bindClockEvents = function () {
this._clock.on('start', function (time, offset) {
offset = Tone.Time(this._clock.ticks, 'i').toSeconds();
this.emit('start', time, offset);
}.bind(this));
this._clock.on('stop', function (time) {
this.emit('stop', time);
}.bind(this));
this._clock.on('pause', function (time) {
this.emit('pause', time);
}.bind(this));
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, either "started", "stopped", or "paused"
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._clock.getStateAtTime(this.now());
}
});
/**
* Start the transport and all sources synced to the transport.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the transport should start.
* @param {TransportTime=} offset The timeline offset to start the transport.
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
* @example
* //start the transport in one second starting at beginning of the 5th measure.
* Tone.Transport.start("+1", "4:0:0");
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.start = function (time, offset) {
//start the clock
if (!this.isUndef(offset)) {
offset = this.toTicks(offset);
}
this._clock.start(time, offset);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the transport and all sources synced to the transport.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the transport should stop.
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
* @example
* Tone.Transport.stop();
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.stop = function (time) {
this._clock.stop(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Pause the transport and all sources synced to the transport.
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.pause = function (time) {
this._clock.pause(time);
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SETTERS/GETTERS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* The time signature as just the numerator over 4.
* For example 4/4 would be just 4 and 6/8 would be 3.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {Number|Array}
* @name timeSignature
* @example
* //common time
* Tone.Transport.timeSignature = 4;
* // 7/8
* Tone.Transport.timeSignature = [7, 8];
* //this will be reduced to a single number
* Tone.Transport.timeSignature; //returns 3.5
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'timeSignature', {
get: function () {
return this._timeSignature;
},
set: function (timeSig) {
if (this.isArray(timeSig)) {
timeSig = timeSig[0] / timeSig[1] * 4;
}
this._timeSignature = timeSig;
}
});
/**
* When the Tone.Transport.loop = true, this is the starting position of the loop.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {TransportTime}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this._loopStart, 'i').toSeconds();
},
set: function (startPosition) {
this._loopStart = this.toTicks(startPosition);
}
});
/**
* When the Tone.Transport.loop = true, this is the ending position of the loop.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {TransportTime}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this._loopEnd, 'i').toSeconds();
},
set: function (endPosition) {
this._loopEnd = this.toTicks(endPosition);
}
});
/**
* Set the loop start and stop at the same time.
* @param {TransportTime} startPosition
* @param {TransportTime} endPosition
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
* @example
* //loop over the first measure
* Tone.Transport.setLoopPoints(0, "1m");
* Tone.Transport.loop = true;
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.setLoopPoints = function (startPosition, endPosition) {
this.loopStart = startPosition;
this.loopEnd = endPosition;
return this;
};
/**
* The swing value. Between 0-1 where 1 equal to
* the note + half the subdivision.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name swing
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'swing', {
get: function () {
return this._swingAmount;
},
set: function (amount) {
//scale the values to a normal range
this._swingAmount = amount;
}
});
/**
* Set the subdivision which the swing will be applied to.
* The default value is an 8th note. Value must be less
* than a quarter note.
*
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {Time}
* @name swingSubdivision
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'swingSubdivision', {
get: function () {
return Tone.Time(this._swingTicks, 'i').toNotation();
},
set: function (subdivision) {
this._swingTicks = this.toTicks(subdivision);
}
});
/**
* The Transport's position in Bars:Beats:Sixteenths.
* Setting the value will jump to that position right away.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {BarsBeatsSixteenths}
* @name position
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'position', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this.ticks, 'i').toBarsBeatsSixteenths();
},
set: function (progress) {
var ticks = this.toTicks(progress);
this.ticks = ticks;
}
});
/**
* The Transport's position in seconds
* Setting the value will jump to that position right away.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {Seconds}
* @name seconds
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'seconds', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this.ticks, 'i').toSeconds();
},
set: function (progress) {
var ticks = this.toTicks(progress);
this.ticks = ticks;
}
});
/**
* The Transport's loop position as a normalized value. Always
* returns 0 if the transport if loop is not true.
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @name progress
* @type {NormalRange}
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'progress', {
get: function () {
if (this.loop) {
return (this.ticks - this._loopStart) / (this._loopEnd - this._loopStart);
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
/**
* The transports current tick position.
*
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {Ticks}
* @name ticks
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'ticks', {
get: function () {
return this._clock.ticks;
},
set: function (t) {
var now = this.now();
//stop everything synced to the transport
if (this.state === Tone.State.Started) {
this.emit('stop', now);
this._clock.ticks = t;
//restart it with the new time
this.emit('start', now, this.seconds);
} else {
this._clock.ticks = t;
}
}
});
/**
* Pulses Per Quarter note. This is the smallest resolution
* the Transport timing supports. This should be set once
* on initialization and not set again. Changing this value
* after other objects have been created can cause problems.
*
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {Number}
* @name PPQ
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'PPQ', {
get: function () {
return this._ppq;
},
set: function (ppq) {
var bpm = this.bpm.value;
this._ppq = ppq;
this.bpm.value = bpm;
}
});
/**
* The hint to the type of playback. Affects tradeoffs between audio
* output latency and responsiveness.
*
* In addition to setting the value in seconds, the latencyHint also
* accepts the strings "interactive" (prioritizes low latency),
* "playback" (prioritizes sustained playback), "balanced" (balances
* latency and performance), and "fastest" (lowest latency, might glitch more often).
* @memberOf Tone.Transport#
* @type {Seconds|String}
* @name latencyHint
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Transport.prototype, 'latencyHint', {
get: function () {
return Tone.Clock.latencyHint;
},
set: function (hint) {
Tone.Clock.latencyHint = hint;
}
});
/**
* Convert from BPM to frequency (factoring in PPQ)
* @param {BPM} bpm The BPM value to convert to frequency
* @return {Frequency} The BPM as a frequency with PPQ factored in.
* @private
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype._fromUnits = function (bpm) {
return 1 / (60 / bpm / this.PPQ);
};
/**
* Convert from frequency (with PPQ) into BPM
* @param {Frequency} freq The clocks frequency to convert to BPM
* @return {BPM} The frequency value as BPM.
* @private
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype._toUnits = function (freq) {
return freq / this.PPQ * 60;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// SYNCING
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Returns the time aligned to the next subdivision
* of the Transport. If the Transport is not started,
* it will return 0.
* Note: this will not work precisely during tempo ramps.
* @param {Time} subdivision The subdivision to quantize to
* @return {Number} The context time of the next subdivision.
* @example
* Tone.Transport.start(); //the transport must be started
* Tone.Transport.nextSubdivision("4n");
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.nextSubdivision = function (subdivision) {
subdivision = this.toSeconds(subdivision);
//if the transport's not started, return 0
var now;
if (this.state === Tone.State.Started) {
now = this._clock._nextTick;
} else {
return 0;
}
var transportPos = Tone.Time(this.ticks, 'i').eval();
var remainingTime = subdivision - transportPos % subdivision;
if (remainingTime === 0) {
remainingTime = subdivision;
}
return now + remainingTime;
};
/**
* Attaches the signal to the tempo control signal so that
* any changes in the tempo will change the signal in the same
* ratio.
*
* @param {Tone.Signal} signal
* @param {number=} ratio Optionally pass in the ratio between
* the two signals. Otherwise it will be computed
* based on their current values.
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.syncSignal = function (signal, ratio) {
if (!ratio) {
//get the sync ratio
if (signal._param.value !== 0) {
ratio = signal._param.value / this.bpm._param.value;
} else {
ratio = 0;
}
}
var ratioSignal = new Tone.Gain(ratio);
this.bpm.chain(ratioSignal, signal._param);
this._syncedSignals.push({
'ratio': ratioSignal,
'signal': signal,
'initial': signal._param.value
});
signal._param.value = 0;
return this;
};
/**
* Unsyncs a previously synced signal from the transport's control.
* See Tone.Transport.syncSignal.
* @param {Tone.Signal} signal
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.unsyncSignal = function (signal) {
for (var i = this._syncedSignals.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var syncedSignal = this._syncedSignals[i];
if (syncedSignal.signal === signal) {
syncedSignal.ratio.dispose();
syncedSignal.signal._param.value = syncedSignal.initial;
this._syncedSignals.splice(i, 1);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Transport} this
* @private
*/
Tone.Transport.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Emitter.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._clock.dispose();
this._clock = null;
this._writable('bpm');
this.bpm = null;
this._timeline.dispose();
this._timeline = null;
this._onceEvents.dispose();
this._onceEvents = null;
this._repeatedEvents.dispose();
this._repeatedEvents = null;
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// INITIALIZATION
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
var TransportConstructor = Tone.Transport;
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
if (typeof Tone.Transport === 'function') {
//a single transport object
Tone.Transport = new Tone.Transport();
} else {
//stop the clock
Tone.Transport.stop();
//get the previous values
var prevSettings = Tone.Transport.get();
//destory the old transport
Tone.Transport.dispose();
//make new Transport insides
TransportConstructor.call(Tone.Transport);
//set the previous config
Tone.Transport.set(prevSettings);
}
});
return Tone.Transport;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Volume is a simple volume node, useful for creating a volume fader.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {Decibels} [volume=0] the initial volume
* @example
* var vol = new Tone.Volume(-12);
* instrument.chain(vol, Tone.Master);
*/
Tone.Volume = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['volume'], Tone.Volume.defaults);
/**
* the output node
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.output = this.input = new Tone.Gain(options.volume, Tone.Type.Decibels);
/**
* The unmuted volume
* @type {Decibels}
* @private
*/
this._unmutedVolume = 0;
/**
* if the volume is muted
* @type {Boolean}
* @private
*/
this._muted = false;
/**
* The volume control in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.volume = this.output.gain;
this._readOnly('volume');
//set the mute initially
this.mute = options.mute;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Volume);
/**
* Defaults
* @type {Object}
* @const
* @static
*/
Tone.Volume.defaults = {
'volume': 0,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.Volume#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* volume.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Volume.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._muted;
},
set: function (mute) {
if (!this._muted && mute) {
this._unmutedVolume = this.volume.value;
//maybe it should ramp here?
this.volume.value = -Infinity;
} else if (this._muted && !mute) {
this.volume.value = this._unmutedVolume;
}
this._muted = mute;
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Volume} this
*/
Tone.Volume.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.input.dispose();
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable('volume');
this.volume.dispose();
this.volume = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Volume;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A single master output which is connected to the
* AudioDestinationNode (aka your speakers).
* It provides useful conveniences such as the ability
* to set the volume and mute the entire application.
* It also gives you the ability to apply master effects to your application.
*
* Like Tone.Transport, A single Tone.Master is created
* on initialization and you do not need to explicitly construct one.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @singleton
* @example
* //the audio will go from the oscillator to the speakers
* oscillator.connect(Tone.Master);
* //a convenience for connecting to the master output is also provided:
* oscillator.toMaster();
* //the above two examples are equivalent.
*/
Tone.Master = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
/**
* The private volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume();
/**
* The volume of the master output.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
//connections
this.input.chain(this.output, this.context.destination);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Master);
/**
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.Master.defaults = {
'volume': 0,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.Master#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* Tone.Master.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Master.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._volume.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._volume.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* Add a master effects chain. NOTE: this will disconnect any nodes which were previously
* chained in the master effects chain.
* @param {AudioNode|Tone...} args All arguments will be connected in a row
* and the Master will be routed through it.
* @return {Tone.Master} this
* @example
* //some overall compression to keep the levels in check
* var masterCompressor = new Tone.Compressor({
* "threshold" : -6,
* "ratio" : 3,
* "attack" : 0.5,
* "release" : 0.1
* });
* //give a little boost to the lows
* var lowBump = new Tone.Filter(200, "lowshelf");
* //route everything through the filter
* //and compressor before going to the speakers
* Tone.Master.chain(lowBump, masterCompressor);
*/
Tone.Master.prototype.chain = function () {
this.input.disconnect();
this.input.chain.apply(this.input, arguments);
arguments[arguments.length - 1].connect(this.output);
};
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.Master} this
*/
Tone.Master.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable('volume');
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this.volume = null;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// AUGMENT TONE's PROTOTYPE
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* Connect 'this' to the master output. Shorthand for this.connect(Tone.Master)
* @returns {Tone} this
* @example
* //connect an oscillator to the master output
* var osc = new Tone.Oscillator().toMaster();
*/
Tone.prototype.toMaster = function () {
this.connect(Tone.Master);
return this;
};
/**
* Also augment AudioNode's prototype to include toMaster
* as a convenience
* @returns {AudioNode} this
*/
AudioNode.prototype.toMaster = function () {
this.connect(Tone.Master);
return this;
};
var MasterConstructor = Tone.Master;
/**
* initialize the module and listen for new audio contexts
*/
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
//a single master output
if (!Tone.prototype.isUndef(Tone.Master)) {
Tone.Master = new MasterConstructor();
} else {
MasterConstructor.prototype.dispose.call(Tone.Master);
MasterConstructor.call(Tone.Master);
}
});
return Tone.Master;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Base class for sources. Sources have start/stop methods
* and the ability to be synced to the
* start/stop of Tone.Transport.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* //Multiple state change events can be chained together,
* //but must be set in the correct order and with ascending times
*
* // OK
* state.start().stop("+0.2");
* // AND
* state.start().stop("+0.2").start("+0.4").stop("+0.7")
*
* // BAD
* state.stop("+0.2").start();
* // OR
* state.start("+0.3").stop("+0.2");
*
*/
Tone.Source = function (options) {
// this.createInsOuts(0, 1);
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Source.defaults);
/**
* The output volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume of the output in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
* @example
* source.volume.value = -6;
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
/**
* Keep track of the scheduled state.
* @type {Tone.TimelineState}
* @private
*/
this._state = new Tone.TimelineState(Tone.State.Stopped);
this._state.memory = 10;
/**
* The synced `start` callback function from the transport
* @type {Function}
* @private
*/
this._synced = false;
/**
* Keep track of all of the scheduled event ids
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._scheduled = [];
//make the output explicitly stereo
this._volume.output.output.channelCount = 2;
this._volume.output.output.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
//mute initially
this.mute = options.mute;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Source);
/**
* The default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Source.defaults = {
'volume': 0,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, either "started" or "stopped".
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.Source#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Source.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
if (this._synced) {
if (Tone.Transport.state === Tone.State.Started) {
return this._state.getValueAtTime(Tone.Transport.seconds);
} else {
return Tone.State.Stopped;
}
} else {
return this._state.getValueAtTime(this.now());
}
}
});
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.Source#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* source.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Source.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._volume.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._volume.mute = mute;
}
});
//overwrite these functions
Tone.Source.prototype._start = Tone.noOp;
Tone.Source.prototype._stop = Tone.noOp;
/**
* Start the source at the specified time. If no time is given,
* start the source now.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the source should be started.
* @returns {Tone.Source} this
* @example
* source.start("+0.5"); //starts the source 0.5 seconds from now
*/
Tone.Source.prototype.start = function (time, offset, duration) {
if (this.isUndef(time) && this._synced) {
time = Tone.Transport.seconds;
} else {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
}
//if it's started, stop it and restart it
if (!this.retrigger && this._state.getValueAtTime(time) === Tone.State.Started) {
this.stop(time);
}
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Started, time);
if (this._synced) {
// add the offset time to the event
var event = this._state.get(time);
event.offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
event.duration = duration;
var sched = Tone.Transport.schedule(function (t) {
this._start(t, offset, duration);
}.bind(this), time);
this._scheduled.push(sched);
} else {
this._start.apply(this, arguments);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the source at the specified time. If no time is given,
* stop the source now.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the source should be stopped.
* @returns {Tone.Source} this
* @example
* source.stop(); // stops the source immediately
*/
Tone.Source.prototype.stop = function (time) {
if (this.isUndef(time) && this._synced) {
time = Tone.Transport.seconds;
} else {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
}
this._state.cancel(time);
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, time);
if (!this._synced) {
this._stop.apply(this, arguments);
} else {
var sched = Tone.Transport.schedule(this._stop.bind(this), time);
this._scheduled.push(sched);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Sync the source to the Transport so that all subsequent
* calls to `start` and `stop` are synced to the TransportTime
* instead of the AudioContext time.
*
* @returns {Tone.Source} this
* @example
* //sync the source so that it plays between 0 and 0.3 on the Transport's timeline
* source.sync().start(0).stop(0.3);
* //start the transport.
* Tone.Transport.start();
*
* @example
* //start the transport with an offset and the sync'ed sources
* //will start in the correct position
* source.sync().start(0.1);
* //the source will be invoked with an offset of 0.4
* Tone.Transport.start("+0.5", 0.5);
*/
Tone.Source.prototype.sync = function () {
this._synced = true;
Tone.Transport.on('start loopStart', function (time, offset) {
if (offset > 0) {
// get the playback state at that time
var stateEvent = this._state.get(offset);
// listen for start events which may occur in the middle of the sync'ed time
if (stateEvent && stateEvent.state === Tone.State.Started && stateEvent.time !== offset) {
// get the offset
var startOffset = offset - this.toSeconds(stateEvent.time);
var duration;
if (stateEvent.duration) {
duration = this.toSeconds(stateEvent.duration) - startOffset;
}
this._start(time, this.toSeconds(stateEvent.offset) + startOffset, duration);
}
}
}.bind(this));
Tone.Transport.on('stop pause loopEnd', function (time) {
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(Tone.Transport.seconds) === Tone.State.Started) {
this._stop(time);
}
}.bind(this));
return this;
};
/**
* Unsync the source to the Transport. See Tone.Source.sync
* @returns {Tone.Source} this
*/
Tone.Source.prototype.unsync = function () {
this._synced = false;
Tone.Transport.off('start stop pause loopEnd loopStart');
// clear all of the scheduled ids
for (var i = 0; i < this._scheduled.length; i++) {
var id = this._scheduled[i];
Tone.Transport.clear(id);
}
this._scheduled = [];
this._state.cancel(0);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Source} this
*/
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.unsync();
this._scheduled = null;
this._writable('volume');
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this.volume = null;
this._state.dispose();
this._state = null;
};
return Tone.Source;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Oscillator supports a number of features including
* phase rotation, multiple oscillator types (see Tone.Oscillator.type),
* and Transport syncing (see Tone.Oscillator.syncFrequency).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Source}
* @param {Frequency} [frequency] Starting frequency
* @param {string} [type] The oscillator type. Read more about type below.
* @example
* //make and start a 440hz sine tone
* var osc = new Tone.Oscillator(440, "sine").toMaster().start();
*/
Tone.Oscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'type'
], Tone.Oscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* the main oscillator
* @type {OscillatorNode}
* @private
*/
this._oscillator = null;
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune control signal.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* the periodic wave
* @type {PeriodicWave}
* @private
*/
this._wave = null;
/**
* The partials of the oscillator
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._partials = this.defaultArg(options.partials, [1]);
/**
* the phase of the oscillator
* between 0 - 360
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._phase = options.phase;
/**
* the type of the oscillator
* @type {string}
* @private
*/
this._type = null;
//setup
this.type = options.type;
this.phase = this._phase;
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Oscillator, Tone.Source);
/**
* the default parameters
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Oscillator.defaults = {
'type': 'sine',
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'phase': 0,
'partials': []
};
/**
* The Oscillator types
* @enum {String}
*/
Tone.Oscillator.Type = {
Sine: 'sine',
Triangle: 'triangle',
Sawtooth: 'sawtooth',
Square: 'square',
Custom: 'custom'
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @private
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
//new oscillator with previous values
this._oscillator = this.context.createOscillator();
this._oscillator.setPeriodicWave(this._wave);
//connect the control signal to the oscillator frequency & detune
this._oscillator.connect(this.output);
this.frequency.connect(this._oscillator.frequency);
this.detune.connect(this._oscillator.detune);
//start the oscillator
this._oscillator.start(this.toSeconds(time));
};
/**
* stop the oscillator
* @private
* @param {Time} [time=now] (optional) timing parameter
* @returns {Tone.Oscillator} this
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
if (this._oscillator) {
this._oscillator.stop(this.toSeconds(time));
this._oscillator = null;
}
return this;
};
/**
* Sync the signal to the Transport's bpm. Any changes to the transports bpm,
* will also affect the oscillators frequency.
* @returns {Tone.Oscillator} this
* @example
* Tone.Transport.bpm.value = 120;
* osc.frequency.value = 440;
* //the ration between the bpm and the frequency will be maintained
* osc.syncFrequency();
* Tone.Transport.bpm.value = 240;
* // the frequency of the oscillator is doubled to 880
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype.syncFrequency = function () {
Tone.Transport.syncSignal(this.frequency);
return this;
};
/**
* Unsync the oscillator's frequency from the Transport.
* See Tone.Oscillator.syncFrequency
* @returns {Tone.Oscillator} this
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype.unsyncFrequency = function () {
Tone.Transport.unsyncSignal(this.frequency);
return this;
};
/**
* The type of the oscillator: either sine, square, triangle, or sawtooth. Also capable of
* setting the first x number of partials of the oscillator. For example: "sine4" would
* set be the first 4 partials of the sine wave and "triangle8" would set the first
* 8 partials of the triangle wave.
*
* Uses PeriodicWave internally even for native types so that it can set the phase.
* PeriodicWave equations are from the
* [Webkit Web Audio implementation](https://code.google.com/p/chromium/codesearch#chromium/src/third_party/WebKit/Source/modules/webaudio/PeriodicWave.cpp&sq=package:chromium).
*
* @memberOf Tone.Oscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name type
* @example
* //set it to a square wave
* osc.type = "square";
* @example
* //set the first 6 partials of a sawtooth wave
* osc.type = "sawtooth6";
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Oscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._type;
},
set: function (type) {
var coefs = this._getRealImaginary(type, this._phase);
var periodicWave = this.context.createPeriodicWave(coefs[0], coefs[1]);
this._wave = periodicWave;
if (this._oscillator !== null) {
this._oscillator.setPeriodicWave(this._wave);
}
this._type = type;
}
});
/**
* Returns the real and imaginary components based
* on the oscillator type.
* @returns {Array} [real, imaginary]
* @private
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype._getRealImaginary = function (type, phase) {
var fftSize = 4096;
var periodicWaveSize = fftSize / 2;
var real = new Float32Array(periodicWaveSize);
var imag = new Float32Array(periodicWaveSize);
var partialCount = 1;
if (type === Tone.Oscillator.Type.Custom) {
partialCount = this._partials.length + 1;
periodicWaveSize = partialCount;
} else {
var partial = /^(sine|triangle|square|sawtooth)(\d+)$/.exec(type);
if (partial) {
partialCount = parseInt(partial[2]) + 1;
type = partial[1];
partialCount = Math.max(partialCount, 2);
periodicWaveSize = partialCount;
}
}
for (var n = 1; n < periodicWaveSize; ++n) {
var piFactor = 2 / (n * Math.PI);
var b;
switch (type) {
case Tone.Oscillator.Type.Sine:
b = n <= partialCount ? 1 : 0;
break;
case Tone.Oscillator.Type.Square:
b = n & 1 ? 2 * piFactor : 0;
break;
case Tone.Oscillator.Type.Sawtooth:
b = piFactor * (n & 1 ? 1 : -1);
break;
case Tone.Oscillator.Type.Triangle:
if (n & 1) {
b = 2 * (piFactor * piFactor) * (n - 1 >> 1 & 1 ? -1 : 1);
} else {
b = 0;
}
break;
case Tone.Oscillator.Type.Custom:
b = this._partials[n - 1];
break;
default:
throw new TypeError('Tone.Oscillator: invalid type: ' + type);
}
if (b !== 0) {
real[n] = -b * Math.sin(phase * n);
imag[n] = b * Math.cos(phase * n);
} else {
real[n] = 0;
imag[n] = 0;
}
}
return [
real,
imag
];
};
/**
* Compute the inverse FFT for a given phase.
* @param {Float32Array} real
* @param {Float32Array} imag
* @param {NormalRange} phase
* @return {AudioRange}
* @private
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype._inverseFFT = function (real, imag, phase) {
var sum = 0;
var len = real.length;
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sum += real[i] * Math.cos(i * phase) + imag[i] * Math.sin(i * phase);
}
return sum;
};
/**
* Returns the initial value of the oscillator.
* @return {AudioRange}
* @private
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype._getInitialValue = function () {
var coefs = this._getRealImaginary(this._type, 0);
var real = coefs[0];
var imag = coefs[1];
var maxValue = 0;
var twoPi = Math.PI * 2;
//check for peaks in 8 places
for (var i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
maxValue = Math.max(this._inverseFFT(real, imag, i / 8 * twoPi), maxValue);
}
return -this._inverseFFT(real, imag, this._phase) / maxValue;
};
/**
* The partials of the waveform. A partial represents
* the amplitude at a harmonic. The first harmonic is the
* fundamental frequency, the second is the octave and so on
* following the harmonic series.
* Setting this value will automatically set the type to "custom".
* The value is an empty array when the type is not "custom".
* @memberOf Tone.Oscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @example
* osc.partials = [1, 0.2, 0.01];
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Oscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
if (this._type !== Tone.Oscillator.Type.Custom) {
return [];
} else {
return this._partials;
}
},
set: function (partials) {
this._partials = partials;
this.type = Tone.Oscillator.Type.Custom;
}
});
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.Oscillator#
* @type {Degrees}
* @name phase
* @example
* osc.phase = 180; //flips the phase of the oscillator
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Oscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._phase * (180 / Math.PI);
},
set: function (phase) {
this._phase = phase * Math.PI / 180;
//reset the type
this.type = this._type;
}
});
/**
* Dispose and disconnect.
* @return {Tone.Oscillator} this
*/
Tone.Oscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
if (this._oscillator !== null) {
this._oscillator.disconnect();
this._oscillator = null;
}
this._wave = null;
this._writable([
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this._partials = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Oscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Zero outputs 0's at audio-rate. The reason this has to be
* it's own class is that many browsers optimize out Tone.Signal
* with a value of 0 and will not process nodes further down the graph.
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.Zero = function () {
/**
* The gain node
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._gain = this.input = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
Tone.Zero._zeros.connect(this._gain);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Zero);
/**
* clean up
* @return {Tone.Zero} this
*/
Tone.Zero.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._gain.dispose();
this._gain = null;
return this;
};
/**
* Generates a constant output of 0. This is so
* the processing graph doesn't optimize out this
* segment of the graph.
* @static
* @private
* @const
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
*/
Tone.Zero._zeros = null;
/**
* initializer function
*/
Tone._initAudioContext(function (audioContext) {
var buffer = audioContext.createBuffer(1, 128, audioContext.sampleRate);
var arr = buffer.getChannelData(0);
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
Tone.Zero._zeros = audioContext.createBufferSource();
Tone.Zero._zeros.channelCount = 1;
Tone.Zero._zeros.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
Tone.Zero._zeros.buffer = buffer;
Tone.Zero._zeros.loop = true;
Tone.Zero._zeros.start(0);
Tone.Zero._zeros.noGC();
});
return Tone.Zero;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class LFO stands for low frequency oscillator. Tone.LFO produces an output signal
* which can be attached to an AudioParam or Tone.Signal
* in order to modulate that parameter with an oscillator. The LFO can
* also be synced to the transport to start/stop and change when the tempo changes.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @param {Frequency|Object} [frequency] The frequency of the oscillation. Typically, LFOs will be
* in the frequency range of 0.1 to 10 hertz.
* @param {number=} min The minimum output value of the LFO.
* @param {number=} max The maximum value of the LFO.
* @example
* var lfo = new Tone.LFO("4n", 400, 4000);
* lfo.connect(filter.frequency);
*/
Tone.LFO = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'min',
'max'
], Tone.LFO.defaults);
/**
* The oscillator.
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._oscillator = new Tone.Oscillator({
'frequency': options.frequency,
'type': options.type
});
/**
* the lfo's frequency
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._oscillator.frequency;
/**
* The amplitude of the LFO, which controls the output range between
* the min and max output. For example if the min is -10 and the max
* is 10, setting the amplitude to 0.5 would make the LFO modulate
* between -5 and 5.
* @type {Number}
* @signal
*/
this.amplitude = this._oscillator.volume;
this.amplitude.units = Tone.Type.NormalRange;
this.amplitude.value = options.amplitude;
/**
* The signal which is output when the LFO is stopped
* @type {Tone.Signal}
* @private
*/
this._stoppedSignal = new Tone.Signal(0, Tone.Type.AudioRange);
/**
* Just outputs zeros.
* @type {Tone.Zero}
* @private
*/
this._zeros = new Tone.Zero();
/**
* The value that the LFO outputs when it's stopped
* @type {AudioRange}
* @private
*/
this._stoppedValue = 0;
/**
* @type {Tone.AudioToGain}
* @private
*/
this._a2g = new Tone.AudioToGain();
/**
* @type {Tone.Scale}
* @private
*/
this._scaler = this.output = new Tone.Scale(options.min, options.max);
/**
* the units of the LFO (used for converting)
* @type {Tone.Type}
* @private
*/
this._units = Tone.Type.Default;
this.units = options.units;
//connect it up
this._oscillator.chain(this._a2g, this._scaler);
this._zeros.connect(this._a2g);
this._stoppedSignal.connect(this._a2g);
this._readOnly([
'amplitude',
'frequency'
]);
this.phase = options.phase;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.LFO, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* the default parameters
*
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.LFO.defaults = {
'type': 'sine',
'min': 0,
'max': 1,
'phase': 0,
'frequency': '4n',
'amplitude': 1,
'units': Tone.Type.Default
};
/**
* Start the LFO.
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the LFO will start
* @returns {Tone.LFO} this
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype.start = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._stoppedSignal.setValueAtTime(0, time);
this._oscillator.start(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the LFO.
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the LFO will stop
* @returns {Tone.LFO} this
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype.stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._stoppedSignal.setValueAtTime(this._stoppedValue, time);
this._oscillator.stop(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Sync the start/stop/pause to the transport
* and the frequency to the bpm of the transport
* @returns {Tone.LFO} this
* @example
* lfo.frequency.value = "8n";
* lfo.sync().start(0)
* //the rate of the LFO will always be an eighth note,
* //even as the tempo changes
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype.sync = function () {
this._oscillator.sync();
this._oscillator.syncFrequency();
return this;
};
/**
* unsync the LFO from transport control
* @returns {Tone.LFO} this
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype.unsync = function () {
this._oscillator.unsync();
this._oscillator.unsyncFrequency();
return this;
};
/**
* The miniumum output of the LFO.
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @type {number}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'min', {
get: function () {
return this._toUnits(this._scaler.min);
},
set: function (min) {
min = this._fromUnits(min);
this._scaler.min = min;
}
});
/**
* The maximum output of the LFO.
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @type {number}
* @name max
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'max', {
get: function () {
return this._toUnits(this._scaler.max);
},
set: function (max) {
max = this._fromUnits(max);
this._scaler.max = max;
}
});
/**
* The type of the oscillator: sine, square, sawtooth, triangle.
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillator.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._oscillator.type = type;
this._stoppedValue = this._oscillator._getInitialValue();
this._stoppedSignal.value = this._stoppedValue;
}
});
/**
* The phase of the LFO.
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @type {number}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillator.phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._oscillator.phase = phase;
this._stoppedValue = this._oscillator._getInitialValue();
this._stoppedSignal.value = this._stoppedValue;
}
});
/**
* The output units of the LFO.
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @type {Tone.Type}
* @name units
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'units', {
get: function () {
return this._units;
},
set: function (val) {
var currentMin = this.min;
var currentMax = this.max;
//convert the min and the max
this._units = val;
this.min = currentMin;
this.max = currentMax;
}
});
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @type {Boolean}
* @name mute
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillator.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._oscillator.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, either "started" or "stopped".
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.LFO#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.LFO.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillator.state;
}
});
/**
* Connect the output of the LFO to an AudioParam, AudioNode, or Tone Node.
* Tone.LFO will automatically convert to the destination units of the
* will get the units from the connected node.
* @param {Tone | AudioParam | AudioNode} node
* @param {number} [outputNum=0] optionally which output to connect from
* @param {number} [inputNum=0] optionally which input to connect to
* @returns {Tone.LFO} this
* @private
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype.connect = function (node) {
if (node.constructor === Tone.Signal || node.constructor === Tone.Param || node.constructor === Tone.TimelineSignal) {
this.convert = node.convert;
this.units = node.units;
}
Tone.Signal.prototype.connect.apply(this, arguments);
return this;
};
/**
* private method borrowed from Param converts
* units from their destination value
* @function
* @private
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype._fromUnits = Tone.Param.prototype._fromUnits;
/**
* private method borrowed from Param converts
* units to their destination value
* @function
* @private
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype._toUnits = Tone.Param.prototype._toUnits;
/**
* disconnect and dispose
* @returns {Tone.LFO} this
*/
Tone.LFO.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'amplitude',
'frequency'
]);
this._oscillator.dispose();
this._oscillator = null;
this._stoppedSignal.dispose();
this._stoppedSignal = null;
this._zeros.dispose();
this._zeros = null;
this._scaler.dispose();
this._scaler = null;
this._a2g.dispose();
this._a2g = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.amplitude = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.LFO;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Limiter will limit the loudness of an incoming signal.
* It is composed of a Tone.Compressor with a fast attack
* and release. Limiters are commonly used to safeguard against
* signal clipping. Unlike a compressor, limiters do not provide
* smooth gain reduction and almost completely prevent
* additional gain above the threshold.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {number} threshold The theshold above which the limiting is applied.
* @example
* var limiter = new Tone.Limiter(-6);
*/
Tone.Limiter = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['threshold'], Tone.Limiter.defaults);
/**
* the compressor
* @private
* @type {Tone.Compressor}
*/
this._compressor = this.input = this.output = new Tone.Compressor({
'attack': 0.001,
'decay': 0.001,
'threshold': options.threshold
});
/**
* The threshold of of the limiter
* @type {Decibel}
* @signal
*/
this.threshold = this._compressor.threshold;
this._readOnly('threshold');
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Limiter);
/**
* The default value
* @type {Object}
* @const
* @static
*/
Tone.Limiter.defaults = { 'threshold': -12 };
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Limiter} this
*/
Tone.Limiter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._compressor.dispose();
this._compressor = null;
this._writable('threshold');
this.threshold = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Limiter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Lowpass is a lowpass feedback comb filter. It is similar to
* Tone.FeedbackCombFilter, but includes a lowpass filter.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {Time|Object} [delayTime] The delay time of the comb filter
* @param {NormalRange=} resonance The resonance (feedback) of the comb filter
* @param {Frequency=} dampening The cutoff of the lowpass filter dampens the
* signal as it is fedback.
*/
Tone.LowpassCombFilter = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'delayTime',
'resonance',
'dampening'
], Tone.LowpassCombFilter.defaults);
/**
* the delay node
* @type {DelayNode}
* @private
*/
this._delay = this.input = new Tone.Delay(options.delayTime);
/**
* The delayTime of the comb filter.
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.delayTime = this._delay.delayTime;
/**
* the lowpass filter
* @type {BiquadFilterNode}
* @private
*/
this._lowpass = this.output = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
this._lowpass.Q.value = -3.0102999566398125;
this._lowpass.type = 'lowpass';
/**
* The dampening control of the feedback
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.dampening = new Tone.Param({
'param': this._lowpass.frequency,
'units': Tone.Type.Frequency,
'value': options.dampening
});
/**
* the feedback gain
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._feedback = new Tone.Gain(options.resonance, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* The amount of feedback of the delayed signal.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.resonance = this._feedback.gain;
//connections
this._delay.chain(this._lowpass, this._feedback, this._delay);
this._readOnly([
'dampening',
'resonance',
'delayTime'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.LowpassCombFilter);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.LowpassCombFilter.defaults = {
'delayTime': 0.1,
'resonance': 0.5,
'dampening': 3000
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.LowpassCombFilter} this
*/
Tone.LowpassCombFilter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'dampening',
'resonance',
'delayTime'
]);
this.dampening.dispose();
this.dampening = null;
this.resonance.dispose();
this.resonance = null;
this._delay.dispose();
this._delay = null;
this.delayTime = null;
this._lowpass.disconnect();
this._lowpass = null;
this._feedback.disconnect();
this._feedback = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.LowpassCombFilter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Merge brings two signals into the left and right
* channels of a single stereo channel.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* var merge = new Tone.Merge().toMaster();
* //routing a sine tone in the left channel
* //and noise in the right channel
* var osc = new Tone.Oscillator().connect(merge.left);
* var noise = new Tone.Noise().connect(merge.right);
* //starting our oscillators
* noise.start();
* osc.start();
*/
Tone.Merge = function () {
this.createInsOuts(2, 0);
/**
* The left input channel.
* Alias for input[0]
* @type {GainNode}
*/
this.left = this.input[0] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* The right input channel.
* Alias for input[1].
* @type {GainNode}
*/
this.right = this.input[1] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the merger node for the two channels
* @type {ChannelMergerNode}
* @private
*/
this._merger = this.output = this.context.createChannelMerger(2);
//connections
this.left.connect(this._merger, 0, 0);
this.right.connect(this._merger, 0, 1);
this.left.channelCount = 1;
this.right.channelCount = 1;
this.left.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
this.right.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Merge);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Merge} this
*/
Tone.Merge.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.left.dispose();
this.left = null;
this.right.dispose();
this.right = null;
this._merger.disconnect();
this._merger = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Merge;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Meter gets the [RMS](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Root_mean_square)
* of an input signal with some averaging applied. It can also get the raw
* value of the input signal.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {String} type Either "level" or "signal".
* @param {Number} smoothing The amount of smoothing applied between frames.
* @example
* var meter = new Tone.Meter();
* var mic = new Tone.UserMedia().start();
* //connect mic to the meter
* mic.connect(meter);
* //the current level of the mic input
* var level = meter.value;
*/
Tone.Meter = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'type',
'smoothing'
], Tone.Meter.defaults);
/**
* The type of the meter, either "level" or "signal".
* A "level" meter will return the volume level (rms) of the
* input signal and a "signal" meter will return
* the signal value of the input.
* @type {String}
*/
this.type = options.type;
/**
* The analyser node which computes the levels.
* @private
* @type {Tone.Analyser}
*/
this.input = this.output = this._analyser = new Tone.Analyser('waveform', 512);
this._analyser.returnType = 'float';
/**
* The amount of carryover between the current and last frame.
* Only applied meter for "level" type.
* @type {Number}
*/
this.smoothing = options.smoothing;
/**
* The last computed value
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._lastValue = 0;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Meter);
/**
* @private
* @enum {String}
*/
Tone.Meter.Type = {
Level: 'level',
Signal: 'signal'
};
/**
* The defaults
* @type {Object}
* @static
* @const
*/
Tone.Meter.defaults = {
'smoothing': 0.8,
'type': Tone.Meter.Type.Level
};
/**
* The current value of the meter. A value of 1 is
* "unity".
* @memberOf Tone.Meter#
* @type {Number}
* @name value
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Meter.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
var signal = this._analyser.analyse();
if (this.type === Tone.Meter.Type.Level) {
//rms
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < signal.length; i++) {
sum += Math.pow(signal[i], 2);
}
var rms = Math.sqrt(sum / signal.length);
//smooth it
rms = Math.max(rms, this._lastValue * this.smoothing);
this._lastValue = rms;
//scale it
var unity = 0.35;
var val = rms / unity;
//scale the output curve
return Math.sqrt(val);
} else {
return signal[0];
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Meter} this
*/
Tone.Meter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._analyser.dispose();
this._analyser = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Meter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Split splits an incoming signal into left and right channels.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* var split = new Tone.Split();
* stereoSignal.connect(split);
*/
Tone.Split = function () {
this.createInsOuts(0, 2);
/**
* @type {ChannelSplitterNode}
* @private
*/
this._splitter = this.input = this.context.createChannelSplitter(2);
/**
* Left channel output.
* Alias for output[0]
* @type {Tone.Gain}
*/
this.left = this.output[0] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* Right channel output.
* Alias for output[1]
* @type {Tone.Gain}
*/
this.right = this.output[1] = new Tone.Gain();
//connections
this._splitter.connect(this.left, 0, 0);
this._splitter.connect(this.right, 1, 0);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Split);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Split} this
*/
Tone.Split.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._splitter.disconnect();
this.left.dispose();
this.left = null;
this.right.dispose();
this.right = null;
this._splitter = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Split;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Mid/Side processing separates the the 'mid' signal
* (which comes out of both the left and the right channel)
* and the 'side' (which only comes out of the the side channels).
*
* Mid = (Left+Right)/sqrt(2); // obtain mid-signal from left and right
* Side = (Left-Right)/sqrt(2); // obtain side-signal from left and righ
*
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
*/
Tone.MidSideSplit = function () {
this.createInsOuts(0, 2);
/**
* split the incoming signal into left and right channels
* @type {Tone.Split}
* @private
*/
this._split = this.input = new Tone.Split();
/**
* The mid send. Connect to mid processing. Alias for
* output[0]
* @type {Tone.Expr}
*/
this.mid = this.output[0] = new Tone.Expr('($0 + $1) * $2');
/**
* The side output. Connect to side processing. Alias for
* output[1]
* @type {Tone.Expr}
*/
this.side = this.output[1] = new Tone.Expr('($0 - $1) * $2');
this._split.connect(this.mid, 0, 0);
this._split.connect(this.mid, 1, 1);
this._split.connect(this.side, 0, 0);
this._split.connect(this.side, 1, 1);
sqrtTwo.connect(this.mid, 0, 2);
sqrtTwo.connect(this.side, 0, 2);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MidSideSplit);
/**
* a constant signal equal to 1 / sqrt(2)
* @type {Number}
* @signal
* @private
* @static
*/
var sqrtTwo = null;
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
sqrtTwo = new Tone.Signal(1 / Math.sqrt(2));
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.MidSideSplit} this
*/
Tone.MidSideSplit.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.mid.dispose();
this.mid = null;
this.side.dispose();
this.side = null;
this._split.dispose();
this._split = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MidSideSplit;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Mid/Side processing separates the the 'mid' signal
* (which comes out of both the left and the right channel)
* and the 'side' (which only comes out of the the side channels).
* MidSideMerge merges the mid and side signal after they've been seperated
* by Tone.MidSideSplit.
*
* Left = (Mid+Side)/sqrt(2); // obtain left signal from mid and side
* Right = (Mid-Side)/sqrt(2); // obtain right signal from mid and side
*
*
* @extends {Tone.StereoEffect}
* @constructor
*/
Tone.MidSideMerge = function () {
this.createInsOuts(2, 0);
/**
* The mid signal input. Alias for
* input[0]
* @type {Tone.Gain}
*/
this.mid = this.input[0] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* recombine the mid/side into Left
* @type {Tone.Expr}
* @private
*/
this._left = new Tone.Expr('($0 + $1) * $2');
/**
* The side signal input. Alias for
* input[1]
* @type {Tone.Gain}
*/
this.side = this.input[1] = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* recombine the mid/side into Right
* @type {Tone.Expr}
* @private
*/
this._right = new Tone.Expr('($0 - $1) * $2');
/**
* Merge the left/right signal back into a stereo signal.
* @type {Tone.Merge}
* @private
*/
this._merge = this.output = new Tone.Merge();
this.mid.connect(this._left, 0, 0);
this.side.connect(this._left, 0, 1);
this.mid.connect(this._right, 0, 0);
this.side.connect(this._right, 0, 1);
this._left.connect(this._merge, 0, 0);
this._right.connect(this._merge, 0, 1);
sqrtTwo.connect(this._left, 0, 2);
sqrtTwo.connect(this._right, 0, 2);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MidSideMerge);
/**
* A constant signal equal to 1 / sqrt(2).
* @type {Number}
* @signal
* @private
* @static
*/
var sqrtTwo = null;
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
sqrtTwo = new Tone.Signal(1 / Math.sqrt(2));
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.MidSideMerge} this
*/
Tone.MidSideMerge.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.mid.dispose();
this.mid = null;
this.side.dispose();
this.side = null;
this._left.dispose();
this._left = null;
this._right.dispose();
this._right = null;
this._merge.dispose();
this._merge = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MidSideMerge;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MidSideCompressor applies two different compressors to the mid
* and side signal components. See Tone.MidSideSplit.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Object} options The options that are passed to the mid and side
* compressors.
* @constructor
*/
Tone.MidSideCompressor = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.MidSideCompressor.defaults);
/**
* the mid/side split
* @type {Tone.MidSideSplit}
* @private
*/
this._midSideSplit = this.input = new Tone.MidSideSplit();
/**
* the mid/side recombination
* @type {Tone.MidSideMerge}
* @private
*/
this._midSideMerge = this.output = new Tone.MidSideMerge();
/**
* The compressor applied to the mid signal
* @type {Tone.Compressor}
*/
this.mid = new Tone.Compressor(options.mid);
/**
* The compressor applied to the side signal
* @type {Tone.Compressor}
*/
this.side = new Tone.Compressor(options.side);
this._midSideSplit.mid.chain(this.mid, this._midSideMerge.mid);
this._midSideSplit.side.chain(this.side, this._midSideMerge.side);
this._readOnly([
'mid',
'side'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MidSideCompressor);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MidSideCompressor.defaults = {
'mid': {
'ratio': 3,
'threshold': -24,
'release': 0.03,
'attack': 0.02,
'knee': 16
},
'side': {
'ratio': 6,
'threshold': -30,
'release': 0.25,
'attack': 0.03,
'knee': 10
}
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.MidSideCompressor} this
*/
Tone.MidSideCompressor.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'mid',
'side'
]);
this.mid.dispose();
this.mid = null;
this.side.dispose();
this.side = null;
this._midSideSplit.dispose();
this._midSideSplit = null;
this._midSideMerge.dispose();
this._midSideMerge = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MidSideCompressor;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Mono coerces the incoming mono or stereo signal into a mono signal
* where both left and right channels have the same value. This can be useful
* for [stereo imaging](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereo_imaging).
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
*/
Tone.Mono = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 0);
/**
* merge the signal
* @type {Tone.Merge}
* @private
*/
this._merge = this.output = new Tone.Merge();
this.input.connect(this._merge, 0, 0);
this.input.connect(this._merge, 0, 1);
this.input.gain.value = this.dbToGain(-10);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Mono);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Mono} this
*/
Tone.Mono.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._merge.dispose();
this._merge = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Mono;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A compressor with seperate controls over low/mid/high dynamics
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {Object} options The low/mid/high compressor settings.
* @example
* var multiband = new Tone.MultibandCompressor({
* "lowFrequency" : 200,
* "highFrequency" : 1300
* "low" : {
* "threshold" : -12
* }
* })
*/
Tone.MultibandCompressor = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(arguments, Tone.MultibandCompressor.defaults);
/**
* split the incoming signal into high/mid/low
* @type {Tone.MultibandSplit}
* @private
*/
this._splitter = this.input = new Tone.MultibandSplit({
'lowFrequency': options.lowFrequency,
'highFrequency': options.highFrequency
});
/**
* low/mid crossover frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.lowFrequency = this._splitter.lowFrequency;
/**
* mid/high crossover frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.highFrequency = this._splitter.highFrequency;
/**
* the output
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* The compressor applied to the low frequencies.
* @type {Tone.Compressor}
*/
this.low = new Tone.Compressor(options.low);
/**
* The compressor applied to the mid frequencies.
* @type {Tone.Compressor}
*/
this.mid = new Tone.Compressor(options.mid);
/**
* The compressor applied to the high frequencies.
* @type {Tone.Compressor}
*/
this.high = new Tone.Compressor(options.high);
//connect the compressor
this._splitter.low.chain(this.low, this.output);
this._splitter.mid.chain(this.mid, this.output);
this._splitter.high.chain(this.high, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'high',
'mid',
'low',
'highFrequency',
'lowFrequency'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MultibandCompressor);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MultibandCompressor.defaults = {
'low': Tone.Compressor.defaults,
'mid': Tone.Compressor.defaults,
'high': Tone.Compressor.defaults,
'lowFrequency': 250,
'highFrequency': 2000
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.MultibandCompressor} this
*/
Tone.MultibandCompressor.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._splitter.dispose();
this._writable([
'high',
'mid',
'low',
'highFrequency',
'lowFrequency'
]);
this.low.dispose();
this.mid.dispose();
this.high.dispose();
this._splitter = null;
this.low = null;
this.mid = null;
this.high = null;
this.lowFrequency = null;
this.highFrequency = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MultibandCompressor;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Panner is an equal power Left/Right Panner and does not
* support 3D. Panner uses the StereoPannerNode when available.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {NormalRange} [initialPan=0] The initail panner value (defaults to 0 = center)
* @example
* //pan the input signal hard right.
* var panner = new Tone.Panner(1);
*/
Tone.Panner = function (initialPan) {
if (this._hasStereoPanner) {
/**
* the panner node
* @type {StereoPannerNode}
* @private
*/
this._panner = this.input = this.output = this.context.createStereoPanner();
/**
* The pan control. -1 = hard left, 1 = hard right.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.pan = this._panner.pan;
} else {
/**
* the dry/wet knob
* @type {Tone.CrossFade}
* @private
*/
this._crossFade = new Tone.CrossFade();
/**
* @type {Tone.Merge}
* @private
*/
this._merger = this.output = new Tone.Merge();
/**
* @type {Tone.Split}
* @private
*/
this._splitter = this.input = new Tone.Split();
/**
* The pan control. -1 = hard left, 1 = hard right.
* @type {AudioRange}
* @signal
*/
this.pan = new Tone.Signal(0, Tone.Type.AudioRange);
/**
* always sends 0
* @type {Tone.Zero}
* @private
*/
this._zero = new Tone.Zero();
/**
* The analog to gain conversion
* @type {Tone.AudioToGain}
* @private
*/
this._a2g = new Tone.AudioToGain();
//CONNECTIONS:
this._zero.connect(this._a2g);
this.pan.chain(this._a2g, this._crossFade.fade);
//left channel is a, right channel is b
this._splitter.connect(this._crossFade, 0, 0);
this._splitter.connect(this._crossFade, 1, 1);
//merge it back together
this._crossFade.a.connect(this._merger, 0, 0);
this._crossFade.b.connect(this._merger, 0, 1);
}
//initial value
this.pan.value = this.defaultArg(initialPan, 0);
this._readOnly('pan');
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Panner);
/**
* indicates if the panner is using the new StereoPannerNode internally
* @type {boolean}
* @private
*/
Tone.Panner.prototype._hasStereoPanner = Tone.prototype.isFunction(Tone.context.createStereoPanner);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Panner} this
*/
Tone.Panner.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable('pan');
if (this._hasStereoPanner) {
this._panner.disconnect();
this._panner = null;
this.pan = null;
} else {
this._zero.dispose();
this._zero = null;
this._crossFade.dispose();
this._crossFade = null;
this._splitter.dispose();
this._splitter = null;
this._merger.dispose();
this._merger = null;
this.pan.dispose();
this.pan = null;
this._a2g.dispose();
this._a2g = null;
}
return this;
};
return Tone.Panner;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A spatialized panner node which supports equalpower or HRTF panning.
* Tries to normalize the API across various browsers. See Tone.Listener
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Number} positionX The initial x position.
* @param {Number} positionY The initial y position.
* @param {Number} positionZ The initial z position.
*/
Tone.Panner3D = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'positionX',
'positionY',
'positionZ'
], Tone.Panner3D.defaults);
/**
* The panner node
* @type {PannerNode}
* @private
*/
this._panner = this.input = this.output = this.context.createPanner();
//set some values
this._panner.panningModel = options.panningModel;
this._panner.maxDistance = options.maxDistance;
this._panner.distanceModel = options.distanceModel;
this._panner.coneOuterGain = options.coneOuterGain;
this._panner.coneOuterAngle = options.coneOuterAngle;
this._panner.coneInnerAngle = options.coneInnerAngle;
this._panner.refDistance = options.refDistance;
this._panner.rolloffFactor = options.rolloffFactor;
/**
* Holds the current orientation
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._orientation = [
options.orientationX,
options.orientationY,
options.orientationZ
];
/**
* Holds the current position
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._position = [
options.positionX,
options.positionY,
options.positionZ
];
// set the default position/orientation
this.orientationX = options.orientationX;
this.orientationY = options.orientationY;
this.orientationZ = options.orientationZ;
this.positionX = options.positionX;
this.positionY = options.positionY;
this.positionZ = options.positionZ;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Panner3D);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
* Defaults according to the specification
*/
Tone.Panner3D.defaults = {
'positionX': 0,
'positionY': 0,
'positionZ': 0,
'orientationX': 0,
'orientationY': 0,
'orientationZ': 0,
'panningModel': 'equalpower',
'maxDistance': 10000,
'distanceModel': 'inverse',
'coneOuterGain': 0,
'coneOuterAngle': 360,
'coneInnerAngle': 360,
'refDistance': 1,
'rolloffFactor': 1
};
/**
* The ramp time which is applied to the setTargetAtTime
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Panner3D.prototype._rampTimeConstant = 0.01;
/**
* Sets the position of the source in 3d space.
* @param {Number} x
* @param {Number} y
* @param {Number} z
* @return {Tone.Panner3D} this
*/
Tone.Panner3D.prototype.setPosition = function (x, y, z) {
if (this._panner.positionX) {
var now = this.now();
this._panner.positionX.setTargetAtTime(x, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._panner.positionY.setTargetAtTime(y, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._panner.positionZ.setTargetAtTime(z, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
} else {
this._panner.setPosition(x, y, z);
}
this._position = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
return this;
};
/**
* Sets the orientation of the source in 3d space.
* @param {Number} x
* @param {Number} y
* @param {Number} z
* @return {Tone.Panner3D} this
*/
Tone.Panner3D.prototype.setOrientation = function (x, y, z) {
if (this._panner.orientationX) {
var now = this.now();
this._panner.orientationX.setTargetAtTime(x, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._panner.orientationY.setTargetAtTime(y, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._panner.orientationZ.setTargetAtTime(z, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
} else {
this._panner.setOrientation(x, y, z);
}
this._orientation = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
return this;
};
/**
* The x position of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name positionX
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, 'positionX', {
set: function (pos) {
this._position[0] = pos;
this.setPosition.apply(this, this._position);
},
get: function () {
return this._position[0];
}
});
/**
* The y position of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name positionY
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, 'positionY', {
set: function (pos) {
this._position[1] = pos;
this.setPosition.apply(this, this._position);
},
get: function () {
return this._position[1];
}
});
/**
* The z position of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name positionZ
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, 'positionZ', {
set: function (pos) {
this._position[2] = pos;
this.setPosition.apply(this, this._position);
},
get: function () {
return this._position[2];
}
});
/**
* The x orientation of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name orientationX
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, 'orientationX', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[0] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[0];
}
});
/**
* The y orientation of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name orientationY
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, 'orientationY', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[1] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[1];
}
});
/**
* The z orientation of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name orientationZ
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, 'orientationZ', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[2] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[2];
}
});
/**
* Proxy a property on the panner to an exposed public propery
* @param {String} prop
* @private
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty = function (prop) {
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Panner3D.prototype, prop, {
set: function (val) {
this._panner[prop] = val;
},
get: function () {
return this._panner[prop];
}
});
};
/**
* The panning model. Either "equalpower" or "HRTF".
* @type {String}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name panningModel
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('panningModel');
/**
* A reference distance for reducing volume as source move further from the listener
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name refDistance
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('refDistance');
/**
* Describes how quickly the volume is reduced as source moves away from listener.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name rolloffFactor
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('rolloffFactor');
/**
* The distance model used by, "linear", "inverse", or "exponential".
* @type {String}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name distanceModel
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('distanceModel');
/**
* The angle, in degrees, inside of which there will be no volume reduction
* @type {Degrees}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name coneInnerAngle
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('coneInnerAngle');
/**
* The angle, in degrees, outside of which the volume will be reduced
* to a constant value of coneOuterGain
* @type {Degrees}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name coneOuterAngle
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('coneOuterAngle');
/**
* The gain outside of the coneOuterAngle
* @type {Gain}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name coneOuterGain
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('coneOuterGain');
/**
* The maximum distance between source and listener,
* after which the volume will not be reduced any further.
* @type {Positive}
* @memberOf Tone.Panner3D#
* @name maxDistance
*/
Tone.Panner3D._aliasProperty('maxDistance');
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Panner3D} this
*/
Tone.Panner3D.prototype.dispose = function () {
this._panner.disconnect();
this._panner = null;
this._orientation = null;
this._position = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Panner3D;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PanVol is a Tone.Panner and Tone.Volume in one.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @constructor
* @param {AudioRange} pan the initial pan
* @param {number} volume The output volume.
* @example
* //pan the incoming signal left and drop the volume
* var panVol = new Tone.PanVol(0.25, -12);
*/
Tone.PanVol = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'pan',
'volume'
], Tone.PanVol.defaults);
/**
* The panning node
* @type {Tone.Panner}
* @private
*/
this._panner = this.input = new Tone.Panner(options.pan);
/**
* The L/R panning control.
* @type {AudioRange}
* @signal
*/
this.pan = this._panner.pan;
/**
* The volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume control in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
//connections
this._panner.connect(this._volume);
this._readOnly([
'pan',
'volume'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PanVol);
/**
* The defaults
* @type {Object}
* @const
* @static
*/
Tone.PanVol.defaults = {
'pan': 0.5,
'volume': 0
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.PanVol} this
*/
Tone.PanVol.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'pan',
'volume'
]);
this._panner.dispose();
this._panner = null;
this.pan = null;
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this.volume = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PanVol;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.CtrlInterpolate will interpolate between given values based
* on the "index" property. Passing in an array or object literal
* will interpolate each of the parameters. Note (i.e. "C3")
* and Time (i.e. "4n + 2") can be interpolated. All other values are
* assumed to be numbers.
* @example
* var interp = new Tone.CtrlInterpolate([0, 2, 9, 4]);
* interp.index = 0.75;
* interp.value; //returns 1.5
*
* @example
* var interp = new Tone.CtrlInterpolate([
* [2, 4, 5],
* [9, 3, 2],
* ]);
* @param {Array} values The array of values to interpolate over
* @param {Positive} index The initial interpolation index.
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.CtrlInterpolate = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'values',
'index'
], Tone.CtrlInterpolate.defaults);
/**
* The values to interpolate between
* @type {Array}
*/
this.values = options.values;
/**
* The interpolated index between values. For example: a value of 1.5
* would interpolate equally between the value at index 1
* and the value at index 2.
* @example
* interp.index = 0;
* interp.value; //returns the value at 0
* interp.index = 0.5;
* interp.value; //returns the value between indices 0 and 1.
* @type {Positive}
*/
this.index = options.index;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.CtrlInterpolate);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.CtrlInterpolate.defaults = {
'index': 0,
'values': []
};
/**
* The current interpolated value based on the index
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.CtrlInterpolate#
* @type {*}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.CtrlInterpolate.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
var index = this.index;
index = Math.min(index, this.values.length - 1);
var lowerPosition = Math.floor(index);
var lower = this.values[lowerPosition];
var upper = this.values[Math.ceil(index)];
return this._interpolate(index - lowerPosition, lower, upper);
}
});
/**
* Internal interpolation routine
* @param {NormalRange} index The index between the lower and upper
* @param {*} lower
* @param {*} upper
* @return {*} The interpolated value
* @private
*/
Tone.CtrlInterpolate.prototype._interpolate = function (index, lower, upper) {
if (this.isArray(lower)) {
var retArray = [];
for (var i = 0; i < lower.length; i++) {
retArray[i] = this._interpolate(index, lower[i], upper[i]);
}
return retArray;
} else if (this.isObject(lower)) {
var retObj = {};
for (var attr in lower) {
retObj[attr] = this._interpolate(index, lower[attr], upper[attr]);
}
return retObj;
} else {
lower = this._toNumber(lower);
upper = this._toNumber(upper);
return (1 - index) * lower + index * upper;
}
};
/**
* Convert from the given type into a number
* @param {Number|String} value
* @return {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.CtrlInterpolate.prototype._toNumber = function (val) {
if (this.isNumber(val)) {
return val;
} else {
//otherwise assume that it's Time...
return this.toSeconds(val);
}
};
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.CtrlInterpolate} this
*/
Tone.CtrlInterpolate.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.values = null;
};
return Tone.CtrlInterpolate;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.CtrlMarkov represents a Markov Chain where each call
* to Tone.CtrlMarkov.next will move to the next state. If the next
* state choice is an array, the next state is chosen randomly with
* even probability for all of the choices. For a weighted probability
* of the next choices, pass in an object with "state" and "probability" attributes.
* The probabilities will be normalized and then chosen. If no next options
* are given for the current state, the state will stay there.
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* var chain = new Tone.CtrlMarkov({
* "beginning" : ["end", "middle"],
* "middle" : "end"
* });
* chain.value = "beginning";
* chain.next(); //returns "end" or "middle" with 50% probability
*
* @example
* var chain = new Tone.CtrlMarkov({
* "beginning" : [{"value" : "end", "probability" : 0.8},
* {"value" : "middle", "probability" : 0.2}],
* "middle" : "end"
* });
* chain.value = "beginning";
* chain.next(); //returns "end" with 80% probability or "middle" with 20%.
* @param {Object} values An object with the state names as the keys
* and the next state(s) as the values.
*/
Tone.CtrlMarkov = function (values, initial) {
/**
* The Markov values with states as the keys
* and next state(s) as the values.
* @type {Object}
*/
this.values = this.defaultArg(values, {});
/**
* The current state of the Markov values. The next
* state will be evaluated and returned when Tone.CtrlMarkov.next
* is invoked.
* @type {String}
*/
this.value = this.defaultArg(initial, Object.keys(this.values)[0]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.CtrlMarkov);
/**
* Returns the next state of the Markov values.
* @return {String}
*/
Tone.CtrlMarkov.prototype.next = function () {
if (this.values.hasOwnProperty(this.value)) {
var next = this.values[this.value];
if (this.isArray(next)) {
var distribution = this._getProbDistribution(next);
var rand = Math.random();
var total = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < distribution.length; i++) {
var dist = distribution[i];
if (rand > total && rand < total + dist) {
var chosen = next[i];
if (this.isObject(chosen)) {
this.value = chosen.value;
} else {
this.value = chosen;
}
}
total += dist;
}
} else {
this.value = next;
}
}
return this.value;
};
/**
* Choose randomly from an array weighted options in the form
* {"state" : string, "probability" : number} or an array of values
* @param {Array} options
* @return {Array} The randomly selected choice
* @private
*/
Tone.CtrlMarkov.prototype._getProbDistribution = function (options) {
var distribution = [];
var total = 0;
var needsNormalizing = false;
for (var i = 0; i < options.length; i++) {
var option = options[i];
if (this.isObject(option)) {
needsNormalizing = true;
distribution[i] = option.probability;
} else {
distribution[i] = 1 / options.length;
}
total += distribution[i];
}
if (needsNormalizing) {
//normalize the values
for (var j = 0; j < distribution.length; j++) {
distribution[j] = distribution[j] / total;
}
}
return distribution;
};
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.CtrlMarkov} this
*/
Tone.CtrlMarkov.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.values = null;
};
return Tone.CtrlMarkov;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Generate patterns from an array of values.
* Has a number of arpeggiation and randomized
* selection patterns.
*
* - "up" - cycles upward
* - "down" - cycles downward
* - "upDown" - up then and down
* - "downUp" - cycles down then and up
* - "alternateUp" - jump up two and down one
* - "alternateDown" - jump down two and up one
* - "random" - randomly select an index
* - "randomWalk" - randomly moves one index away from the current position
* - "randomOnce" - randomly select an index without repeating until all values have been chosen.
*
* @param {Array} values An array of options to choose from.
* @param {Tone.CtrlPattern.Type=} type The name of the pattern.
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.CtrlPattern = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'values',
'type'
], Tone.CtrlPattern.defaults);
/**
* The array of values to arpeggiate over
* @type {Array}
*/
this.values = options.values;
/**
* The current position in the values array
* @type {Number}
*/
this.index = 0;
/**
* The type placeholder
* @type {Tone.CtrlPattern.Type}
* @private
*/
this._type = null;
/**
* Shuffled values for the RandomOnce type
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._shuffled = null;
/**
* The direction of the movement
* @type {String}
* @private
*/
this._direction = null;
this.type = options.type;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.CtrlPattern);
/**
* The Control Patterns
* @type {Object}
* @static
*/
Tone.CtrlPattern.Type = {
Up: 'up',
Down: 'down',
UpDown: 'upDown',
DownUp: 'downUp',
AlternateUp: 'alternateUp',
AlternateDown: 'alternateDown',
Random: 'random',
RandomWalk: 'randomWalk',
RandomOnce: 'randomOnce'
};
/**
* The default values.
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.CtrlPattern.defaults = {
'type': Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up,
'values': []
};
/**
* The value at the current index of the pattern.
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.CtrlPattern#
* @type {*}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.CtrlPattern.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
//some safeguards
if (this.values.length === 0) {
return;
} else if (this.values.length === 1) {
return this.values[0];
}
this.index = Math.min(this.index, this.values.length - 1);
var val = this.values[this.index];
if (this.type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.RandomOnce) {
if (this.values.length !== this._shuffled.length) {
this._shuffleValues();
}
val = this.values[this._shuffled[this.index]];
}
return val;
}
});
/**
* The pattern used to select the next
* item from the values array
* @memberOf Tone.CtrlPattern#
* @type {Tone.CtrlPattern.Type}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.CtrlPattern.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._type = type;
this._shuffled = null;
//the first index
if (this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.UpDown || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.RandomOnce || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.AlternateUp) {
this.index = 0;
} else if (this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.DownUp || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.AlternateDown) {
this.index = this.values.length - 1;
}
//the direction
if (this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.UpDown || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.AlternateUp) {
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up;
} else if (this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.DownUp || this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.AlternateDown) {
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down;
}
//randoms
if (this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.RandomOnce) {
this._shuffleValues();
} else if (this._type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Random) {
this.index = Math.floor(Math.random() * this.values.length);
}
}
});
/**
* Return the next value given the current position
* and pattern.
* @return {*} The next value
*/
Tone.CtrlPattern.prototype.next = function () {
var type = this.type;
//choose the next index
if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up) {
this.index++;
if (this.index >= this.values.length) {
this.index = 0;
}
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down) {
this.index--;
if (this.index < 0) {
this.index = this.values.length - 1;
}
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.UpDown || type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.DownUp) {
if (this._direction === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up) {
this.index++;
} else {
this.index--;
}
if (this.index < 0) {
this.index = 1;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up;
} else if (this.index >= this.values.length) {
this.index = this.values.length - 2;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down;
}
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Random) {
this.index = Math.floor(Math.random() * this.values.length);
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.RandomWalk) {
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
this.index--;
this.index = Math.max(this.index, 0);
} else {
this.index++;
this.index = Math.min(this.index, this.values.length - 1);
}
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.RandomOnce) {
this.index++;
if (this.index >= this.values.length) {
this.index = 0;
//reshuffle the values for next time
this._shuffleValues();
}
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.AlternateUp) {
if (this._direction === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up) {
this.index += 2;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down;
} else {
this.index -= 1;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up;
}
if (this.index >= this.values.length) {
this.index = 0;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up;
}
} else if (type === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.AlternateDown) {
if (this._direction === Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up) {
this.index += 1;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down;
} else {
this.index -= 2;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up;
}
if (this.index < 0) {
this.index = this.values.length - 1;
this._direction = Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Down;
}
}
return this.value;
};
/**
* Shuffles the values and places the results into the _shuffled
* @private
*/
Tone.CtrlPattern.prototype._shuffleValues = function () {
var copy = [];
this._shuffled = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.values.length; i++) {
copy[i] = i;
}
while (copy.length > 0) {
var randVal = copy.splice(Math.floor(copy.length * Math.random()), 1);
this._shuffled.push(randVal[0]);
}
};
/**
* Clean up
* @returns {Tone.CtrlPattern} this
*/
Tone.CtrlPattern.prototype.dispose = function () {
this._shuffled = null;
this.values = null;
};
return Tone.CtrlPattern;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Choose a random value.
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* var randomWalk = new Tone.CtrlRandom({
* "min" : 0,
* "max" : 10,
* "integer" : true
* });
* randomWalk.eval();
*
* @param {Number|Time=} min The minimum return value.
* @param {Number|Time=} max The maximum return value.
*/
Tone.CtrlRandom = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'min',
'max'
], Tone.CtrlRandom.defaults);
/**
* The minimum return value
* @type {Number|Time}
*/
this.min = options.min;
/**
* The maximum return value
* @type {Number|Time}
*/
this.max = options.max;
/**
* If the return value should be an integer
* @type {Boolean}
*/
this.integer = options.integer;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.CtrlRandom);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.CtrlRandom.defaults = {
'min': 0,
'max': 1,
'integer': false
};
/**
* Return a random value between min and max.
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.CtrlRandom#
* @type {*}
* @name value
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.CtrlRandom.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
var min = this.toSeconds(this.min);
var max = this.toSeconds(this.max);
var rand = Math.random();
var val = rand * min + (1 - rand) * max;
if (this.integer) {
val = Math.floor(val);
}
return val;
}
});
return Tone.CtrlRandom;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Buffer loading and storage. Tone.Buffer is used internally by all
* classes that make requests for audio files such as Tone.Player,
* Tone.Sampler and Tone.Convolver.
*
* Aside from load callbacks from individual buffers, Tone.Buffer
* provides static methods which keep track of the loading progress
* of all of the buffers. These methods are Tone.Buffer.on("load" / "progress" / "error")
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {AudioBuffer|string} url The url to load, or the audio buffer to set.
* @param {Function=} onload A callback which is invoked after the buffer is loaded.
* It's recommended to use Tone.Buffer.onload instead
* since it will give you a callback when ALL buffers are loaded.
* @param {Function=} onerror The callback to invoke if there is an error
* @example
* var buffer = new Tone.Buffer("path/to/sound.mp3", function(){
* //the buffer is now available.
* var buff = buffer.get();
* });
*/
Tone.Buffer = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload',
'onerror'
], Tone.Buffer.defaults);
/**
* stores the loaded AudioBuffer
* @type {AudioBuffer}
* @private
*/
this._buffer = null;
/**
* indicates if the buffer should be reversed or not
* @type {Boolean}
* @private
*/
this._reversed = options.reverse;
/**
* The XHR
* @type {XMLHttpRequest}
* @private
*/
this._xhr = null;
if (options.url instanceof AudioBuffer || options.url instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
this.set(options.url);
// invoke the onload callback
if (options.onload) {
options.onload(this);
}
} else if (this.isString(options.url)) {
this.load(options.url, options.onload, options.onerror);
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Buffer);
/**
* the default parameters
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Buffer.defaults = {
'url': undefined,
'reverse': false
};
/**
* Pass in an AudioBuffer or Tone.Buffer to set the value
* of this buffer.
* @param {AudioBuffer|Tone.Buffer} buffer the buffer
* @returns {Tone.Buffer} this
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.set = function (buffer) {
if (buffer instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
this._buffer = buffer.get();
} else {
this._buffer = buffer;
}
return this;
};
/**
* @return {AudioBuffer} The audio buffer stored in the object.
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.get = function () {
return this._buffer;
};
/**
* Makes an xhr reqest for the selected url then decodes
* the file as an audio buffer. Invokes
* the callback once the audio buffer loads.
* @param {String} url The url of the buffer to load.
* filetype support depends on the
* browser.
* @returns {Promise} returns a Promise which resolves with the Tone.Buffer
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.load = function (url, onload, onerror) {
var promise = new Promise(function (load, error) {
this._xhr = Tone.Buffer.load(url, //success
function (buff) {
this._xhr = null;
this.set(buff);
load(this);
if (onload) {
onload(this);
}
}.bind(this), //error
function (err) {
this._xhr = null;
error(err);
if (onerror) {
onerror(err);
}
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
return promise;
};
/**
* dispose and disconnect
* @returns {Tone.Buffer} this
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Emitter.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._buffer = null;
if (this._xhr) {
Tone.Buffer._currentDownloads--;
this._xhr.abort();
this._xhr = null;
}
return this;
};
/**
* If the buffer is loaded or not
* @memberOf Tone.Buffer#
* @type {Boolean}
* @name loaded
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Buffer.prototype, 'loaded', {
get: function () {
return this.length > 0;
}
});
/**
* The duration of the buffer.
* @memberOf Tone.Buffer#
* @type {Number}
* @name duration
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Buffer.prototype, 'duration', {
get: function () {
if (this._buffer) {
return this._buffer.duration;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
/**
* The length of the buffer in samples
* @memberOf Tone.Buffer#
* @type {Number}
* @name length
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Buffer.prototype, 'length', {
get: function () {
if (this._buffer) {
return this._buffer.length;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
/**
* The number of discrete audio channels. Returns 0 if no buffer
* is loaded.
* @memberOf Tone.Buffer#
* @type {Number}
* @name numberOfChannels
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Buffer.prototype, 'numberOfChannels', {
get: function () {
if (this._buffer) {
return this._buffer.numberOfChannels;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
/**
* Set the audio buffer from the array
* @param {Float32Array} array The array to fill the audio buffer
* @param {Number} [channels=1] The number of channels contained in the array.
* If the channel is more than 1, the input array
* is expected to be a multidimensional array
* with dimensions equal to the number of channels.
* @return {Tone.Buffer} this
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.fromArray = function (array) {
var isMultidimensional = array[0].length > 0;
var channels = isMultidimensional ? array.length : 1;
var len = isMultidimensional ? array[0].length : array.length;
var buffer = this.context.createBuffer(channels, len, this.context.sampleRate);
if (!isMultidimensional && channels === 1) {
array = [array];
}
for (var c = 0; c < channels; c++) {
if (this.isFunction(buffer.copyToChannel)) {
buffer.copyToChannel(array[c], c);
} else {
var channel = buffer.getChannelData(c);
var channelArray = array[c];
for (var i = 0; i < channelArray.length; i++) {
channel[i] = channelArray[i];
}
}
}
this._buffer = buffer;
return this;
};
/**
* Get the buffer as an array. Single channel buffers will return a 1-dimensional
* Float32Array, and multichannel buffers will return multidimensional arrays.
* @param {Number=} channel Optionally only copy a single channel from the array.
* @return {Array}
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.toArray = function (channel) {
if (this.isNumber(channel)) {
return this._buffer.getChannelData(channel);
} else {
var ret = [];
for (var c = 0; c < this.numberOfChannels; c++) {
ret[c] = new Float32Array(this.length);
if (this.isFunction(this._buffer.copyFromChannel)) {
this._buffer.copyFromChannel(ret[c], c);
} else {
var channelData = this._buffer.getChannelData(c);
var retArray = ret[c];
for (var i = 0; i < channelData.length; i++) {
retArray[i] = channelData[i];
}
}
}
if (ret.length === 1) {
return ret[0];
} else {
return ret;
}
}
};
/**
* Cut a subsection of the array and return a buffer of the
* subsection. Does not modify the original buffer
* @param {Time} start The time to start the slice
* @param {Time=} end The end time to slice. If none is given
* will default to the end of the buffer
* @return {Tone.Buffer} this
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype.slice = function (start, end) {
end = this.defaultArg(end, this.duration);
var startSamples = Math.floor(this.context.sampleRate * this.toSeconds(start));
var endSamples = Math.floor(this.context.sampleRate * this.toSeconds(end));
var replacement = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.numberOfChannels; i++) {
replacement[i] = this.toArray(i).slice(startSamples, endSamples);
}
var retBuffer = new Tone.Buffer().fromArray(replacement);
return retBuffer;
};
/**
* Reverse the buffer.
* @private
* @return {Tone.Buffer} this
*/
Tone.Buffer.prototype._reverse = function () {
if (this.loaded) {
for (var i = 0; i < this._buffer.numberOfChannels; i++) {
Array.prototype.reverse.call(this._buffer.getChannelData(i));
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Reverse the buffer.
* @memberOf Tone.Buffer#
* @type {Boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Buffer.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this._reversed;
},
set: function (rev) {
if (this._reversed !== rev) {
this._reversed = rev;
this._reverse();
}
}
});
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// STATIC METHODS
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//statically inherits Emitter methods
Tone.Emitter.mixin(Tone.Buffer);
/**
* the static queue for all of the xhr requests
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue = [];
/**
* the total number of downloads
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Buffer._currentDownloads = 0;
/**
* A path which is prefixed before every url.
* @type {String}
* @static
*/
Tone.Buffer.baseUrl = '';
/**
* Loads a url using XMLHttpRequest.
* @param {String} url
* @param {Function} onload
* @param {Function} onerror
* @param {Function} onprogress
* @return {XMLHttpRequest}
*/
Tone.Buffer.load = function (url, onload, onerror) {
//default
onload = onload || Tone.noOp;
function onError(e) {
if (onerror) {
onerror(e);
} else {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
function onProgress() {
//calculate the progress
var totalProgress = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue.length; i++) {
totalProgress += Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue[i].progress;
}
Tone.Buffer.emit('progress', totalProgress / Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue.length);
}
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open('GET', Tone.Buffer.baseUrl + url, true);
request.responseType = 'arraybuffer';
//start out as 0
request.progress = 0;
Tone.Buffer._currentDownloads++;
Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue.push(request);
request.addEventListener('load', function () {
if (request.status === 200) {
Tone.context.decodeAudioData(request.response, function (buff) {
request.progress = 1;
onProgress();
onload(buff);
Tone.Buffer._currentDownloads--;
if (Tone.Buffer._currentDownloads === 0) {
// clear the downloads
Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue = [];
//emit the event at the end
Tone.Buffer.emit('load');
}
}, function () {
onError('Tone.Buffer: could not decode audio data: ' + url);
});
} else {
onError('Tone.Buffer: could not locate file: ' + url);
}
});
request.addEventListener('error', onError);
request.addEventListener('progress', function (event) {
if (event.lengthComputable) {
//only go to 95%, the last 5% is when the audio is decoded
request.progress = event.loaded / event.total * 0.95;
onProgress();
}
});
request.send();
return request;
};
/**
* Stop all of the downloads in progress
* @return {Tone.Buffer}
*/
Tone.Buffer.stopDownloads = function () {
Tone.Buffer._downloadQueue.forEach(function (request) {
request.abort();
});
Tone.Buffer._currentDownloads = 0;
return Tone.Buffer;
};
/**
* Checks a url's extension to see if the current browser can play that file type.
* @param {String} url The url/extension to test
* @return {Boolean} If the file extension can be played
* @static
* @example
* Tone.Buffer.supportsType("wav"); //returns true
* Tone.Buffer.supportsType("path/to/file.wav"); //returns true
*/
Tone.Buffer.supportsType = function (url) {
var extension = url.split('.');
extension = extension[extension.length - 1];
var response = document.createElement('audio').canPlayType('audio/' + extension);
return response !== '';
};
return Tone.Buffer;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A data structure for holding multiple buffers.
*
* @param {Object|Array} urls An object literal or array
* of urls to load.
* @param {Function=} callback The callback to invoke when
* the buffers are loaded.
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* //load a whole bank of piano samples
* var pianoSamples = new Tone.Buffers({
* "C4" : "path/to/C4.mp3"
* "C#4" : "path/to/C#4.mp3"
* "D4" : "path/to/D4.mp3"
* "D#4" : "path/to/D#4.mp3"
* ...
* }, function(){
* //play one of the samples when they all load
* player.buffer = pianoSamples.get("C4");
* player.start();
* });
*
*/
Tone.Buffers = function (urls, onload, baseUrl) {
/**
* All of the buffers
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
this._buffers = {};
/**
* A path which is prefixed before every url.
* @type {String}
*/
this.baseUrl = this.defaultArg(baseUrl, '');
urls = this._flattenUrls(urls);
this._loadingCount = 0;
//add each one
for (var key in urls) {
this._loadingCount++;
this.add(key, urls[key], this._bufferLoaded.bind(this, onload));
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Buffers);
/**
* True if the buffers object has a buffer by that name.
* @param {String|Number} name The key or index of the
* buffer.
* @return {Boolean}
*/
Tone.Buffers.prototype.has = function (name) {
return this._buffers.hasOwnProperty(name);
};
/**
* Get a buffer by name. If an array was loaded,
* then use the array index.
* @param {String|Number} name The key or index of the
* buffer.
* @return {Tone.Buffer}
*/
Tone.Buffers.prototype.get = function (name) {
if (this.has(name)) {
return this._buffers[name];
} else {
throw new Error('Tone.Buffers: no buffer named ' + name);
}
};
/**
* A buffer was loaded. decrement the counter.
* @param {Function} callback
* @private
*/
Tone.Buffers.prototype._bufferLoaded = function (callback) {
this._loadingCount--;
if (this._loadingCount === 0 && callback) {
callback(this);
}
};
/**
* If the buffers are loaded or not
* @memberOf Tone.Buffers#
* @type {Boolean}
* @name loaded
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Buffers.prototype, 'loaded', {
get: function () {
var isLoaded = true;
for (var buffName in this._buffers) {
var buff = this.get(buffName);
isLoaded = isLoaded && buff.loaded;
}
return isLoaded;
}
});
/**
* Add a buffer by name and url to the Buffers
* @param {String} name A unique name to give
* the buffer
* @param {String|Tone.Buffer|Audiobuffer} url Either the url of the bufer,
* or a buffer which will be added
* with the given name.
* @param {Function=} callback The callback to invoke
* when the url is loaded.
*/
Tone.Buffers.prototype.add = function (name, url, callback) {
callback = this.defaultArg(callback, Tone.noOp);
if (url instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
this._buffers[name] = url;
callback(this);
} else if (url instanceof AudioBuffer) {
this._buffers[name] = new Tone.Buffer(url);
callback(this);
} else if (this.isString(url)) {
this._buffers[name] = new Tone.Buffer(this.baseUrl + url, callback);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Flatten an object into a single depth object.
* thanks to https://gist.github.com/penguinboy/762197
* @param {Object} ob
* @return {Object}
* @private
*/
Tone.Buffers.prototype._flattenUrls = function (ob) {
var toReturn = {};
for (var i in ob) {
if (!ob.hasOwnProperty(i))
continue;
if (this.isObject(ob[i])) {
var flatObject = this._flattenUrls(ob[i]);
for (var x in flatObject) {
if (!flatObject.hasOwnProperty(x))
continue;
toReturn[i + '.' + x] = flatObject[x];
}
} else {
toReturn[i] = ob[i];
}
}
return toReturn;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Buffers} this
*/
Tone.Buffers.prototype.dispose = function () {
for (var name in this._buffers) {
this._buffers[name].dispose();
}
this._buffers = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Buffers;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* buses are another way of routing audio
*
* augments Tone.prototype to include send and recieve
*/
/**
* All of the routes
*
* @type {Object}
* @static
* @private
*/
var Buses = {};
/**
* Send this signal to the channel name.
* @param {string} channelName A named channel to send the signal to.
* @param {Decibels} amount The amount of the source to send to the bus.
* @return {GainNode} The gain node which connects this node to the desired channel.
* Can be used to adjust the levels of the send.
* @example
* source.send("reverb", -12);
*/
Tone.prototype.send = function (channelName, amount) {
if (!Buses.hasOwnProperty(channelName)) {
Buses[channelName] = this.context.createGain();
}
amount = this.defaultArg(amount, 0);
var sendKnob = new Tone.Gain(amount, Tone.Type.Decibels);
this.output.chain(sendKnob, Buses[channelName]);
return sendKnob;
};
/**
* Recieve the input from the desired channelName to the input
*
* @param {string} channelName A named channel to send the signal to.
* @param {AudioNode} [input] If no input is selected, the
* input of the current node is
* chosen.
* @returns {Tone} this
* @example
* reverbEffect.receive("reverb");
*/
Tone.prototype.receive = function (channelName, input) {
if (!Buses.hasOwnProperty(channelName)) {
Buses[channelName] = this.context.createGain();
}
if (this.isUndef(input)) {
input = this.input;
}
Buses[channelName].connect(input);
return this;
};
//remove all the send/receives when a new audio context is passed in
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
Buses = {};
});
return Tone;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Draw is useful for synchronizing visuals and audio events.
* Callbacks from Tone.Transport or any of the Tone.Event classes
* always happen _before_ the scheduled time and are not synchronized
* to the animation frame so they are not good for triggering tightly
* synchronized visuals and sound. Tone.Draw makes it easy to schedule
* callbacks using the AudioContext time and uses requestAnimationFrame.
*
* @singleton
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* Tone.Transport.schedule(function(time){
* //use the time argument to schedule a callback with Tone.Draw
* Tone.Draw.schedule(function(){
* //do drawing or DOM manipulation here
* }, time)
* }, "+0.5")
*/
Tone.Draw = function () {
/**
* All of the events.
* @type {Tone.Timeline}
* @private
*/
this._events = new Tone.Timeline();
/**
* The duration after which events are not invoked.
* @type {Number}
* @default 0.25
*/
this.expiration = 0.25;
/**
* The amount of time before the scheduled time
* that the callback can be invoked. Default is
* half the time of an animation frame (0.008 seconds).
* @type {Number}
* @default 0.008
*/
this.anticipation = 0.008;
/**
* The draw loop
* @type {Function}
* @private
*/
this._boundDrawLoop = this._drawLoop.bind(this);
//start the loop
this._drawLoop();
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Draw);
/**
* Schedule a function at the given time to be invoked
* on the nearest animation frame.
* @param {Function} callback Callback is invoked at the given time.
* @param {Time} time The time relative to the AudioContext time
* to invoke the callback.
* @return {Tone.Draw} this
*/
Tone.Draw.prototype.schedule = function (callback, time) {
this._events.add({
callback: callback,
time: this.toSeconds(time)
});
return this;
};
/**
* Cancel events scheduled after the given time
* @param {Time=} after Time after which scheduled events will
* be removed from the scheduling timeline.
* @return {Tone.Draw} this
*/
Tone.Draw.prototype.cancel = function (after) {
this._events.cancel(this.toSeconds(after));
return this;
};
/**
* The draw loop
* @private
*/
Tone.Draw.prototype._drawLoop = function () {
requestAnimationFrame(this._boundDrawLoop);
var now = Tone.now();
while (this._events.length && this._events.peek().time - this.anticipation <= now) {
var event = this._events.shift();
if (now - event.time <= this.expiration) {
event.callback();
}
}
};
//make a singleton
Tone.Draw = new Tone.Draw();
return Tone.Draw;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Both Tone.Panner3D and Tone.Listener have a position in 3D space
* using a right-handed cartesian coordinate system.
* The units used in the coordinate system are not defined;
* these coordinates are independent/invariant of any particular
* units such as meters or feet. Tone.Panner3D objects have an forward
* vector representing the direction the sound is projecting. Additionally,
* they have a sound cone representing how directional the sound is.
* For example, the sound could be omnidirectional, in which case it would
* be heard anywhere regardless of its forward, or it can be more directional
* and heard only if it is facing the listener. Tone.Listener objects
* (representing a person's ears) have an forward and up vector
* representing in which direction the person is facing. Because both the
* source stream and the listener can be moving, they both have a velocity
* vector representing both the speed and direction of movement. Taken together,
* these two velocities can be used to generate a doppler shift effect which changes the pitch.
*
* Note: the position of the Listener will have no effect on nodes not connected to a Tone.Panner3D
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @singleton
* @param {Number} positionX The initial x position.
* @param {Number} positionY The initial y position.
* @param {Number} positionZ The initial z position.
*/
Tone.Listener = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'positionX',
'positionY',
'positionZ'
], ListenerConstructor.defaults);
/**
* The listener node
* @type {AudioListener}
* @private
*/
this._listener = this.context.listener;
/**
* Holds the current forward orientation
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._orientation = [
options.forwardX,
options.forwardY,
options.forwardZ,
options.upX,
options.upY,
options.upZ
];
/**
* Holds the current position
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._position = [
options.positionX,
options.positionY,
options.positionZ
];
// set the default position/forward
this.forwardX = options.forwardX;
this.forwardY = options.forwardY;
this.forwardZ = options.forwardZ;
this.upX = options.upX;
this.upY = options.upY;
this.upZ = options.upZ;
this.positionX = options.positionX;
this.positionY = options.positionY;
this.positionZ = options.positionZ;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Listener);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
* Defaults according to the specification
*/
Tone.Listener.defaults = {
'positionX': 0,
'positionY': 0,
'positionZ': 0,
'forwardX': 0,
'forwardY': 0,
'forwardZ': 1,
'upX': 0,
'upY': 1,
'upZ': 0
};
/**
* The ramp time which is applied to the setTargetAtTime
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
Tone.Listener.prototype._rampTimeConstant = 0.01;
/**
* Sets the position of the listener in 3d space.
* @param {Number} x
* @param {Number} y
* @param {Number} z
* @return {Tone.Listener} this
*/
Tone.Listener.prototype.setPosition = function (x, y, z) {
if (this._listener.positionX) {
var now = this.now();
this._listener.positionX.setTargetAtTime(x, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.positionY.setTargetAtTime(y, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.positionZ.setTargetAtTime(z, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
} else {
this._listener.setPosition(x, y, z);
}
this._position = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
return this;
};
/**
* Sets the orientation of the listener using two vectors, the forward
* vector (which direction the listener is facing) and the up vector
* (which the up direction of the listener). An up vector
* of 0, 0, 1 is equivalent to the listener standing up in the Z direction.
* @param {Number} x
* @param {Number} y
* @param {Number} z
* @param {Number} upX
* @param {Number} upY
* @param {Number} upZ
* @return {Tone.Listener} this
*/
Tone.Listener.prototype.setOrientation = function (x, y, z, upX, upY, upZ) {
if (this._listener.forwardX) {
var now = this.now();
this._listener.forwardX.setTargetAtTime(x, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.forwardY.setTargetAtTime(y, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.forwardZ.setTargetAtTime(z, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.upX.setTargetAtTime(upX, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.upY.setTargetAtTime(upY, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
this._listener.upZ.setTargetAtTime(upZ, now, this._rampTimeConstant);
} else {
this._listener.setOrientation(x, y, z, upX, upY, upZ);
}
this._orientation = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
return this;
};
/**
* The x position of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name positionX
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'positionX', {
set: function (pos) {
this._position[0] = pos;
this.setPosition.apply(this, this._position);
},
get: function () {
return this._position[0];
}
});
/**
* The y position of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name positionY
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'positionY', {
set: function (pos) {
this._position[1] = pos;
this.setPosition.apply(this, this._position);
},
get: function () {
return this._position[1];
}
});
/**
* The z position of the panner object.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name positionZ
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'positionZ', {
set: function (pos) {
this._position[2] = pos;
this.setPosition.apply(this, this._position);
},
get: function () {
return this._position[2];
}
});
/**
* The x coordinate of the listeners front direction. i.e.
* which way they are facing.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name forwardX
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'forwardX', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[0] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[0];
}
});
/**
* The y coordinate of the listeners front direction. i.e.
* which way they are facing.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name forwardY
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'forwardY', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[1] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[1];
}
});
/**
* The z coordinate of the listeners front direction. i.e.
* which way they are facing.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name forwardZ
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'forwardZ', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[2] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[2];
}
});
/**
* The x coordinate of the listener's up direction. i.e.
* the direction the listener is standing in.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name upX
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'upX', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[3] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[3];
}
});
/**
* The y coordinate of the listener's up direction. i.e.
* the direction the listener is standing in.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name upY
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'upY', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[4] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[4];
}
});
/**
* The z coordinate of the listener's up direction. i.e.
* the direction the listener is standing in.
* @type {Number}
* @memberOf Tone.Listener#
* @name upZ
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Listener.prototype, 'upZ', {
set: function (pos) {
this._orientation[5] = pos;
this.setOrientation.apply(this, this._orientation);
},
get: function () {
return this._orientation[5];
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Listener} this
*/
Tone.Listener.prototype.dispose = function () {
this._listener.disconnect();
this._listener = null;
this._orientation = null;
this._position = null;
return this;
};
//SINGLETON SETUP
var ListenerConstructor = Tone.Listener;
Tone._initAudioContext(function () {
if (typeof Tone.Listener === 'function') {
//a single listener object
Tone.Listener = new Tone.Listener();
} else {
//make new Listener insides
ListenerConstructor.call(Tone.Listener);
}
});
//END SINGLETON SETUP
return Tone.Listener;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Effect is the base class for effects. Connect the effect between
* the effectSend and effectReturn GainNodes, then control the amount of
* effect which goes to the output using the wet control.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {NormalRange|Object} [wet] The starting wet value.
*/
Tone.Effect = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
//get all of the defaults
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['wet'], Tone.Effect.defaults);
/**
* the drywet knob to control the amount of effect
* @type {Tone.CrossFade}
* @private
*/
this._dryWet = new Tone.CrossFade(options.wet);
/**
* The wet control is how much of the effected
* will pass through to the output. 1 = 100% effected
* signal, 0 = 100% dry signal.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.wet = this._dryWet.fade;
/**
* connect the effectSend to the input of hte effect
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this.effectSend = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* connect the output of the effect to the effectReturn
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this.effectReturn = new Tone.Gain();
//connections
this.input.connect(this._dryWet.a);
this.input.connect(this.effectSend);
this.effectReturn.connect(this._dryWet.b);
this._dryWet.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly(['wet']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Effect);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Effect.defaults = { 'wet': 1 };
/**
* chains the effect in between the effectSend and effectReturn
* @param {Tone} effect
* @private
* @returns {Tone.Effect} this
*/
Tone.Effect.prototype.connectEffect = function (effect) {
this.effectSend.chain(effect, this.effectReturn);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Effect} this
*/
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._dryWet.dispose();
this._dryWet = null;
this.effectSend.dispose();
this.effectSend = null;
this.effectReturn.dispose();
this.effectReturn = null;
this._writable(['wet']);
this.wet = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Effect;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.AutoFilter is a Tone.Filter with a Tone.LFO connected to the filter cutoff frequency.
* Setting the LFO rate and depth allows for control over the filter modulation rate
* and depth.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {Time|Object} [frequency] The rate of the LFO.
* @param {Frequency=} baseFrequency The lower value of the LFOs oscillation
* @param {Frequency=} octaves The number of octaves above the baseFrequency
* @example
* //create an autofilter and start it's LFO
* var autoFilter = new Tone.AutoFilter("4n").toMaster().start();
* //route an oscillator through the filter and start it
* var oscillator = new Tone.Oscillator().connect(autoFilter).start();
*/
Tone.AutoFilter = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'baseFrequency',
'octaves'
], Tone.AutoFilter.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* the lfo which drives the filter cutoff
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfo = new Tone.LFO({
'frequency': options.frequency,
'amplitude': options.depth
});
/**
* The range of the filter modulating between the min and max frequency.
* 0 = no modulation. 1 = full modulation.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.depth = this._lfo.amplitude;
/**
* How fast the filter modulates between min and max.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._lfo.frequency;
/**
* The filter node
* @type {Tone.Filter}
*/
this.filter = new Tone.Filter(options.filter);
/**
* The octaves placeholder
* @type {Positive}
* @private
*/
this._octaves = 0;
//connections
this.connectEffect(this.filter);
this._lfo.connect(this.filter.frequency);
this.type = options.type;
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'depth'
]);
this.octaves = options.octaves;
this.baseFrequency = options.baseFrequency;
};
//extend Effect
Tone.extend(Tone.AutoFilter, Tone.Effect);
/**
* defaults
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.AutoFilter.defaults = {
'frequency': 1,
'type': 'sine',
'depth': 1,
'baseFrequency': 200,
'octaves': 2.6,
'filter': {
'type': 'lowpass',
'rolloff': -12,
'Q': 1
}
};
/**
* Start the effect.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the LFO will start.
* @returns {Tone.AutoFilter} this
*/
Tone.AutoFilter.prototype.start = function (time) {
this._lfo.start(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the effect.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the LFO will stop.
* @returns {Tone.AutoFilter} this
*/
Tone.AutoFilter.prototype.stop = function (time) {
this._lfo.stop(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Sync the filter to the transport.
* @param {Time} [delay=0] Delay time before starting the effect after the
* Transport has started.
* @returns {Tone.AutoFilter} this
*/
Tone.AutoFilter.prototype.sync = function (delay) {
this._lfo.sync(delay);
return this;
};
/**
* Unsync the filter from the transport.
* @returns {Tone.AutoFilter} this
*/
Tone.AutoFilter.prototype.unsync = function () {
this._lfo.unsync();
return this;
};
/**
* Type of oscillator attached to the AutoFilter.
* Possible values: "sine", "square", "triangle", "sawtooth".
* @memberOf Tone.AutoFilter#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoFilter.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._lfo.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._lfo.type = type;
}
});
/**
* The minimum value of the filter's cutoff frequency.
* @memberOf Tone.AutoFilter#
* @type {Frequency}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoFilter.prototype, 'baseFrequency', {
get: function () {
return this._lfo.min;
},
set: function (freq) {
this._lfo.min = this.toFrequency(freq);
//and set the max
this.octaves = this._octaves;
}
});
/**
* The maximum value of the filter's cutoff frequency.
* @memberOf Tone.AutoFilter#
* @type {Positive}
* @name octaves
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoFilter.prototype, 'octaves', {
get: function () {
return this._octaves;
},
set: function (oct) {
this._octaves = oct;
this._lfo.max = this.baseFrequency * Math.pow(2, oct);
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.AutoFilter} this
*/
Tone.AutoFilter.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._lfo.dispose();
this._lfo = null;
this.filter.dispose();
this.filter = null;
this._writable([
'frequency',
'depth'
]);
this.frequency = null;
this.depth = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AutoFilter;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.AutoPanner is a Tone.Panner with an LFO connected to the pan amount.
* More on using autopanners [here](https://www.ableton.com/en/blog/autopan-chopper-effect-and-more-liveschool/).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {Frequency|Object} [frequency] Rate of left-right oscillation.
* @example
* //create an autopanner and start it's LFO
* var autoPanner = new Tone.AutoPanner("4n").toMaster().start();
* //route an oscillator through the panner and start it
* var oscillator = new Tone.Oscillator().connect(autoPanner).start();
*/
Tone.AutoPanner = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['frequency'], Tone.AutoPanner.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* the lfo which drives the panning
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfo = new Tone.LFO({
'frequency': options.frequency,
'amplitude': options.depth,
'min': -1,
'max': 1
});
/**
* The amount of panning between left and right.
* 0 = always center. 1 = full range between left and right.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.depth = this._lfo.amplitude;
/**
* the panner node which does the panning
* @type {Tone.Panner}
* @private
*/
this._panner = new Tone.Panner();
/**
* How fast the panner modulates between left and right.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._lfo.frequency;
//connections
this.connectEffect(this._panner);
this._lfo.connect(this._panner.pan);
this.type = options.type;
this._readOnly([
'depth',
'frequency'
]);
};
//extend Effect
Tone.extend(Tone.AutoPanner, Tone.Effect);
/**
* defaults
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.AutoPanner.defaults = {
'frequency': 1,
'type': 'sine',
'depth': 1
};
/**
* Start the effect.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the LFO will start.
* @returns {Tone.AutoPanner} this
*/
Tone.AutoPanner.prototype.start = function (time) {
this._lfo.start(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the effect.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the LFO will stop.
* @returns {Tone.AutoPanner} this
*/
Tone.AutoPanner.prototype.stop = function (time) {
this._lfo.stop(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Sync the panner to the transport.
* @param {Time} [delay=0] Delay time before starting the effect after the
* Transport has started.
* @returns {Tone.AutoPanner} this
*/
Tone.AutoPanner.prototype.sync = function (delay) {
this._lfo.sync(delay);
return this;
};
/**
* Unsync the panner from the transport
* @returns {Tone.AutoPanner} this
*/
Tone.AutoPanner.prototype.unsync = function () {
this._lfo.unsync();
return this;
};
/**
* Type of oscillator attached to the AutoFilter.
* Possible values: "sine", "square", "triangle", "sawtooth".
* @memberOf Tone.AutoFilter#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoPanner.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._lfo.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._lfo.type = type;
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.AutoPanner} this
*/
Tone.AutoPanner.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._lfo.dispose();
this._lfo = null;
this._panner.dispose();
this._panner = null;
this._writable([
'depth',
'frequency'
]);
this.frequency = null;
this.depth = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AutoPanner;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.AutoWah connects a Tone.Follower to a bandpass filter (Tone.Filter).
* The frequency of the filter is adjusted proportionally to the
* incoming signal's amplitude. Inspiration from [Tuna.js](https://github.com/Dinahmoe/tuna).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {Frequency|Object} [baseFrequency] The frequency the filter is set
* to at the low point of the wah
* @param {Positive} [octaves] The number of octaves above the baseFrequency
* the filter will sweep to when fully open
* @param {Decibels} [sensitivity] The decibel threshold sensitivity for
* the incoming signal. Normal range of -40 to 0.
* @example
* var autoWah = new Tone.AutoWah(50, 6, -30).toMaster();
* //initialize the synth and connect to autowah
* var synth = new Synth.connect(autoWah);
* //Q value influences the effect of the wah - default is 2
* autoWah.Q.value = 6;
* //more audible on higher notes
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "8n")
*/
Tone.AutoWah = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'baseFrequency',
'octaves',
'sensitivity'
], Tone.AutoWah.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* The envelope follower. Set the attack/release
* timing to adjust how the envelope is followed.
* @type {Tone.Follower}
* @private
*/
this.follower = new Tone.Follower(options.follower);
/**
* scales the follower value to the frequency domain
* @type {Tone}
* @private
*/
this._sweepRange = new Tone.ScaleExp(0, 1, 0.5);
/**
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._baseFrequency = options.baseFrequency;
/**
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._octaves = options.octaves;
/**
* the input gain to adjust the sensitivity
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._inputBoost = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* @type {BiquadFilterNode}
* @private
*/
this._bandpass = new Tone.Filter({
'rolloff': -48,
'frequency': 0,
'Q': options.Q
});
/**
* @type {Tone.Filter}
* @private
*/
this._peaking = new Tone.Filter(0, 'peaking');
this._peaking.gain.value = options.gain;
/**
* The gain of the filter.
* @type {Number}
* @signal
*/
this.gain = this._peaking.gain;
/**
* The quality of the filter.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.Q = this._bandpass.Q;
//the control signal path
this.effectSend.chain(this._inputBoost, this.follower, this._sweepRange);
this._sweepRange.connect(this._bandpass.frequency);
this._sweepRange.connect(this._peaking.frequency);
//the filtered path
this.effectSend.chain(this._bandpass, this._peaking, this.effectReturn);
//set the initial value
this._setSweepRange();
this.sensitivity = options.sensitivity;
this._readOnly([
'gain',
'Q'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.AutoWah, Tone.Effect);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.AutoWah.defaults = {
'baseFrequency': 100,
'octaves': 6,
'sensitivity': 0,
'Q': 2,
'gain': 2,
'follower': {
'attack': 0.3,
'release': 0.5
}
};
/**
* The number of octaves that the filter will sweep above the
* baseFrequency.
* @memberOf Tone.AutoWah#
* @type {Number}
* @name octaves
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoWah.prototype, 'octaves', {
get: function () {
return this._octaves;
},
set: function (octaves) {
this._octaves = octaves;
this._setSweepRange();
}
});
/**
* The base frequency from which the sweep will start from.
* @memberOf Tone.AutoWah#
* @type {Frequency}
* @name baseFrequency
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoWah.prototype, 'baseFrequency', {
get: function () {
return this._baseFrequency;
},
set: function (baseFreq) {
this._baseFrequency = baseFreq;
this._setSweepRange();
}
});
/**
* The sensitivity to control how responsive to the input signal the filter is.
* @memberOf Tone.AutoWah#
* @type {Decibels}
* @name sensitivity
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AutoWah.prototype, 'sensitivity', {
get: function () {
return this.gainToDb(1 / this._inputBoost.gain.value);
},
set: function (sensitivy) {
this._inputBoost.gain.value = 1 / this.dbToGain(sensitivy);
}
});
/**
* sets the sweep range of the scaler
* @private
*/
Tone.AutoWah.prototype._setSweepRange = function () {
this._sweepRange.min = this._baseFrequency;
this._sweepRange.max = Math.min(this._baseFrequency * Math.pow(2, this._octaves), this.context.sampleRate / 2);
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.AutoWah} this
*/
Tone.AutoWah.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.follower.dispose();
this.follower = null;
this._sweepRange.dispose();
this._sweepRange = null;
this._bandpass.dispose();
this._bandpass = null;
this._peaking.dispose();
this._peaking = null;
this._inputBoost.dispose();
this._inputBoost = null;
this._writable([
'gain',
'Q'
]);
this.gain = null;
this.Q = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AutoWah;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Bitcrusher downsamples the incoming signal to a different bitdepth.
* Lowering the bitdepth of the signal creates distortion. Read more about Bitcrushing
* on [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bitcrusher).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {Number} bits The number of bits to downsample the signal. Nominal range
* of 1 to 8.
* @example
* //initialize crusher and route a synth through it
* var crusher = new Tone.BitCrusher(4).toMaster();
* var synth = new Tone.MonoSynth().connect(crusher);
*/
Tone.BitCrusher = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['bits'], Tone.BitCrusher.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
var invStepSize = 1 / Math.pow(2, options.bits - 1);
/**
* Subtract the input signal and the modulus of the input signal
* @type {Tone.Subtract}
* @private
*/
this._subtract = new Tone.Subtract();
/**
* The mod function
* @type {Tone.Modulo}
* @private
*/
this._modulo = new Tone.Modulo(invStepSize);
/**
* keeps track of the bits
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._bits = options.bits;
//connect it up
this.effectSend.fan(this._subtract, this._modulo);
this._modulo.connect(this._subtract, 0, 1);
this._subtract.connect(this.effectReturn);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.BitCrusher, Tone.Effect);
/**
* the default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.BitCrusher.defaults = { 'bits': 4 };
/**
* The bit depth of the effect. Nominal range of 1-8.
* @memberOf Tone.BitCrusher#
* @type {number}
* @name bits
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BitCrusher.prototype, 'bits', {
get: function () {
return this._bits;
},
set: function (bits) {
this._bits = bits;
var invStepSize = 1 / Math.pow(2, bits - 1);
this._modulo.value = invStepSize;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.BitCrusher} this
*/
Tone.BitCrusher.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._subtract.dispose();
this._subtract = null;
this._modulo.dispose();
this._modulo = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.BitCrusher;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.ChebyShev is a Chebyshev waveshaper, an effect which is good
* for making different types of distortion sounds.
* Note that odd orders sound very different from even ones,
* and order = 1 is no change.
* Read more at [music.columbia.edu](http://music.columbia.edu/cmc/musicandcomputers/chapter4/04_06.php).
*
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @constructor
* @param {Positive|Object} [order] The order of the chebyshev polynomial. Normal range between 1-100.
* @example
* //create a new cheby
* var cheby = new Tone.Chebyshev(50);
* //create a monosynth connected to our cheby
* synth = new Tone.MonoSynth().connect(cheby);
*/
Tone.Chebyshev = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['order'], Tone.Chebyshev.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._shaper = new Tone.WaveShaper(4096);
/**
* holds onto the order of the filter
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._order = options.order;
this.connectEffect(this._shaper);
this.order = options.order;
this.oversample = options.oversample;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Chebyshev, Tone.Effect);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Chebyshev.defaults = {
'order': 1,
'oversample': 'none'
};
/**
* get the coefficient for that degree
* @param {number} x the x value
* @param {number} degree
* @param {Object} memo memoize the computed value.
* this speeds up computation greatly.
* @return {number} the coefficient
* @private
*/
Tone.Chebyshev.prototype._getCoefficient = function (x, degree, memo) {
if (memo.hasOwnProperty(degree)) {
return memo[degree];
} else if (degree === 0) {
memo[degree] = 0;
} else if (degree === 1) {
memo[degree] = x;
} else {
memo[degree] = 2 * x * this._getCoefficient(x, degree - 1, memo) - this._getCoefficient(x, degree - 2, memo);
}
return memo[degree];
};
/**
* The order of the Chebyshev polynomial which creates
* the equation which is applied to the incoming
* signal through a Tone.WaveShaper. The equations
* are in the form:
* order 2: 2x^2 + 1
* order 3: 4x^3 + 3x
* @memberOf Tone.Chebyshev#
* @type {Positive}
* @name order
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Chebyshev.prototype, 'order', {
get: function () {
return this._order;
},
set: function (order) {
this._order = order;
var curve = new Array(4096);
var len = curve.length;
for (var i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
var x = i * 2 / len - 1;
if (x === 0) {
//should output 0 when input is 0
curve[i] = 0;
} else {
curve[i] = this._getCoefficient(x, order, {});
}
}
this._shaper.curve = curve;
}
});
/**
* The oversampling of the effect. Can either be "none", "2x" or "4x".
* @memberOf Tone.Chebyshev#
* @type {string}
* @name oversample
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Chebyshev.prototype, 'oversample', {
get: function () {
return this._shaper.oversample;
},
set: function (oversampling) {
this._shaper.oversample = oversampling;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Chebyshev} this
*/
Tone.Chebyshev.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._shaper.dispose();
this._shaper = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Chebyshev;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Base class for Stereo effects. Provides effectSendL/R and effectReturnL/R.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
*/
Tone.StereoEffect = function () {
this.createInsOuts(1, 1);
//get the defaults
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['wet'], Tone.Effect.defaults);
/**
* the drywet knob to control the amount of effect
* @type {Tone.CrossFade}
* @private
*/
this._dryWet = new Tone.CrossFade(options.wet);
/**
* The wet control, i.e. how much of the effected
* will pass through to the output.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.wet = this._dryWet.fade;
/**
* then split it
* @type {Tone.Split}
* @private
*/
this._split = new Tone.Split();
/**
* the effects send LEFT
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.effectSendL = this._split.left;
/**
* the effects send RIGHT
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.effectSendR = this._split.right;
/**
* the stereo effect merger
* @type {Tone.Merge}
* @private
*/
this._merge = new Tone.Merge();
/**
* the effect return LEFT
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.effectReturnL = this._merge.left;
/**
* the effect return RIGHT
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.effectReturnR = this._merge.right;
//connections
this.input.connect(this._split);
//dry wet connections
this.input.connect(this._dryWet, 0, 0);
this._merge.connect(this._dryWet, 0, 1);
this._dryWet.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly(['wet']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.StereoEffect, Tone.Effect);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.StereoEffect} this
*/
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._dryWet.dispose();
this._dryWet = null;
this._split.dispose();
this._split = null;
this._merge.dispose();
this._merge = null;
this.effectSendL = null;
this.effectSendR = null;
this.effectReturnL = null;
this.effectReturnR = null;
this._writable(['wet']);
this.wet = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.StereoEffect;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.FeedbackEffect provides a loop between an
* audio source and its own output. This is a base-class
* for feedback effects.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {NormalRange|Object} [feedback] The initial feedback value.
*/
Tone.FeedbackEffect = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['feedback']);
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.FeedbackEffect.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* the gain which controls the feedback
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackGain = new Tone.Gain(options.feedback, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* The amount of signal which is fed back into the effect input.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.feedback = this._feedbackGain.gain;
//the feedback loop
this.effectReturn.chain(this._feedbackGain, this.effectSend);
this._readOnly(['feedback']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FeedbackEffect, Tone.Effect);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.FeedbackEffect.defaults = { 'feedback': 0.125 };
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.FeedbackEffect} this
*/
Tone.FeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable(['feedback']);
this._feedbackGain.dispose();
this._feedbackGain = null;
this.feedback = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FeedbackEffect;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Just like a stereo feedback effect, but the feedback is routed from left to right
* and right to left instead of on the same channel.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.FeedbackEffect}
*/
Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['feedback'], Tone.FeedbackEffect.defaults);
Tone.StereoEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* The amount of feedback from the output
* back into the input of the effect (routed
* across left and right channels).
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.feedback = new Tone.Signal(options.feedback, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* the left side feeback
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackLR = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the right side feeback
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackRL = new Tone.Gain();
//connect it up
this.effectReturnL.chain(this._feedbackLR, this.effectSendR);
this.effectReturnR.chain(this._feedbackRL, this.effectSendL);
this.feedback.fan(this._feedbackLR.gain, this._feedbackRL.gain);
this._readOnly(['feedback']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect, Tone.FeedbackEffect);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect} this
*/
Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable(['feedback']);
this.feedback.dispose();
this.feedback = null;
this._feedbackLR.dispose();
this._feedbackLR = null;
this._feedbackRL.dispose();
this._feedbackRL = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Chorus is a stereo chorus effect with feedback composed of
* a left and right delay with a Tone.LFO applied to the delayTime of each channel.
* Inspiration from [Tuna.js](https://github.com/Dinahmoe/tuna/blob/master/tuna.js).
* Read more on the chorus effect on [SoundOnSound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/jun04/articles/synthsecrets.htm).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect}
* @param {Frequency|Object} [frequency] The frequency of the LFO.
* @param {Milliseconds} [delayTime] The delay of the chorus effect in ms.
* @param {NormalRange} [depth] The depth of the chorus.
* @example
* var chorus = new Tone.Chorus(4, 2.5, 0.5);
* var synth = new Tone.PolySynth(4, Tone.MonoSynth).connect(chorus);
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(["C3","E3","G3"], "8n");
*/
Tone.Chorus = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'delayTime',
'depth'
], Tone.Chorus.defaults);
Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* the depth of the chorus
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._depth = options.depth;
/**
* the delayTime
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._delayTime = options.delayTime / 1000;
/**
* the lfo which controls the delayTime
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoL = new Tone.LFO({
'frequency': options.frequency,
'min': 0,
'max': 1
});
/**
* another LFO for the right side with a 180 degree phase diff
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoR = new Tone.LFO({
'frequency': options.frequency,
'min': 0,
'max': 1,
'phase': 180
});
/**
* delay for left
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._delayNodeL = new Tone.Delay();
/**
* delay for right
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._delayNodeR = new Tone.Delay();
/**
* The frequency of the LFO which modulates the delayTime.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._lfoL.frequency;
//connections
this.effectSendL.chain(this._delayNodeL, this.effectReturnL);
this.effectSendR.chain(this._delayNodeR, this.effectReturnR);
//and pass through to make the detune apparent
this.effectSendL.connect(this.effectReturnL);
this.effectSendR.connect(this.effectReturnR);
//lfo setup
this._lfoL.connect(this._delayNodeL.delayTime);
this._lfoR.connect(this._delayNodeR.delayTime);
//start the lfo
this._lfoL.start();
this._lfoR.start();
//have one LFO frequency control the other
this._lfoL.frequency.connect(this._lfoR.frequency);
//set the initial values
this.depth = this._depth;
this.frequency.value = options.frequency;
this.type = options.type;
this._readOnly(['frequency']);
this.spread = options.spread;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Chorus, Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Chorus.defaults = {
'frequency': 1.5,
'delayTime': 3.5,
'depth': 0.7,
'feedback': 0.1,
'type': 'sine',
'spread': 180
};
/**
* The depth of the effect. A depth of 1 makes the delayTime
* modulate between 0 and 2*delayTime (centered around the delayTime).
* @memberOf Tone.Chorus#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name depth
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Chorus.prototype, 'depth', {
get: function () {
return this._depth;
},
set: function (depth) {
this._depth = depth;
var deviation = this._delayTime * depth;
this._lfoL.min = Math.max(this._delayTime - deviation, 0);
this._lfoL.max = this._delayTime + deviation;
this._lfoR.min = Math.max(this._delayTime - deviation, 0);
this._lfoR.max = this._delayTime + deviation;
}
});
/**
* The delayTime in milliseconds of the chorus. A larger delayTime
* will give a more pronounced effect. Nominal range a delayTime
* is between 2 and 20ms.
* @memberOf Tone.Chorus#
* @type {Milliseconds}
* @name delayTime
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Chorus.prototype, 'delayTime', {
get: function () {
return this._delayTime * 1000;
},
set: function (delayTime) {
this._delayTime = delayTime / 1000;
this.depth = this._depth;
}
});
/**
* The oscillator type of the LFO.
* @memberOf Tone.Chorus#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Chorus.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._lfoL.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._lfoL.type = type;
this._lfoR.type = type;
}
});
/**
* Amount of stereo spread. When set to 0, both LFO's will be panned centrally.
* When set to 180, LFO's will be panned hard left and right respectively.
* @memberOf Tone.Chorus#
* @type {Degrees}
* @name spread
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Chorus.prototype, 'spread', {
get: function () {
return this._lfoR.phase - this._lfoL.phase; //180
},
set: function (spread) {
this._lfoL.phase = 90 - spread / 2;
this._lfoR.phase = spread / 2 + 90;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Chorus} this
*/
Tone.Chorus.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._lfoL.dispose();
this._lfoL = null;
this._lfoR.dispose();
this._lfoR = null;
this._delayNodeL.dispose();
this._delayNodeL = null;
this._delayNodeR.dispose();
this._delayNodeR = null;
this._writable('frequency');
this.frequency = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Chorus;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Convolver is a wrapper around the Native Web Audio
* [ConvolverNode](http://webaudio.github.io/web-audio-api/#the-convolvernode-interface).
* Convolution is useful for reverb and filter emulation. Read more about convolution reverb on
* [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolution_reverb).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {string|Tone.Buffer|Object} [url] The URL of the impulse response or the Tone.Buffer
* contianing the impulse response.
* @param {Function} onload The callback to invoke when the url is loaded.
* @example
* //initializing the convolver with an impulse response
* var convolver = new Tone.Convolver("./path/to/ir.wav").toMaster();
*/
Tone.Convolver = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.Convolver.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* convolver node
* @type {ConvolverNode}
* @private
*/
this._convolver = this.context.createConvolver();
/**
* the convolution buffer
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
* @private
*/
this._buffer = new Tone.Buffer();
if (this.isString(options.url)) {
this._buffer.load(options.url, function (buffer) {
this.buffer = buffer;
options.onload();
}.bind(this));
} else if (options.url) {
this.buffer = options.url;
options.onload();
}
this.connectEffect(this._convolver);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Convolver, Tone.Effect);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Convolver.defaults = { 'onload': Tone.noOp };
/**
* The convolver's buffer
* @memberOf Tone.Convolver#
* @type {AudioBuffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Convolver.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
return this._buffer.get();
},
set: function (buffer) {
this._buffer.set(buffer);
this._convolver.buffer = this._buffer.get();
}
});
/**
* Load an impulse response url as an audio buffer.
* Decodes the audio asynchronously and invokes
* the callback once the audio buffer loads.
* @param {string} url The url of the buffer to load.
* filetype support depends on the
* browser.
* @param {function=} callback
* @returns {Promise}
*/
Tone.Convolver.prototype.load = function (url, callback) {
return this._buffer.load(url, function (buff) {
this.buffer = buff;
if (callback) {
callback();
}
}.bind(this));
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Convolver} this
*/
Tone.Convolver.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._convolver.disconnect();
this._convolver = null;
this._buffer.dispose();
this._buffer = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Convolver;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Distortion is a simple distortion effect using Tone.WaveShaper.
* Algorithm from [a stackoverflow answer](http://stackoverflow.com/a/22313408).
*
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @constructor
* @param {Number|Object} [distortion] The amount of distortion (nominal range of 0-1)
* @example
* var dist = new Tone.Distortion(0.8).toMaster();
* var fm = new Tone.SimpleFM().connect(dist);
* //this sounds good on bass notes
* fm.triggerAttackRelease("A1", "8n");
*/
Tone.Distortion = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['distortion'], Tone.Distortion.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* @type {Tone.WaveShaper}
* @private
*/
this._shaper = new Tone.WaveShaper(4096);
/**
* holds the distortion amount
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._distortion = options.distortion;
this.connectEffect(this._shaper);
this.distortion = options.distortion;
this.oversample = options.oversample;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Distortion, Tone.Effect);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Distortion.defaults = {
'distortion': 0.4,
'oversample': 'none'
};
/**
* The amount of distortion.
* @memberOf Tone.Distortion#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name distortion
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Distortion.prototype, 'distortion', {
get: function () {
return this._distortion;
},
set: function (amount) {
this._distortion = amount;
var k = amount * 100;
var deg = Math.PI / 180;
this._shaper.setMap(function (x) {
if (Math.abs(x) < 0.001) {
//should output 0 when input is 0
return 0;
} else {
return (3 + k) * x * 20 * deg / (Math.PI + k * Math.abs(x));
}
});
}
});
/**
* The oversampling of the effect. Can either be "none", "2x" or "4x".
* @memberOf Tone.Distortion#
* @type {string}
* @name oversample
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Distortion.prototype, 'oversample', {
get: function () {
return this._shaper.oversample;
},
set: function (oversampling) {
this._shaper.oversample = oversampling;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Distortion} this
*/
Tone.Distortion.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._shaper.dispose();
this._shaper = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Distortion;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.FeedbackDelay is a DelayNode in which part of output
* signal is fed back into the delay.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.FeedbackEffect}
* @param {Time|Object} [delayTime] The delay applied to the incoming signal.
* @param {NormalRange=} feedback The amount of the effected signal which
* is fed back through the delay.
* @example
* var feedbackDelay = new Tone.FeedbackDelay("8n", 0.5).toMaster();
* var tom = new Tone.DrumSynth({
* "octaves" : 4,
* "pitchDecay" : 0.1
* }).connect(feedbackDelay);
* tom.triggerAttackRelease("A2","32n");
*/
Tone.FeedbackDelay = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'delayTime',
'feedback'
], Tone.FeedbackDelay.defaults);
Tone.FeedbackEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* the delay node
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._delayNode = new Tone.Delay(options.delayTime);
/**
* The delayTime of the DelayNode.
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.delayTime = this._delayNode.delayTime;
// connect it up
this.connectEffect(this._delayNode);
this._readOnly(['delayTime']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FeedbackDelay, Tone.FeedbackEffect);
/**
* The default values.
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.FeedbackDelay.defaults = { 'delayTime': 0.25 };
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.FeedbackDelay} this
*/
Tone.FeedbackDelay.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.FeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._delayNode.dispose();
this._delayNode = null;
this._writable(['delayTime']);
this.delayTime = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FeedbackDelay;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* an array of comb filter delay values from Freeverb implementation
* @static
* @private
* @type {Array}
*/
var combFilterTunings = [
1557 / 44100,
1617 / 44100,
1491 / 44100,
1422 / 44100,
1277 / 44100,
1356 / 44100,
1188 / 44100,
1116 / 44100
];
/**
* an array of allpass filter frequency values from Freeverb implementation
* @private
* @static
* @type {Array}
*/
var allpassFilterFrequencies = [
225,
556,
441,
341
];
/**
* @class Tone.Freeverb is a reverb based on [Freeverb](https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/pasp/Freeverb.html).
* Read more on reverb on [SoundOnSound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/may00/articles/reverb.htm).
*
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @constructor
* @param {NormalRange|Object} [roomSize] Correlated to the decay time.
* @param {Frequency} [dampening] The cutoff frequency of a lowpass filter as part
* of the reverb.
* @example
* var freeverb = new Tone.Freeverb().toMaster();
* freeverb.dampening.value = 1000;
* //routing synth through the reverb
* var synth = new Tone.AMSynth().connect(freeverb);
*/
Tone.Freeverb = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'roomSize',
'dampening'
], Tone.Freeverb.defaults);
Tone.StereoEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* The roomSize value between. A larger roomSize
* will result in a longer decay.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.roomSize = new Tone.Signal(options.roomSize, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* The amount of dampening of the reverberant signal.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.dampening = new Tone.Signal(options.dampening, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* the comb filters
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._combFilters = [];
/**
* the allpass filters on the left
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._allpassFiltersL = [];
/**
* the allpass filters on the right
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._allpassFiltersR = [];
//make the allpass filters on teh right
for (var l = 0; l < allpassFilterFrequencies.length; l++) {
var allpassL = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
allpassL.type = 'allpass';
allpassL.frequency.value = allpassFilterFrequencies[l];
this._allpassFiltersL.push(allpassL);
}
//make the allpass filters on the left
for (var r = 0; r < allpassFilterFrequencies.length; r++) {
var allpassR = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
allpassR.type = 'allpass';
allpassR.frequency.value = allpassFilterFrequencies[r];
this._allpassFiltersR.push(allpassR);
}
//make the comb filters
for (var c = 0; c < combFilterTunings.length; c++) {
var lfpf = new Tone.LowpassCombFilter(combFilterTunings[c]);
if (c < combFilterTunings.length / 2) {
this.effectSendL.chain(lfpf, this._allpassFiltersL[0]);
} else {
this.effectSendR.chain(lfpf, this._allpassFiltersR[0]);
}
this.roomSize.connect(lfpf.resonance);
this.dampening.connect(lfpf.dampening);
this._combFilters.push(lfpf);
}
//chain the allpass filters togetehr
this.connectSeries.apply(this, this._allpassFiltersL);
this.connectSeries.apply(this, this._allpassFiltersR);
this._allpassFiltersL[this._allpassFiltersL.length - 1].connect(this.effectReturnL);
this._allpassFiltersR[this._allpassFiltersR.length - 1].connect(this.effectReturnR);
this._readOnly([
'roomSize',
'dampening'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Freeverb, Tone.StereoEffect);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Freeverb.defaults = {
'roomSize': 0.7,
'dampening': 3000
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Freeverb} this
*/
Tone.Freeverb.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
for (var al = 0; al < this._allpassFiltersL.length; al++) {
this._allpassFiltersL[al].disconnect();
this._allpassFiltersL[al] = null;
}
this._allpassFiltersL = null;
for (var ar = 0; ar < this._allpassFiltersR.length; ar++) {
this._allpassFiltersR[ar].disconnect();
this._allpassFiltersR[ar] = null;
}
this._allpassFiltersR = null;
for (var cf = 0; cf < this._combFilters.length; cf++) {
this._combFilters[cf].dispose();
this._combFilters[cf] = null;
}
this._combFilters = null;
this._writable([
'roomSize',
'dampening'
]);
this.roomSize.dispose();
this.roomSize = null;
this.dampening.dispose();
this.dampening = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Freeverb;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* an array of the comb filter delay time values
* @private
* @static
* @type {Array}
*/
var combFilterDelayTimes = [
1687 / 25000,
1601 / 25000,
2053 / 25000,
2251 / 25000
];
/**
* the resonances of each of the comb filters
* @private
* @static
* @type {Array}
*/
var combFilterResonances = [
0.773,
0.802,
0.753,
0.733
];
/**
* the allpass filter frequencies
* @private
* @static
* @type {Array}
*/
var allpassFilterFreqs = [
347,
113,
37
];
/**
* @class Tone.JCReverb is a simple [Schroeder Reverberator](https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~jos/pasp/Schroeder_Reverberators.html)
* tuned by John Chowning in 1970.
* It is made up of three allpass filters and four Tone.FeedbackCombFilter.
*
*
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @constructor
* @param {NormalRange|Object} [roomSize] Coorelates to the decay time.
* @example
* var reverb = new Tone.JCReverb(0.4).connect(Tone.Master);
* var delay = new Tone.FeedbackDelay(0.5);
* //connecting the synth to reverb through delay
* var synth = new Tone.DuoSynth().chain(delay, reverb);
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("A4","8n");
*/
Tone.JCReverb = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['roomSize'], Tone.JCReverb.defaults);
Tone.StereoEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* room size control values between [0,1]
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.roomSize = new Tone.Signal(options.roomSize, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* scale the room size
* @type {Tone.Scale}
* @private
*/
this._scaleRoomSize = new Tone.Scale(-0.733, 0.197);
/**
* a series of allpass filters
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._allpassFilters = [];
/**
* parallel feedback comb filters
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackCombFilters = [];
//make the allpass filters
for (var af = 0; af < allpassFilterFreqs.length; af++) {
var allpass = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
allpass.type = 'allpass';
allpass.frequency.value = allpassFilterFreqs[af];
this._allpassFilters.push(allpass);
}
//and the comb filters
for (var cf = 0; cf < combFilterDelayTimes.length; cf++) {
var fbcf = new Tone.FeedbackCombFilter(combFilterDelayTimes[cf], 0.1);
this._scaleRoomSize.connect(fbcf.resonance);
fbcf.resonance.value = combFilterResonances[cf];
this._allpassFilters[this._allpassFilters.length - 1].connect(fbcf);
if (cf < combFilterDelayTimes.length / 2) {
fbcf.connect(this.effectReturnL);
} else {
fbcf.connect(this.effectReturnR);
}
this._feedbackCombFilters.push(fbcf);
}
//chain the allpass filters together
this.roomSize.connect(this._scaleRoomSize);
this.connectSeries.apply(this, this._allpassFilters);
this.effectSendL.connect(this._allpassFilters[0]);
this.effectSendR.connect(this._allpassFilters[0]);
this._readOnly(['roomSize']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.JCReverb, Tone.StereoEffect);
/**
* the default values
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.JCReverb.defaults = { 'roomSize': 0.5 };
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.JCReverb} this
*/
Tone.JCReverb.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
for (var apf = 0; apf < this._allpassFilters.length; apf++) {
this._allpassFilters[apf].disconnect();
this._allpassFilters[apf] = null;
}
this._allpassFilters = null;
for (var fbcf = 0; fbcf < this._feedbackCombFilters.length; fbcf++) {
this._feedbackCombFilters[fbcf].dispose();
this._feedbackCombFilters[fbcf] = null;
}
this._feedbackCombFilters = null;
this._writable(['roomSize']);
this.roomSize.dispose();
this.roomSize = null;
this._scaleRoomSize.dispose();
this._scaleRoomSize = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.JCReverb;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Mid/Side processing separates the the 'mid' signal
* (which comes out of both the left and the right channel)
* and the 'side' (which only comes out of the the side channels)
* and effects them separately before being recombined.
* Applies a Mid/Side seperation and recombination.
* Algorithm found in [kvraudio forums](http://www.kvraudio.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=212587).
*
* This is a base-class for Mid/Side Effects.
*
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @constructor
*/
Tone.MidSideEffect = function () {
Tone.Effect.apply(this, arguments);
/**
* The mid/side split
* @type {Tone.MidSideSplit}
* @private
*/
this._midSideSplit = new Tone.MidSideSplit();
/**
* The mid/side merge
* @type {Tone.MidSideMerge}
* @private
*/
this._midSideMerge = new Tone.MidSideMerge();
/**
* The mid send. Connect to mid processing
* @type {Tone.Expr}
* @private
*/
this.midSend = this._midSideSplit.mid;
/**
* The side send. Connect to side processing
* @type {Tone.Expr}
* @private
*/
this.sideSend = this._midSideSplit.side;
/**
* The mid return connection
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.midReturn = this._midSideMerge.mid;
/**
* The side return connection
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this.sideReturn = this._midSideMerge.side;
//the connections
this.effectSend.connect(this._midSideSplit);
this._midSideMerge.connect(this.effectReturn);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MidSideEffect, Tone.Effect);
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.MidSideEffect} this
*/
Tone.MidSideEffect.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._midSideSplit.dispose();
this._midSideSplit = null;
this._midSideMerge.dispose();
this._midSideMerge = null;
this.midSend = null;
this.sideSend = null;
this.midReturn = null;
this.sideReturn = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MidSideEffect;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Phaser is a phaser effect. Phasers work by changing the phase
* of different frequency components of an incoming signal. Read more on
* [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phaser_(effect)).
* Inspiration for this phaser comes from [Tuna.js](https://github.com/Dinahmoe/tuna/).
*
* @extends {Tone.StereoEffect}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency|Object} [frequency] The speed of the phasing.
* @param {number} [octaves] The octaves of the effect.
* @param {Frequency} [baseFrequency] The base frequency of the filters.
* @example
* var phaser = new Tone.Phaser({
* "frequency" : 15,
* "octaves" : 5,
* "baseFrequency" : 1000
* }).toMaster();
* var synth = new Tone.FMSynth().connect(phaser);
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("E3", "2n");
*/
Tone.Phaser = function () {
//set the defaults
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'octaves',
'baseFrequency'
], Tone.Phaser.defaults);
Tone.StereoEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* the lfo which controls the frequency on the left side
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoL = new Tone.LFO(options.frequency, 0, 1);
/**
* the lfo which controls the frequency on the right side
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoR = new Tone.LFO(options.frequency, 0, 1);
this._lfoR.phase = 180;
/**
* the base modulation frequency
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._baseFrequency = options.baseFrequency;
/**
* the octaves of the phasing
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._octaves = options.octaves;
/**
* The quality factor of the filters
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.Q = new Tone.Signal(options.Q, Tone.Type.Positive);
/**
* the array of filters for the left side
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._filtersL = this._makeFilters(options.stages, this._lfoL, this.Q);
/**
* the array of filters for the left side
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._filtersR = this._makeFilters(options.stages, this._lfoR, this.Q);
/**
* the frequency of the effect
* @type {Tone.Signal}
*/
this.frequency = this._lfoL.frequency;
this.frequency.value = options.frequency;
//connect them up
this.effectSendL.connect(this._filtersL[0]);
this.effectSendR.connect(this._filtersR[0]);
this._filtersL[options.stages - 1].connect(this.effectReturnL);
this._filtersR[options.stages - 1].connect(this.effectReturnR);
//control the frequency with one LFO
this._lfoL.frequency.connect(this._lfoR.frequency);
//set the options
this.baseFrequency = options.baseFrequency;
this.octaves = options.octaves;
//start the lfo
this._lfoL.start();
this._lfoR.start();
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'Q'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Phaser, Tone.StereoEffect);
/**
* defaults
* @static
* @type {object}
*/
Tone.Phaser.defaults = {
'frequency': 0.5,
'octaves': 3,
'stages': 10,
'Q': 10,
'baseFrequency': 350
};
/**
* @param {number} stages
* @returns {Array} the number of filters all connected together
* @private
*/
Tone.Phaser.prototype._makeFilters = function (stages, connectToFreq, Q) {
var filters = new Array(stages);
//make all the filters
for (var i = 0; i < stages; i++) {
var filter = this.context.createBiquadFilter();
filter.type = 'allpass';
Q.connect(filter.Q);
connectToFreq.connect(filter.frequency);
filters[i] = filter;
}
this.connectSeries.apply(this, filters);
return filters;
};
/**
* The number of octaves the phase goes above
* the baseFrequency
* @memberOf Tone.Phaser#
* @type {Positive}
* @name octaves
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Phaser.prototype, 'octaves', {
get: function () {
return this._octaves;
},
set: function (octaves) {
this._octaves = octaves;
var max = this._baseFrequency * Math.pow(2, octaves);
this._lfoL.max = max;
this._lfoR.max = max;
}
});
/**
* The the base frequency of the filters.
* @memberOf Tone.Phaser#
* @type {number}
* @name baseFrequency
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Phaser.prototype, 'baseFrequency', {
get: function () {
return this._baseFrequency;
},
set: function (freq) {
this._baseFrequency = freq;
this._lfoL.min = freq;
this._lfoR.min = freq;
this.octaves = this._octaves;
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Phaser} this
*/
Tone.Phaser.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'Q'
]);
this.Q.dispose();
this.Q = null;
this._lfoL.dispose();
this._lfoL = null;
this._lfoR.dispose();
this._lfoR = null;
for (var i = 0; i < this._filtersL.length; i++) {
this._filtersL[i].disconnect();
this._filtersL[i] = null;
}
this._filtersL = null;
for (var j = 0; j < this._filtersR.length; j++) {
this._filtersR[j].disconnect();
this._filtersR[j] = null;
}
this._filtersR = null;
this.frequency = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Phaser;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PingPongDelay is a feedback delay effect where the echo is heard
* first in one channel and next in the opposite channel. In a stereo
* system these are the right and left channels.
* PingPongDelay in more simplified terms is two Tone.FeedbackDelays
* with independent delay values. Each delay is routed to one channel
* (left or right), and the channel triggered second will always
* trigger at the same interval after the first.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect}
* @param {Time|Object} [delayTime] The delayTime between consecutive echos.
* @param {NormalRange=} feedback The amount of the effected signal which
* is fed back through the delay.
* @example
* var pingPong = new Tone.PingPongDelay("4n", 0.2).toMaster();
* var drum = new Tone.DrumSynth().connect(pingPong);
* drum.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "32n");
*/
Tone.PingPongDelay = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'delayTime',
'feedback'
], Tone.PingPongDelay.defaults);
Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* the delay node on the left side
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._leftDelay = new Tone.Delay(0, options.maxDelayTime);
/**
* the delay node on the right side
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._rightDelay = new Tone.Delay(0, options.maxDelayTime);
/**
* the predelay on the right side
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._rightPreDelay = new Tone.Delay(0, options.maxDelayTime);
/**
* the delay time signal
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.delayTime = new Tone.Signal(options.delayTime, Tone.Type.Time);
//connect it up
this.effectSendL.chain(this._leftDelay, this.effectReturnL);
this.effectSendR.chain(this._rightPreDelay, this._rightDelay, this.effectReturnR);
this.delayTime.fan(this._leftDelay.delayTime, this._rightDelay.delayTime, this._rightPreDelay.delayTime);
//rearranged the feedback to be after the rightPreDelay
this._feedbackLR.disconnect();
this._feedbackLR.connect(this._rightDelay);
this._readOnly(['delayTime']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PingPongDelay, Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.PingPongDelay.defaults = {
'delayTime': 0.25,
'maxDelayTime': 1
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.PingPongDelay} this
*/
Tone.PingPongDelay.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoXFeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._leftDelay.dispose();
this._leftDelay = null;
this._rightDelay.dispose();
this._rightDelay = null;
this._rightPreDelay.dispose();
this._rightPreDelay = null;
this._writable(['delayTime']);
this.delayTime.dispose();
this.delayTime = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PingPongDelay;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PitchShift does near-realtime pitch shifting to the incoming signal.
* The effect is achieved by speeding up or slowing down the delayTime
* of a DelayNode using a sawtooth wave.
* Algorithm found in [this pdf](http://dsp-book.narod.ru/soundproc.pdf).
* Additional reference by [Miller Pucket](http://msp.ucsd.edu/techniques/v0.11/book-html/node115.html).
*
* @extends {Tone.FeedbackEffect}
* @param {Interval=} pitch The interval to transpose the incoming signal by.
*/
Tone.PitchShift = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['pitch'], Tone.PitchShift.defaults);
Tone.FeedbackEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* The pitch signal
* @type {Tone.Signal}
* @private
*/
this._frequency = new Tone.Signal(0);
/**
* Uses two DelayNodes to cover up the jump in
* the sawtooth wave.
* @type {DelayNode}
* @private
*/
this._delayA = new Tone.Delay(0, 1);
/**
* The first LFO.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoA = new Tone.LFO({
'min': 0,
'max': 0.1,
'type': 'sawtooth'
}).connect(this._delayA.delayTime);
/**
* The second DelayNode
* @type {DelayNode}
* @private
*/
this._delayB = new Tone.Delay(0, 1);
/**
* The first LFO.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoB = new Tone.LFO({
'min': 0,
'max': 0.1,
'type': 'sawtooth',
'phase': 180
}).connect(this._delayB.delayTime);
/**
* Crossfade quickly between the two delay lines
* to cover up the jump in the sawtooth wave
* @type {Tone.CrossFade}
* @private
*/
this._crossFade = new Tone.CrossFade();
/**
* LFO which alternates between the two
* delay lines to cover up the disparity in the
* sawtooth wave.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._crossFadeLFO = new Tone.LFO({
'min': 0,
'max': 1,
'type': 'triangle',
'phase': 90
}).connect(this._crossFade.fade);
/**
* The delay node
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackDelay = new Tone.Delay(options.delayTime);
/**
* The amount of delay on the input signal
* @type {Time}
* @signal
*/
this.delayTime = this._feedbackDelay.delayTime;
this._readOnly('delayTime');
/**
* Hold the current pitch
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._pitch = options.pitch;
/**
* Hold the current windowSize
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._windowSize = options.windowSize;
//connect the two delay lines up
this._delayA.connect(this._crossFade.a);
this._delayB.connect(this._crossFade.b);
//connect the frequency
this._frequency.fan(this._lfoA.frequency, this._lfoB.frequency, this._crossFadeLFO.frequency);
//route the input
this.effectSend.fan(this._delayA, this._delayB);
this._crossFade.chain(this._feedbackDelay, this.effectReturn);
//start the LFOs at the same time
var now = this.now();
this._lfoA.start(now);
this._lfoB.start(now);
this._crossFadeLFO.start(now);
//set the initial value
this.windowSize = this._windowSize;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PitchShift, Tone.FeedbackEffect);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.PitchShift.defaults = {
'pitch': 0,
'windowSize': 0.1,
'delayTime': 0,
'feedback': 0
};
/**
* Repitch the incoming signal by some interval (measured
* in semi-tones).
* @memberOf Tone.PitchShift#
* @type {Interval}
* @name pitch
* @example
* pitchShift.pitch = -12; //down one octave
* pitchShift.pitch = 7; //up a fifth
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PitchShift.prototype, 'pitch', {
get: function () {
return this._pitch;
},
set: function (interval) {
this._pitch = interval;
var factor = 0;
if (interval < 0) {
this._lfoA.min = 0;
this._lfoA.max = this._windowSize;
this._lfoB.min = 0;
this._lfoB.max = this._windowSize;
factor = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(interval - 1) + 1;
} else {
this._lfoA.min = this._windowSize;
this._lfoA.max = 0;
this._lfoB.min = this._windowSize;
this._lfoB.max = 0;
factor = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(interval) - 1;
}
this._frequency.value = factor * (1.2 / this._windowSize);
}
});
/**
* The window size corresponds roughly to the sample length in a looping sampler.
* Smaller values are desirable for a less noticeable delay time of the pitch shifted
* signal, but larger values will result in smoother pitch shifting for larger intervals.
* A nominal range of 0.03 to 0.1 is recommended.
* @memberOf Tone.PitchShift#
* @type {Time}
* @name windowSize
* @example
* pitchShift.windowSize = 0.1;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PitchShift.prototype, 'windowSize', {
get: function () {
return this._windowSize;
},
set: function (size) {
this._windowSize = this.toSeconds(size);
this.pitch = this._pitch;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.PitchShift} this
*/
Tone.PitchShift.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.FeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._frequency.dispose();
this._frequency = null;
this._delayA.disconnect();
this._delayA = null;
this._delayB.disconnect();
this._delayB = null;
this._lfoA.dispose();
this._lfoA = null;
this._lfoB.dispose();
this._lfoB = null;
this._crossFade.dispose();
this._crossFade = null;
this._crossFadeLFO.dispose();
this._crossFadeLFO = null;
this._writable('delayTime');
this._feedbackDelay.dispose();
this._feedbackDelay = null;
this.delayTime = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PitchShift;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Base class for stereo feedback effects where the effectReturn
* is fed back into the same channel.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.FeedbackEffect}
*/
Tone.StereoFeedbackEffect = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['feedback'], Tone.FeedbackEffect.defaults);
Tone.StereoEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* controls the amount of feedback
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.feedback = new Tone.Signal(options.feedback, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* the left side feeback
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackL = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the right side feeback
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._feedbackR = new Tone.Gain();
//connect it up
this.effectReturnL.chain(this._feedbackL, this.effectSendL);
this.effectReturnR.chain(this._feedbackR, this.effectSendR);
this.feedback.fan(this._feedbackL.gain, this._feedbackR.gain);
this._readOnly(['feedback']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.StereoFeedbackEffect, Tone.FeedbackEffect);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.StereoFeedbackEffect} this
*/
Tone.StereoFeedbackEffect.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable(['feedback']);
this.feedback.dispose();
this.feedback = null;
this._feedbackL.dispose();
this._feedbackL = null;
this._feedbackR.dispose();
this._feedbackR = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.StereoFeedbackEffect;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Applies a width factor to the mid/side seperation.
* 0 is all mid and 1 is all side.
* Algorithm found in [kvraudio forums](http://www.kvraudio.com/forum/viewtopic.php?t=212587).
*
*
* Mid *= 2*(1-width)
* Side *= 2*width
*
*
* @extends {Tone.MidSideEffect}
* @constructor
* @param {NormalRange|Object} [width] The stereo width. A width of 0 is mono and 1 is stereo. 0.5 is no change.
*/
Tone.StereoWidener = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['width'], Tone.StereoWidener.defaults);
Tone.MidSideEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* The width control. 0 = 100% mid. 1 = 100% side. 0.5 = no change.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.width = new Tone.Signal(options.width, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* Mid multiplier
* @type {Tone.Expr}
* @private
*/
this._midMult = new Tone.Expr('$0 * ($1 * (1 - $2))');
/**
* Side multiplier
* @type {Tone.Expr}
* @private
*/
this._sideMult = new Tone.Expr('$0 * ($1 * $2)');
/**
* constant output of 2
* @type {Tone}
* @private
*/
this._two = new Tone.Signal(2);
//the mid chain
this._two.connect(this._midMult, 0, 1);
this.width.connect(this._midMult, 0, 2);
//the side chain
this._two.connect(this._sideMult, 0, 1);
this.width.connect(this._sideMult, 0, 2);
//connect it to the effect send/return
this.midSend.chain(this._midMult, this.midReturn);
this.sideSend.chain(this._sideMult, this.sideReturn);
this._readOnly(['width']);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.StereoWidener, Tone.MidSideEffect);
/**
* the default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.StereoWidener.defaults = { 'width': 0.5 };
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.StereoWidener} this
*/
Tone.StereoWidener.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.MidSideEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable(['width']);
this.width.dispose();
this.width = null;
this._midMult.dispose();
this._midMult = null;
this._sideMult.dispose();
this._sideMult = null;
this._two.dispose();
this._two = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.StereoWidener;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Tremolo modulates the amplitude of an incoming signal using a Tone.LFO.
* The type, frequency, and depth of the LFO is controllable.
*
* @extends {Tone.StereoEffect}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency} [frequency] The rate of the effect.
* @param {NormalRange} [depth] The depth of the effect.
* @example
* //create a tremolo and start it's LFO
* var tremolo = new Tone.Tremolo(9, 0.75).toMaster().start();
* //route an oscillator through the tremolo and start it
* var oscillator = new Tone.Oscillator().connect(tremolo).start();
*/
Tone.Tremolo = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'depth'
], Tone.Tremolo.defaults);
Tone.StereoEffect.call(this, options);
/**
* The tremelo LFO in the left channel
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoL = new Tone.LFO({
'phase': options.spread,
'min': 1,
'max': 0
});
/**
* The tremelo LFO in the left channel
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfoR = new Tone.LFO({
'phase': options.spread,
'min': 1,
'max': 0
});
/**
* Where the gain is multiplied
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._amplitudeL = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* Where the gain is multiplied
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._amplitudeR = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* The frequency of the tremolo.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The depth of the effect. A depth of 0, has no effect
* on the amplitude, and a depth of 1 makes the amplitude
* modulate fully between 0 and 1.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.depth = new Tone.Signal(options.depth, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'depth'
]);
this.effectSendL.chain(this._amplitudeL, this.effectReturnL);
this.effectSendR.chain(this._amplitudeR, this.effectReturnR);
this._lfoL.connect(this._amplitudeL.gain);
this._lfoR.connect(this._amplitudeR.gain);
this.frequency.fan(this._lfoL.frequency, this._lfoR.frequency);
this.depth.fan(this._lfoR.amplitude, this._lfoL.amplitude);
this.type = options.type;
this.spread = options.spread;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Tremolo, Tone.StereoEffect);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Tremolo.defaults = {
'frequency': 10,
'type': 'sine',
'depth': 0.5,
'spread': 180
};
/**
* Start the tremolo.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the tremolo begins.
* @returns {Tone.Tremolo} this
*/
Tone.Tremolo.prototype.start = function (time) {
this._lfoL.start(time);
this._lfoR.start(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the tremolo.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the tremolo stops.
* @returns {Tone.Tremolo} this
*/
Tone.Tremolo.prototype.stop = function (time) {
this._lfoL.stop(time);
this._lfoR.stop(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Sync the effect to the transport.
* @param {Time} [delay=0] Delay time before starting the effect after the
* Transport has started.
* @returns {Tone.AutoFilter} this
*/
Tone.Tremolo.prototype.sync = function (delay) {
this._lfoL.sync(delay);
this._lfoR.sync(delay);
return this;
};
/**
* Unsync the filter from the transport
* @returns {Tone.Tremolo} this
*/
Tone.Tremolo.prototype.unsync = function () {
this._lfoL.unsync();
this._lfoR.unsync();
return this;
};
/**
* The Tremolo's oscillator type.
* @memberOf Tone.Tremolo#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Tremolo.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._lfoL.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._lfoL.type = type;
this._lfoR.type = type;
}
});
/**
* Amount of stereo spread. When set to 0, both LFO's will be panned centrally.
* When set to 180, LFO's will be panned hard left and right respectively.
* @memberOf Tone.Tremolo#
* @type {Degrees}
* @name spread
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Tremolo.prototype, 'spread', {
get: function () {
return this._lfoR.phase - this._lfoL.phase; //180
},
set: function (spread) {
this._lfoL.phase = 90 - spread / 2;
this._lfoR.phase = spread / 2 + 90;
}
});
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Tremolo} this
*/
Tone.Tremolo.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.StereoEffect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'depth'
]);
this._lfoL.dispose();
this._lfoL = null;
this._lfoR.dispose();
this._lfoR = null;
this._amplitudeL.dispose();
this._amplitudeL = null;
this._amplitudeR.dispose();
this._amplitudeR = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.depth = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Tremolo;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A Vibrato effect composed of a Tone.Delay and a Tone.LFO. The LFO
* modulates the delayTime of the delay, causing the pitch to rise
* and fall.
* @extends {Tone.Effect}
* @param {Frequency} frequency The frequency of the vibrato.
* @param {NormalRange} depth The amount the pitch is modulated.
*/
Tone.Vibrato = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'depth'
], Tone.Vibrato.defaults);
Tone.Effect.call(this, options);
/**
* The delay node used for the vibrato effect
* @type {Tone.Delay}
* @private
*/
this._delayNode = new Tone.Delay(0, options.maxDelay);
/**
* The LFO used to control the vibrato
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._lfo = new Tone.LFO({
'type': options.type,
'min': 0,
'max': options.maxDelay,
'frequency': options.frequency,
'phase': -90 //offse the phase so the resting position is in the center
}).start().connect(this._delayNode.delayTime);
/**
* The frequency of the vibrato
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._lfo.frequency;
/**
* The depth of the vibrato.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.depth = this._lfo.amplitude;
this.depth.value = options.depth;
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'depth'
]);
this.effectSend.chain(this._delayNode, this.effectReturn);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Vibrato, Tone.Effect);
/**
* The defaults
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.Vibrato.defaults = {
'maxDelay': 0.005,
'frequency': 5,
'depth': 0.1,
'type': 'sine'
};
/**
* Type of oscillator attached to the Vibrato.
* @memberOf Tone.Vibrato#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Vibrato.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._lfo.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._lfo.type = type;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Vibrato} this
*/
Tone.Vibrato.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Effect.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._delayNode.dispose();
this._delayNode = null;
this._lfo.dispose();
this._lfo = null;
this._writable([
'frequency',
'depth'
]);
this.frequency = null;
this.depth = null;
};
return Tone.Vibrato;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Event abstracts away Tone.Transport.schedule and provides a schedulable
* callback for a single or repeatable events along the timeline.
*
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {function} callback The callback to invoke at the time.
* @param {*} value The value or values which should be passed to
* the callback function on invocation.
* @example
* var chord = new Tone.Event(function(time, chord){
* //the chord as well as the exact time of the event
* //are passed in as arguments to the callback function
* }, ["D4", "E4", "F4"]);
* //start the chord at the beginning of the transport timeline
* chord.start();
* //loop it every measure for 8 measures
* chord.loop = 8;
* chord.loopEnd = "1m";
*/
Tone.Event = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'callback',
'value'
], Tone.Event.defaults);
/**
* Loop value
* @type {Boolean|Positive}
* @private
*/
this._loop = options.loop;
/**
* The callback to invoke.
* @type {Function}
*/
this.callback = options.callback;
/**
* The value which is passed to the
* callback function.
* @type {*}
* @private
*/
this.value = options.value;
/**
* When the note is scheduled to start.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = this.toTicks(options.loopStart);
/**
* When the note is scheduled to start.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = this.toTicks(options.loopEnd);
/**
* Tracks the scheduled events
* @type {Tone.TimelineState}
* @private
*/
this._state = new Tone.TimelineState(Tone.State.Stopped);
/**
* The playback speed of the note. A speed of 1
* is no change.
* @private
* @type {Positive}
*/
this._playbackRate = 1;
/**
* A delay time from when the event is scheduled to start
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._startOffset = 0;
/**
* The probability that the callback will be invoked
* at the scheduled time.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @example
* //the callback will be invoked 50% of the time
* event.probability = 0.5;
*/
this.probability = options.probability;
/**
* If set to true, will apply small (+/-0.02 seconds) random variation
* to the callback time. If the value is given as a time, it will randomize
* by that amount.
* @example
* event.humanize = true;
* @type {Boolean|Time}
*/
this.humanize = options.humanize;
/**
* If mute is true, the callback won't be
* invoked.
* @type {Boolean}
*/
this.mute = options.mute;
//set the initial values
this.playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Event);
/**
* The default values
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.Event.defaults = {
'callback': Tone.noOp,
'loop': false,
'loopEnd': '1m',
'loopStart': 0,
'playbackRate': 1,
'value': null,
'probability': 1,
'mute': false,
'humanize': false
};
/**
* Reschedule all of the events along the timeline
* with the updated values.
* @param {Time} after Only reschedules events after the given time.
* @return {Tone.Event} this
* @private
*/
Tone.Event.prototype._rescheduleEvents = function (after) {
//if no argument is given, schedules all of the events
after = this.defaultArg(after, -1);
this._state.forEachFrom(after, function (event) {
var duration;
if (event.state === Tone.State.Started) {
if (!this.isUndef(event.id)) {
Tone.Transport.clear(event.id);
}
var startTick = event.time + Math.round(this.startOffset / this._playbackRate);
if (this._loop) {
duration = Infinity;
if (this.isNumber(this._loop)) {
duration = this._loop * this._getLoopDuration();
}
var nextEvent = this._state.getAfter(startTick);
if (nextEvent !== null) {
duration = Math.min(duration, nextEvent.time - startTick);
}
if (duration !== Infinity) {
//schedule a stop since it's finite duration
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, startTick + duration + 1);
duration = Tone.Time(duration, 'i');
}
var interval = Tone.Time(this._getLoopDuration(), 'i');
event.id = Tone.Transport.scheduleRepeat(this._tick.bind(this), interval, Tone.TransportTime(startTick, 'i'), duration);
} else {
event.id = Tone.Transport.schedule(this._tick.bind(this), startTick + 'i');
}
}
}.bind(this));
return this;
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the note, either "started" or "stopped".
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._state.getValueAtTime(Tone.Transport.ticks);
}
});
/**
* The start from the scheduled start time
* @type {Ticks}
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @name startOffset
* @private
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'startOffset', {
get: function () {
return this._startOffset;
},
set: function (offset) {
this._startOffset = offset;
}
});
/**
* Start the note at the given time.
* @param {TimelinePosition} time When the note should start.
* @return {Tone.Event} this
*/
Tone.Event.prototype.start = function (time) {
time = this.toTicks(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(time) === Tone.State.Stopped) {
this._state.add({
'state': Tone.State.Started,
'time': time,
'id': undefined
});
this._rescheduleEvents(time);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the Event at the given time.
* @param {TimelinePosition} time When the note should stop.
* @return {Tone.Event} this
*/
Tone.Event.prototype.stop = function (time) {
this.cancel(time);
time = this.toTicks(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(time) === Tone.State.Started) {
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, time);
var previousEvent = this._state.getBefore(time);
var reschedulTime = time;
if (previousEvent !== null) {
reschedulTime = previousEvent.time;
}
this._rescheduleEvents(reschedulTime);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Cancel all scheduled events greater than or equal to the given time
* @param {TimelinePosition} [time=0] The time after which events will be cancel.
* @return {Tone.Event} this
*/
Tone.Event.prototype.cancel = function (time) {
time = this.defaultArg(time, -Infinity);
time = this.toTicks(time);
this._state.forEachFrom(time, function (event) {
Tone.Transport.clear(event.id);
});
this._state.cancel(time);
return this;
};
/**
* The callback function invoker. Also
* checks if the Event is done playing
* @param {Number} time The time of the event in seconds
* @private
*/
Tone.Event.prototype._tick = function (time) {
if (!this.mute && this._state.getValueAtTime(Tone.Transport.ticks) === Tone.State.Started) {
if (this.probability < 1 && Math.random() > this.probability) {
return;
}
if (this.humanize) {
var variation = 0.02;
if (!this.isBoolean(this.humanize)) {
variation = this.toSeconds(this.humanize);
}
time += (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * variation;
}
this.callback(time, this.value);
}
};
/**
* Get the duration of the loop.
* @return {Ticks}
* @private
*/
Tone.Event.prototype._getLoopDuration = function () {
return Math.round((this._loopEnd - this._loopStart) / this._playbackRate);
};
/**
* If the note should loop or not
* between Tone.Event.loopStart and
* Tone.Event.loopEnd. An integer
* value corresponds to the number of
* loops the Event does after it starts.
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @type {Boolean|Positive}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this._loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this._loop = loop;
this._rescheduleEvents();
}
});
/**
* The playback rate of the note. Defaults to 1.
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @type {Positive}
* @name playbackRate
* @example
* note.loop = true;
* //repeat the note twice as fast
* note.playbackRate = 2;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
this._rescheduleEvents();
}
});
/**
* The loopEnd point is the time the event will loop
* if Tone.Event.loop is true.
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @type {TransportTime}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this._loopEnd, 'i').toNotation();
},
set: function (loopEnd) {
this._loopEnd = this.toTicks(loopEnd);
if (this._loop) {
this._rescheduleEvents();
}
}
});
/**
* The time when the loop should start.
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @type {TransportTime}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this._loopStart, 'i').toNotation();
},
set: function (loopStart) {
this._loopStart = this.toTicks(loopStart);
if (this._loop) {
this._rescheduleEvents();
}
}
});
/**
* The current progress of the loop interval.
* Returns 0 if the event is not started yet or
* it is not set to loop.
* @memberOf Tone.Event#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name progress
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Event.prototype, 'progress', {
get: function () {
if (this._loop) {
var ticks = Tone.Transport.ticks;
var lastEvent = this._state.get(ticks);
if (lastEvent !== null && lastEvent.state === Tone.State.Started) {
var loopDuration = this._getLoopDuration();
var progress = (ticks - lastEvent.time) % loopDuration;
return progress / loopDuration;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
return 0;
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.Event} this
*/
Tone.Event.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.cancel();
this._state.dispose();
this._state = null;
this.callback = null;
this.value = null;
};
return Tone.Event;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Loop creates a looped callback at the
* specified interval. The callback can be
* started, stopped and scheduled along
* the Transport's timeline.
* @example
* var loop = new Tone.Loop(function(time){
* //triggered every eighth note.
* console.log(time);
* }, "8n").start(0);
* Tone.Transport.start();
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with the event.
* @param {Time} interval The time between successive callback calls.
*/
Tone.Loop = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'callback',
'interval'
], Tone.Loop.defaults);
/**
* The event which produces the callbacks
*/
this._event = new Tone.Event({
'callback': this._tick.bind(this),
'loop': true,
'loopEnd': options.interval,
'playbackRate': options.playbackRate,
'probability': options.probability
});
/**
* The callback to invoke with the next event in the pattern
* @type {Function}
*/
this.callback = options.callback;
//set the iterations
this.iterations = options.iterations;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Loop);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Loop.defaults = {
'interval': '4n',
'callback': Tone.noOp,
'playbackRate': 1,
'iterations': Infinity,
'probability': true,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Start the loop at the specified time along the Transport's
* timeline.
* @param {TimelinePosition=} time When to start the Loop.
* @return {Tone.Loop} this
*/
Tone.Loop.prototype.start = function (time) {
this._event.start(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the loop at the given time.
* @param {TimelinePosition=} time When to stop the Arpeggio
* @return {Tone.Loop} this
*/
Tone.Loop.prototype.stop = function (time) {
this._event.stop(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Cancel all scheduled events greater than or equal to the given time
* @param {TimelinePosition} [time=0] The time after which events will be cancel.
* @return {Tone.Loop} this
*/
Tone.Loop.prototype.cancel = function (time) {
this._event.cancel(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Internal function called when the notes should be called
* @param {Number} time The time the event occurs
* @private
*/
Tone.Loop.prototype._tick = function (time) {
this.callback(time);
};
/**
* The state of the Loop, either started or stopped.
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {String}
* @name state
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._event.state;
}
});
/**
* The progress of the loop as a value between 0-1. 0, when
* the loop is stopped or done iterating.
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name progress
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'progress', {
get: function () {
return this._event.progress;
}
});
/**
* The time between successive callbacks.
* @example
* loop.interval = "8n"; //loop every 8n
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {Time}
* @name interval
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'interval', {
get: function () {
return this._event.loopEnd;
},
set: function (interval) {
this._event.loopEnd = interval;
}
});
/**
* The playback rate of the loop. The normal playback rate is 1 (no change).
* A `playbackRate` of 2 would be twice as fast.
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {Time}
* @name playbackRate
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._event.playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._event.playbackRate = rate;
}
});
/**
* Random variation +/-0.01s to the scheduled time.
* Or give it a time value which it will randomize by.
* @type {Boolean|Time}
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @name humanize
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'humanize', {
get: function () {
return this._event.humanize;
},
set: function (variation) {
this._event.humanize = variation;
}
});
/**
* The probably of the callback being invoked.
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name probability
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'probability', {
get: function () {
return this._event.probability;
},
set: function (prob) {
this._event.probability = prob;
}
});
/**
* Muting the Loop means that no callbacks are invoked.
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {Boolean}
* @name mute
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._event.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._event.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* The number of iterations of the loop. The default
* value is Infinity (loop forever).
* @memberOf Tone.Loop#
* @type {Positive}
* @name iterations
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Loop.prototype, 'iterations', {
get: function () {
if (this._event.loop === true) {
return Infinity;
} else {
return this._event.loop;
}
return this._pattern.index;
},
set: function (iters) {
if (iters === Infinity) {
this._event.loop = true;
} else {
this._event.loop = iters;
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.Loop} this
*/
Tone.Loop.prototype.dispose = function () {
this._event.dispose();
this._event = null;
this.callback = null;
};
return Tone.Loop;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Part is a collection Tone.Events which can be
* started/stoped and looped as a single unit.
*
* @extends {Tone.Event}
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke on each event
* @param {Array} events the array of events
* @example
* var part = new Tone.Part(function(time, note){
* //the notes given as the second element in the array
* //will be passed in as the second argument
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(note, "8n", time);
* }, [[0, "C2"], ["0:2", "C3"], ["0:3:2", "G2"]]);
* @example
* //use an array of objects as long as the object has a "time" attribute
* var part = new Tone.Part(function(time, value){
* //the value is an object which contains both the note and the velocity
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(value.note, "8n", time, value.velocity);
* }, [{"time" : 0, "note" : "C3", "velocity": 0.9},
* {"time" : "0:2", "note" : "C4", "velocity": 0.5}
* ]).start(0);
*/
Tone.Part = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'callback',
'events'
], Tone.Part.defaults);
/**
* If the part is looping or not
* @type {Boolean|Positive}
* @private
*/
this._loop = options.loop;
/**
* When the note is scheduled to start.
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = this.toTicks(options.loopStart);
/**
* When the note is scheduled to start.
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = this.toTicks(options.loopEnd);
/**
* The playback rate of the part
* @type {Positive}
* @private
*/
this._playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
/**
* private holder of probability value
* @type {NormalRange}
* @private
*/
this._probability = options.probability;
/**
* the amount of variation from the
* given time.
* @type {Boolean|Time}
* @private
*/
this._humanize = options.humanize;
/**
* The start offset
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._startOffset = 0;
/**
* Keeps track of the current state
* @type {Tone.TimelineState}
* @private
*/
this._state = new Tone.TimelineState(Tone.State.Stopped);
/**
* An array of Objects.
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._events = [];
/**
* The callback to invoke at all the scheduled events.
* @type {Function}
*/
this.callback = options.callback;
/**
* If mute is true, the callback won't be
* invoked.
* @type {Boolean}
*/
this.mute = options.mute;
//add the events
var events = this.defaultArg(options.events, []);
if (!this.isUndef(options.events)) {
for (var i = 0; i < events.length; i++) {
if (Array.isArray(events[i])) {
this.add(events[i][0], events[i][1]);
} else {
this.add(events[i]);
}
}
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Part, Tone.Event);
/**
* The default values
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.Part.defaults = {
'callback': Tone.noOp,
'loop': false,
'loopEnd': '1m',
'loopStart': 0,
'playbackRate': 1,
'probability': 1,
'humanize': false,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Start the part at the given time.
* @param {TransportTime} time When to start the part.
* @param {Time=} offset The offset from the start of the part
* to begin playing at.
* @return {Tone.Part} this
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.start = function (time, offset) {
var ticks = this.toTicks(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(ticks) !== Tone.State.Started) {
if (this._loop) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, this._loopStart);
} else {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
}
offset = this.toTicks(offset);
this._state.add({
'state': Tone.State.Started,
'time': ticks,
'offset': offset
});
this._forEach(function (event) {
this._startNote(event, ticks, offset);
});
}
return this;
};
/**
* Start the event in the given event at the correct time given
* the ticks and offset and looping.
* @param {Tone.Event} event
* @param {Ticks} ticks
* @param {Ticks} offset
* @private
*/
Tone.Part.prototype._startNote = function (event, ticks, offset) {
ticks -= offset;
if (this._loop) {
if (event.startOffset >= this._loopStart && event.startOffset < this._loopEnd) {
if (event.startOffset < offset) {
//start it on the next loop
ticks += this._getLoopDuration();
}
event.start(Tone.TransportTime(ticks, 'i'));
} else if (event.startOffset < this._loopStart && event.startOffset >= offset) {
event.loop = false;
event.start(Tone.TransportTime(ticks, 'i'));
}
} else {
if (event.startOffset >= offset) {
event.start(Tone.TransportTime(ticks, 'i'));
}
}
};
/**
* The start from the scheduled start time
* @type {Ticks}
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @name startOffset
* @private
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'startOffset', {
get: function () {
return this._startOffset;
},
set: function (offset) {
this._startOffset = offset;
this._forEach(function (event) {
event.startOffset += this._startOffset;
});
}
});
/**
* Stop the part at the given time.
* @param {TimelinePosition} time When to stop the part.
* @return {Tone.Part} this
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.stop = function (time) {
var ticks = this.toTicks(time);
this._state.cancel(ticks);
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, ticks);
this._forEach(function (event) {
event.stop(time);
});
return this;
};
/**
* Get/Set an Event's value at the given time.
* If a value is passed in and no event exists at
* the given time, one will be created with that value.
* If two events are at the same time, the first one will
* be returned.
* @example
* part.at("1m"); //returns the part at the first measure
*
* part.at("2m", "C2"); //set the value at "2m" to C2.
* //if an event didn't exist at that time, it will be created.
* @param {TransportTime} time The time of the event to get or set.
* @param {*=} value If a value is passed in, the value of the
* event at the given time will be set to it.
* @return {Tone.Event} the event at the time
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.at = function (time, value) {
time = Tone.TransportTime(time);
var tickTime = Tone.Time(1, 'i').toSeconds();
for (var i = 0; i < this._events.length; i++) {
var event = this._events[i];
if (Math.abs(time.toTicks() - event.startOffset) < tickTime) {
if (!this.isUndef(value)) {
event.value = value;
}
return event;
}
}
//if there was no event at that time, create one
if (!this.isUndef(value)) {
this.add(time, value);
//return the new event
return this._events[this._events.length - 1];
} else {
return null;
}
};
/**
* Add a an event to the part.
* @param {Time} time The time the note should start.
* If an object is passed in, it should
* have a 'time' attribute and the rest
* of the object will be used as the 'value'.
* @param {Tone.Event|*} value
* @returns {Tone.Part} this
* @example
* part.add("1m", "C#+11");
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.add = function (time, value) {
//extract the parameters
if (time.hasOwnProperty('time')) {
value = time;
time = value.time;
}
time = this.toTicks(time);
var event;
if (value instanceof Tone.Event) {
event = value;
event.callback = this._tick.bind(this);
} else {
event = new Tone.Event({
'callback': this._tick.bind(this),
'value': value
});
}
//the start offset
event.startOffset = time;
//initialize the values
event.set({
'loopEnd': this.loopEnd,
'loopStart': this.loopStart,
'loop': this.loop,
'humanize': this.humanize,
'playbackRate': this.playbackRate,
'probability': this.probability
});
this._events.push(event);
//start the note if it should be played right now
this._restartEvent(event);
return this;
};
/**
* Restart the given event
* @param {Tone.Event} event
* @private
*/
Tone.Part.prototype._restartEvent = function (event) {
this._state.forEach(function (stateEvent) {
if (stateEvent.state === Tone.State.Started) {
this._startNote(event, stateEvent.time, stateEvent.offset);
} else {
//stop the note
event.stop(Tone.TransportTime(stateEvent.time, 'i'));
}
}.bind(this));
};
/**
* Remove an event from the part. Will recursively iterate
* into nested parts to find the event.
* @param {Time} time The time of the event
* @param {*} value Optionally select only a specific event value
* @return {Tone.Part} this
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.remove = function (time, value) {
//extract the parameters
if (time.hasOwnProperty('time')) {
value = time;
time = value.time;
}
time = this.toTicks(time);
for (var i = this._events.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var event = this._events[i];
if (event instanceof Tone.Part) {
event.remove(time, value);
} else {
if (event.startOffset === time) {
if (this.isUndef(value) || !this.isUndef(value) && event.value === value) {
this._events.splice(i, 1);
event.dispose();
}
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Remove all of the notes from the group.
* @return {Tone.Part} this
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.removeAll = function () {
this._forEach(function (event) {
event.dispose();
});
this._events = [];
return this;
};
/**
* Cancel scheduled state change events: i.e. "start" and "stop".
* @param {TimelinePosition} after The time after which to cancel the scheduled events.
* @return {Tone.Part} this
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.cancel = function (after) {
after = this.toTicks(after);
this._forEach(function (event) {
event.cancel(after);
});
this._state.cancel(after);
return this;
};
/**
* Iterate over all of the events
* @param {Function} callback
* @param {Object} ctx The context
* @private
*/
Tone.Part.prototype._forEach = function (callback, ctx) {
ctx = this.defaultArg(ctx, this);
for (var i = this._events.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
var e = this._events[i];
if (e instanceof Tone.Part) {
e._forEach(callback, ctx);
} else {
callback.call(ctx, e);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Set the attribute of all of the events
* @param {String} attr the attribute to set
* @param {*} value The value to set it to
* @private
*/
Tone.Part.prototype._setAll = function (attr, value) {
this._forEach(function (event) {
event[attr] = value;
});
};
/**
* Internal tick method
* @param {Number} time The time of the event in seconds
* @private
*/
Tone.Part.prototype._tick = function (time, value) {
if (!this.mute) {
this.callback(time, value);
}
};
/**
* Determine if the event should be currently looping
* given the loop boundries of this Part.
* @param {Tone.Event} event The event to test
* @private
*/
Tone.Part.prototype._testLoopBoundries = function (event) {
if (event.startOffset < this._loopStart || event.startOffset >= this._loopEnd) {
event.cancel(0);
} else {
//reschedule it if it's stopped
if (event.state === Tone.State.Stopped) {
this._restartEvent(event);
}
}
};
/**
* The probability of the notes being triggered.
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @name probability
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'probability', {
get: function () {
return this._probability;
},
set: function (prob) {
this._probability = prob;
this._setAll('probability', prob);
}
});
/**
* If set to true, will apply small random variation
* to the callback time. If the value is given as a time, it will randomize
* by that amount.
* @example
* event.humanize = true;
* @type {Boolean|Time}
* @name humanize
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'humanize', {
get: function () {
return this._humanize;
},
set: function (variation) {
this._humanize = variation;
this._setAll('humanize', variation);
}
});
/**
* If the part should loop or not
* between Tone.Part.loopStart and
* Tone.Part.loopEnd. An integer
* value corresponds to the number of
* loops the Part does after it starts.
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @type {Boolean|Positive}
* @name loop
* @example
* //loop the part 8 times
* part.loop = 8;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this._loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this._loop = loop;
this._forEach(function (event) {
event._loopStart = this._loopStart;
event._loopEnd = this._loopEnd;
event.loop = loop;
this._testLoopBoundries(event);
});
}
});
/**
* The loopEnd point determines when it will
* loop if Tone.Part.loop is true.
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @type {TransportTime}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this._loopEnd, 'i').toNotation();
},
set: function (loopEnd) {
this._loopEnd = this.toTicks(loopEnd);
if (this._loop) {
this._forEach(function (event) {
event.loopEnd = loopEnd;
this._testLoopBoundries(event);
});
}
}
});
/**
* The loopStart point determines when it will
* loop if Tone.Part.loop is true.
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @type {TransportTime}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return Tone.TransportTime(this._loopStart, 'i').toNotation();
},
set: function (loopStart) {
this._loopStart = this.toTicks(loopStart);
if (this._loop) {
this._forEach(function (event) {
event.loopStart = this.loopStart;
this._testLoopBoundries(event);
});
}
}
});
/**
* The playback rate of the part
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @type {Positive}
* @name playbackRate
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
this._setAll('playbackRate', rate);
}
});
/**
* The number of scheduled notes in the part.
* @memberOf Tone.Part#
* @type {Positive}
* @name length
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Part.prototype, 'length', {
get: function () {
return this._events.length;
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.Part} this
*/
Tone.Part.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.removeAll();
this._state.dispose();
this._state = null;
this.callback = null;
this._events = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Part;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Pattern arpeggiates between the given notes
* in a number of patterns. See Tone.CtrlPattern for
* a full list of patterns.
* @example
* var pattern = new Tone.Pattern(function(time, note){
* //the order of the notes passed in depends on the pattern
* }, ["C2", "D4", "E5", "A6"], "upDown");
* @extends {Tone.Loop}
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with the
* event.
* @param {Array} values The values to arpeggiate over.
*/
Tone.Pattern = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'callback',
'values',
'pattern'
], Tone.Pattern.defaults);
Tone.Loop.call(this, options);
/**
* The pattern manager
* @type {Tone.CtrlPattern}
* @private
*/
this._pattern = new Tone.CtrlPattern({
'values': options.values,
'type': options.pattern,
'index': options.index
});
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Pattern, Tone.Loop);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Pattern.defaults = {
'pattern': Tone.CtrlPattern.Type.Up,
'values': []
};
/**
* Internal function called when the notes should be called
* @param {Number} time The time the event occurs
* @private
*/
Tone.Pattern.prototype._tick = function (time) {
this.callback(time, this._pattern.value);
this._pattern.next();
};
/**
* The current index in the values array.
* @memberOf Tone.Pattern#
* @type {Positive}
* @name index
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Pattern.prototype, 'index', {
get: function () {
return this._pattern.index;
},
set: function (i) {
this._pattern.index = i;
}
});
/**
* The array of events.
* @memberOf Tone.Pattern#
* @type {Array}
* @name values
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Pattern.prototype, 'values', {
get: function () {
return this._pattern.values;
},
set: function (vals) {
this._pattern.values = vals;
}
});
/**
* The current value of the pattern.
* @memberOf Tone.Pattern#
* @type {*}
* @name value
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Pattern.prototype, 'value', {
get: function () {
return this._pattern.value;
}
});
/**
* The pattern type. See Tone.CtrlPattern for the full list of patterns.
* @memberOf Tone.Pattern#
* @type {String}
* @name pattern
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Pattern.prototype, 'pattern', {
get: function () {
return this._pattern.type;
},
set: function (pattern) {
this._pattern.type = pattern;
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.Pattern} this
*/
Tone.Pattern.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Loop.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._pattern.dispose();
this._pattern = null;
};
return Tone.Pattern;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class A sequence is an alternate notation of a part. Instead
* of passing in an array of [time, event] pairs, pass
* in an array of events which will be spaced at the
* given subdivision. Sub-arrays will subdivide that beat
* by the number of items are in the array.
* Sequence notation inspiration from [Tidal](http://yaxu.org/tidal/)
* @param {Function} callback The callback to invoke with every note
* @param {Array} events The sequence
* @param {Time} subdivision The subdivision between which events are placed.
* @extends {Tone.Part}
* @example
* var seq = new Tone.Sequence(function(time, note){
* console.log(note);
* //straight quater notes
* }, ["C4", "E4", "G4", "A4"], "4n");
* @example
* var seq = new Tone.Sequence(function(time, note){
* console.log(note);
* //subdivisions are given as subarrays
* }, ["C4", ["E4", "D4", "E4"], "G4", ["A4", "G4"]]);
*/
Tone.Sequence = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'callback',
'events',
'subdivision'
], Tone.Sequence.defaults);
//remove the events
var events = options.events;
delete options.events;
Tone.Part.call(this, options);
/**
* The subdivison of each note
* @type {Ticks}
* @private
*/
this._subdivision = this.toTicks(options.subdivision);
//if no time was passed in, the loop end is the end of the cycle
if (this.isUndef(options.loopEnd) && !this.isUndef(events)) {
this._loopEnd = events.length * this._subdivision;
}
//defaults to looping
this._loop = true;
//add all of the events
if (!this.isUndef(events)) {
for (var i = 0; i < events.length; i++) {
this.add(i, events[i]);
}
}
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Sequence, Tone.Part);
/**
* The default values.
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Sequence.defaults = { 'subdivision': '4n' };
/**
* The subdivision of the sequence. This can only be
* set in the constructor. The subdivision is the
* interval between successive steps.
* @type {Time}
* @memberOf Tone.Sequence#
* @name subdivision
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sequence.prototype, 'subdivision', {
get: function () {
return Tone.Time(this._subdivision, 'i').toNotation();
}
});
/**
* Get/Set an index of the sequence. If the index contains a subarray,
* a Tone.Sequence representing that sub-array will be returned.
* @example
* var sequence = new Tone.Sequence(playNote, ["E4", "C4", "F#4", ["A4", "Bb3"]])
* sequence.at(0)// => returns "E4"
* //set a value
* sequence.at(0, "G3");
* //get a nested sequence
* sequence.at(3).at(1)// => returns "Bb3"
* @param {Positive} index The index to get or set
* @param {*} value Optionally pass in the value to set at the given index.
*/
Tone.Sequence.prototype.at = function (index, value) {
//if the value is an array,
if (this.isArray(value)) {
//remove the current event at that index
this.remove(index);
}
//call the parent's method
return Tone.Part.prototype.at.call(this, this._indexTime(index), value);
};
/**
* Add an event at an index, if there's already something
* at that index, overwrite it. If `value` is an array,
* it will be parsed as a subsequence.
* @param {Number} index The index to add the event to
* @param {*} value The value to add at that index
* @returns {Tone.Sequence} this
*/
Tone.Sequence.prototype.add = function (index, value) {
if (value === null) {
return this;
}
if (this.isArray(value)) {
//make a subsequence and add that to the sequence
var subSubdivision = Math.round(this._subdivision / value.length);
value = new Tone.Sequence(this._tick.bind(this), value, Tone.Time(subSubdivision, 'i'));
}
Tone.Part.prototype.add.call(this, this._indexTime(index), value);
return this;
};
/**
* Remove a value from the sequence by index
* @param {Number} index The index of the event to remove
* @returns {Tone.Sequence} this
*/
Tone.Sequence.prototype.remove = function (index, value) {
Tone.Part.prototype.remove.call(this, this._indexTime(index), value);
return this;
};
/**
* Get the time of the index given the Sequence's subdivision
* @param {Number} index
* @return {Time} The time of that index
* @private
*/
Tone.Sequence.prototype._indexTime = function (index) {
if (index instanceof Tone.TransportTime) {
return index;
} else {
return Tone.TransportTime(index * this._subdivision + this.startOffset, 'i');
}
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.Sequence} this
*/
Tone.Sequence.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Part.prototype.dispose.call(this);
return this;
};
return Tone.Sequence;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PulseOscillator is a pulse oscillator with control over pulse width,
* also known as the duty cycle. At 50% duty cycle (width = 0.5) the wave is
* a square and only odd-numbered harmonics are present. At all other widths
* even-numbered harmonics are present. Read more
* [here](https://wigglewave.wordpress.com/2014/08/16/pulse-waveforms-and-harmonics/).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @param {Frequency} [frequency] The frequency of the oscillator
* @param {NormalRange} [width] The width of the pulse
* @example
* var pulse = new Tone.PulseOscillator("E5", 0.4).toMaster().start();
*/
Tone.PulseOscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'width'
], Tone.Oscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* The width of the pulse.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.width = new Tone.Signal(options.width, Tone.Type.NormalRange);
/**
* gate the width amount
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._widthGate = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* the sawtooth oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._sawtooth = new Tone.Oscillator({
frequency: options.frequency,
detune: options.detune,
type: 'sawtooth',
phase: options.phase
});
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._sawtooth.frequency;
/**
* The detune in cents.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this._sawtooth.detune;
/**
* Threshold the signal to turn it into a square
* @type {Tone.WaveShaper}
* @private
*/
this._thresh = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (val) {
if (val < 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
});
//connections
this._sawtooth.chain(this._thresh, this.output);
this.width.chain(this._widthGate, this._thresh);
this._readOnly([
'width',
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PulseOscillator, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* The default parameters.
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.PulseOscillator.defaults = {
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'phase': 0,
'width': 0.2
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.PulseOscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._sawtooth.start(time);
this._widthGate.gain.setValueAtTime(1, time);
};
/**
* stop the oscillator
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.PulseOscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._sawtooth.stop(time);
//the width is still connected to the output.
//that needs to be stopped also
this._widthGate.gain.setValueAtTime(0, time);
};
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.PulseOscillator#
* @type {Degrees}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PulseOscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._sawtooth.phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._sawtooth.phase = phase;
}
});
/**
* The type of the oscillator. Always returns "pulse".
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.PulseOscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PulseOscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return 'pulse';
}
});
/**
* The partials of the waveform. Cannot set partials for this waveform type
* @memberOf Tone.PulseOscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @private
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PulseOscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
return [];
}
});
/**
* Clean up method.
* @return {Tone.PulseOscillator} this
*/
Tone.PulseOscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._sawtooth.dispose();
this._sawtooth = null;
this._writable([
'width',
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
this.width.dispose();
this.width = null;
this._widthGate.dispose();
this._widthGate = null;
this._thresh.dispose();
this._thresh = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PulseOscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PWMOscillator modulates the width of a Tone.PulseOscillator
* at the modulationFrequency. This has the effect of continuously
* changing the timbre of the oscillator by altering the harmonics
* generated.
*
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency} frequency The starting frequency of the oscillator.
* @param {Frequency} modulationFrequency The modulation frequency of the width of the pulse.
* @example
* var pwm = new Tone.PWMOscillator("Ab3", 0.3).toMaster().start();
*/
Tone.PWMOscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'modulationFrequency'
], Tone.PWMOscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* the pulse oscillator
* @type {Tone.PulseOscillator}
* @private
*/
this._pulse = new Tone.PulseOscillator(options.modulationFrequency);
//change the pulse oscillator type
this._pulse._sawtooth.type = 'sine';
/**
* the modulator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Oscillator({
'frequency': options.frequency,
'detune': options.detune,
'phase': options.phase
});
/**
* Scale the oscillator so it doesn't go silent
* at the extreme values.
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._scale = new Tone.Multiply(2);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._modulator.frequency;
/**
* The detune of the oscillator.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this._modulator.detune;
/**
* The modulation rate of the oscillator.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.modulationFrequency = this._pulse.frequency;
//connections
this._modulator.chain(this._scale, this._pulse.width);
this._pulse.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'modulationFrequency',
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PWMOscillator, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.PWMOscillator.defaults = {
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'phase': 0,
'modulationFrequency': 0.4
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @private
*/
Tone.PWMOscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._modulator.start(time);
this._pulse.start(time);
};
/**
* stop the oscillator
* @param {Time} time (optional) timing parameter
* @private
*/
Tone.PWMOscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._modulator.stop(time);
this._pulse.stop(time);
};
/**
* The type of the oscillator. Always returns "pwm".
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.PWMOscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PWMOscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return 'pwm';
}
});
/**
* The partials of the waveform. Cannot set partials for this waveform type
* @memberOf Tone.PWMOscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @private
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PWMOscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
return [];
}
});
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.PWMOscillator#
* @type {number}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.PWMOscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._modulator.phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._modulator.phase = phase;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.PWMOscillator} this
*/
Tone.PWMOscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._pulse.dispose();
this._pulse = null;
this._scale.dispose();
this._scale = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this._writable([
'modulationFrequency',
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
this.modulationFrequency = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PWMOscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.FMOscillator
*
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency} frequency The starting frequency of the oscillator.
* @param {String} type The type of the carrier oscillator.
* @param {String} modulationType The type of the modulator oscillator.
* @example
* //a sine oscillator frequency-modulated by a square wave
* var fmOsc = new Tone.FMOscillator("Ab3", "sine", "square").toMaster().start();
*/
Tone.FMOscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'type',
'modulationType'
], Tone.FMOscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* The carrier oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._carrier = new Tone.Oscillator(options.frequency, options.type);
/**
* The oscillator's frequency
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune control signal.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this._carrier.detune;
this.detune.value = options.detune;
/**
* The modulation index which is in essence the depth or amount of the modulation. In other terms it is the
* ratio of the frequency of the modulating signal (mf) to the amplitude of the
* modulating signal (ma) -- as in ma/mf.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.modulationIndex = new Tone.Multiply(options.modulationIndex);
this.modulationIndex.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* The modulating oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Oscillator(options.frequency, options.modulationType);
/**
* Harmonicity is the frequency ratio between the carrier and the modulator oscillators.
* A harmonicity of 1 gives both oscillators the same frequency.
* Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch the modulator an octave below carrier
* synth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* the node where the modulation happens
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationNode = new Tone.Gain(0);
//connections
this.frequency.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this._modulator.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.modulationIndex, this._modulationNode);
this._modulator.connect(this._modulationNode.gain);
this._modulationNode.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this._carrier.connect(this.output);
this.detune.connect(this._modulator.detune);
this.phase = options.phase;
this._readOnly([
'modulationIndex',
'frequency',
'detune',
'harmonicity'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FMOscillator, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.FMOscillator.defaults = {
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'phase': 0,
'modulationIndex': 2,
'modulationType': 'square',
'harmonicity': 1
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @private
*/
Tone.FMOscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._modulator.start(time);
this._carrier.start(time);
};
/**
* stop the oscillator
* @param {Time} time (optional) timing parameter
* @private
*/
Tone.FMOscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._modulator.stop(time);
this._carrier.stop(time);
};
/**
* The type of the carrier oscillator
* @memberOf Tone.FMOscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FMOscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._carrier.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._carrier.type = type;
}
});
/**
* The type of the modulator oscillator
* @memberOf Tone.FMOscillator#
* @type {String}
* @name modulationType
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FMOscillator.prototype, 'modulationType', {
get: function () {
return this._modulator.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._modulator.type = type;
}
});
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.FMOscillator#
* @type {number}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FMOscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._carrier.phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._carrier.phase = phase;
this._modulator.phase = phase;
}
});
/**
* The partials of the carrier waveform. A partial represents
* the amplitude at a harmonic. The first harmonic is the
* fundamental frequency, the second is the octave and so on
* following the harmonic series.
* Setting this value will automatically set the type to "custom".
* The value is an empty array when the type is not "custom".
* @memberOf Tone.FMOscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @example
* osc.partials = [1, 0.2, 0.01];
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FMOscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
return this._carrier.partials;
},
set: function (partials) {
this._carrier.partials = partials;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.FMOscillator} this
*/
Tone.FMOscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'modulationIndex',
'frequency',
'detune',
'harmonicity'
]);
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this._carrier.dispose();
this._carrier = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this._modulationNode.dispose();
this._modulationNode = null;
this.modulationIndex.dispose();
this.modulationIndex = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FMOscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.AMOscillator
*
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency} frequency The starting frequency of the oscillator.
* @param {String} type The type of the carrier oscillator.
* @param {String} modulationType The type of the modulator oscillator.
* @example
* //a sine oscillator frequency-modulated by a square wave
* var fmOsc = new Tone.AMOscillator("Ab3", "sine", "square").toMaster().start();
*/
Tone.AMOscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'type',
'modulationType'
], Tone.AMOscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* The carrier oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._carrier = new Tone.Oscillator(options.frequency, options.type);
/**
* The oscillator's frequency
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this._carrier.frequency;
/**
* The detune control signal.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this._carrier.detune;
this.detune.value = options.detune;
/**
* The modulating oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Oscillator(options.frequency, options.modulationType);
/**
* convert the -1,1 output to 0,1
* @type {Tone.AudioToGain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationScale = new Tone.AudioToGain();
/**
* Harmonicity is the frequency ratio between the carrier and the modulator oscillators.
* A harmonicity of 1 gives both oscillators the same frequency.
* Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch the modulator an octave below carrier
* synth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* the node where the modulation happens
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationNode = new Tone.Gain(0);
//connections
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this._modulator.frequency);
this.detune.connect(this._modulator.detune);
this._modulator.chain(this._modulationScale, this._modulationNode.gain);
this._carrier.chain(this._modulationNode, this.output);
this.phase = options.phase;
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'detune',
'harmonicity'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.AMOscillator, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.AMOscillator.defaults = {
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'phase': 0,
'modulationType': 'square',
'harmonicity': 1
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @private
*/
Tone.AMOscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._modulator.start(time);
this._carrier.start(time);
};
/**
* stop the oscillator
* @param {Time} time (optional) timing parameter
* @private
*/
Tone.AMOscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._modulator.stop(time);
this._carrier.stop(time);
};
/**
* The type of the carrier oscillator
* @memberOf Tone.AMOscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AMOscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._carrier.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._carrier.type = type;
}
});
/**
* The type of the modulator oscillator
* @memberOf Tone.AMOscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name modulationType
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AMOscillator.prototype, 'modulationType', {
get: function () {
return this._modulator.type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._modulator.type = type;
}
});
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.AMOscillator#
* @type {number}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AMOscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._carrier.phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._carrier.phase = phase;
this._modulator.phase = phase;
}
});
/**
* The partials of the carrier waveform. A partial represents
* the amplitude at a harmonic. The first harmonic is the
* fundamental frequency, the second is the octave and so on
* following the harmonic series.
* Setting this value will automatically set the type to "custom".
* The value is an empty array when the type is not "custom".
* @memberOf Tone.AMOscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @example
* osc.partials = [1, 0.2, 0.01];
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.AMOscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
return this._carrier.partials;
},
set: function (partials) {
this._carrier.partials = partials;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.AMOscillator} this
*/
Tone.AMOscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'detune',
'harmonicity'
]);
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this._carrier.dispose();
this._carrier = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this._modulationNode.dispose();
this._modulationNode = null;
this._modulationScale.dispose();
this._modulationScale = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AMOscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.FatOscillator
*
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency} frequency The starting frequency of the oscillator.
* @param {String} type The type of the carrier oscillator.
* @param {String} modulationType The type of the modulator oscillator.
* @example
* //a sine oscillator frequency-modulated by a square wave
* var fmOsc = new Tone.FatOscillator("Ab3", "sine", "square").toMaster().start();
*/
Tone.FatOscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'type',
'spread'
], Tone.FatOscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* The oscillator's frequency
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune control signal.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* The array of oscillators
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._oscillators = [];
/**
* The total spread of the oscillators
* @type {Cents}
* @private
*/
this._spread = options.spread;
/**
* The type of the oscillator
* @type {String}
* @private
*/
this._type = options.type;
/**
* The phase of the oscillators
* @type {Degrees}
* @private
*/
this._phase = options.phase;
/**
* The partials array
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._partials = this.defaultArg(options.partials, []);
//set the count initially
this.count = options.count;
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FatOscillator, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.FatOscillator.defaults = {
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'phase': 0,
'spread': 20,
'count': 3,
'type': 'sawtooth'
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @private
*/
Tone.FatOscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.start(time);
});
};
/**
* stop the oscillator
* @param {Time} time (optional) timing parameter
* @private
*/
Tone.FatOscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.stop(time);
});
};
/**
* Iterate over all of the oscillators
* @param {Function} iterator The iterator function
* @private
*/
Tone.FatOscillator.prototype._forEach = function (iterator) {
for (var i = 0; i < this._oscillators.length; i++) {
iterator.call(this, this._oscillators[i], i);
}
};
/**
* The type of the carrier oscillator
* @memberOf Tone.FatOscillator#
* @type {string}
* @name type
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FatOscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
return this._type;
},
set: function (type) {
this._type = type;
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.type = type;
});
}
});
/**
* The detune spread between the oscillators. If "count" is
* set to 3 oscillators and the "spread" is set to 40,
* the three oscillators would be detuned like this: [-20, 0, 20]
* for a total detune spread of 40 cents.
* @memberOf Tone.FatOscillator#
* @type {Cents}
* @name spread
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FatOscillator.prototype, 'spread', {
get: function () {
return this._spread;
},
set: function (spread) {
this._spread = spread;
if (this._oscillators.length > 1) {
var start = -spread / 2;
var step = spread / (this._oscillators.length - 1);
this._forEach(function (osc, i) {
osc.detune.value = start + step * i;
});
}
}
});
/**
* The number of detuned oscillators
* @memberOf Tone.FatOscillator#
* @type {Number}
* @name count
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FatOscillator.prototype, 'count', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillators.length;
},
set: function (count) {
count = Math.max(count, 1);
if (this._oscillators.length !== count) {
// var partials = this.partials;
// var type = this.type;
//dispose the previous oscillators
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.dispose();
});
this._oscillators = [];
for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) {
var osc = new Tone.Oscillator();
if (this.type === Tone.Oscillator.Type.Custom) {
osc.partials = this._partials;
} else {
osc.type = this._type;
}
osc.phase = this._phase;
osc.volume.value = -6 - count;
this.frequency.connect(osc.frequency);
this.detune.connect(osc.detune);
osc.connect(this.output);
this._oscillators[i] = osc;
}
//set the spread
this.spread = this._spread;
if (this.state === Tone.State.Started) {
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.start();
});
}
}
}
});
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.FatOscillator#
* @type {Number}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FatOscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._phase = phase;
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.phase = phase;
});
}
});
/**
* The partials of the carrier waveform. A partial represents
* the amplitude at a harmonic. The first harmonic is the
* fundamental frequency, the second is the octave and so on
* following the harmonic series.
* Setting this value will automatically set the type to "custom".
* The value is an empty array when the type is not "custom".
* @memberOf Tone.FatOscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @example
* osc.partials = [1, 0.2, 0.01];
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.FatOscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
return this._partials;
},
set: function (partials) {
this._partials = partials;
this._type = Tone.Oscillator.Type.Custom;
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.partials = partials;
});
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.FatOscillator} this
*/
Tone.FatOscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this._forEach(function (osc) {
osc.dispose();
});
this._oscillators = null;
this._partials = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FatOscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.OmniOscillator aggregates Tone.Oscillator, Tone.PulseOscillator,
* Tone.PWMOscillator, Tone.FMOscillator, Tone.AMOscillator, and Tone.FatOscillator
* into one class. The oscillator class can be changed by setting the `type`.
* `omniOsc.type = "pwm"` will set it to the Tone.PWMOscillator. Prefixing
* any of the basic types ("sine", "square4", etc.) with "fm", "am", or "fat"
* will use the FMOscillator, AMOscillator or FatOscillator respectively.
* For example: `omniOsc.type = "fatsawtooth"` will create set the oscillator
* to a FatOscillator of type "sawtooth".
*
* @extends {Tone.Oscillator}
* @constructor
* @param {Frequency} frequency The initial frequency of the oscillator.
* @param {String} type The type of the oscillator.
* @example
* var omniOsc = new Tone.OmniOscillator("C#4", "pwm");
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'frequency',
'type'
], Tone.OmniOscillator.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune control
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* the type of the oscillator source
* @type {String}
* @private
*/
this._sourceType = undefined;
/**
* the oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
* @private
*/
this._oscillator = null;
//set the oscillator
this.type = options.type;
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
//set the options
this.set(options);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.OmniOscillator, Tone.Oscillator);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @type {Object}
* @const
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator.defaults = {
'frequency': 440,
'detune': 0,
'type': 'sine',
'phase': 0
};
/**
* @enum {String}
* @private
*/
var OmniOscType = {
Pulse: 'PulseOscillator',
PWM: 'PWMOscillator',
Osc: 'Oscillator',
FM: 'FMOscillator',
AM: 'AMOscillator',
Fat: 'FatOscillator'
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time to start the oscillator
* @private
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype._start = function (time) {
this._oscillator.start(time);
};
/**
* start the oscillator
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time to start the oscillator
* @private
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype._stop = function (time) {
this._oscillator.stop(time);
};
/**
* The type of the oscillator. Can be any of the basic types: sine, square, triangle, sawtooth. Or
* prefix the basic types with "fm", "am", or "fat" to use the FMOscillator, AMOscillator or FatOscillator
* types. The oscillator could also be set to "pwm" or "pulse". All of the parameters of the
* oscillator's class are accessible when the oscillator is set to that type, but throws an error
* when it's not.
*
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {String}
* @name type
* @example
* omniOsc.type = "pwm";
* //modulationFrequency is parameter which is available
* //only when the type is "pwm".
* omniOsc.modulationFrequency.value = 0.5;
* @example
* //an square wave frequency modulated by a sawtooth
* omniOsc.type = "fmsquare";
* omniOsc.modulationType = "sawtooth";
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
var prefix = '';
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.FM) {
prefix = 'fm';
} else if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.AM) {
prefix = 'am';
} else if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.Fat) {
prefix = 'fat';
}
return prefix + this._oscillator.type;
},
set: function (type) {
if (type.substr(0, 2) === 'fm') {
this._createNewOscillator(OmniOscType.FM);
this._oscillator.type = type.substr(2);
} else if (type.substr(0, 2) === 'am') {
this._createNewOscillator(OmniOscType.AM);
this._oscillator.type = type.substr(2);
} else if (type.substr(0, 3) === 'fat') {
this._createNewOscillator(OmniOscType.Fat);
this._oscillator.type = type.substr(3);
} else if (type === 'pwm') {
this._createNewOscillator(OmniOscType.PWM);
} else if (type === 'pulse') {
this._createNewOscillator(OmniOscType.Pulse);
} else {
this._createNewOscillator(OmniOscType.Osc);
this._oscillator.type = type;
}
}
});
/**
* The partials of the waveform. A partial represents
* the amplitude at a harmonic. The first harmonic is the
* fundamental frequency, the second is the octave and so on
* following the harmonic series.
* Setting this value will automatically set the type to "custom".
* The value is an empty array when the type is not "custom".
* This is not available on "pwm" and "pulse" oscillator types.
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {Array}
* @name partials
* @example
* osc.partials = [1, 0.2, 0.01];
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'partials', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillator.partials;
},
set: function (partials) {
this._oscillator.partials = partials;
}
});
/**
* Set a member/attribute of the oscillator.
* @param {Object|String} params
* @param {number=} value
* @param {Time=} rampTime
* @returns {Tone.OmniOscillator} this
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype.set = function (params, value) {
//make sure the type is set first
if (params === 'type') {
this.type = value;
} else if (this.isObject(params) && params.hasOwnProperty('type')) {
this.type = params.type;
}
//then set the rest
Tone.prototype.set.apply(this, arguments);
return this;
};
/**
* connect the oscillator to the frequency and detune signals
* @private
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype._createNewOscillator = function (oscType) {
if (oscType !== this._sourceType) {
this._sourceType = oscType;
var OscillatorConstructor = Tone[oscType];
//short delay to avoid clicks on the change
var now = this.now() + this.blockTime;
if (this._oscillator !== null) {
var oldOsc = this._oscillator;
oldOsc.stop(now);
//dispose the old one
setTimeout(function () {
oldOsc.dispose();
oldOsc = null;
}, this.blockTime * 1000);
}
this._oscillator = new OscillatorConstructor();
this.frequency.connect(this._oscillator.frequency);
this.detune.connect(this._oscillator.detune);
this._oscillator.connect(this.output);
if (this.state === Tone.State.Started) {
this._oscillator.start(now);
}
}
};
/**
* The phase of the oscillator in degrees.
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {Degrees}
* @name phase
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'phase', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillator.phase;
},
set: function (phase) {
this._oscillator.phase = phase;
}
});
/**
* The width of the oscillator (only if the oscillator is set to "pulse")
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
* @name width
* @example
* var omniOsc = new Tone.OmniOscillator(440, "pulse");
* //can access the width attribute only if type === "pulse"
* omniOsc.width.value = 0.2;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'width', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.Pulse) {
return this._oscillator.width;
}
}
});
/**
* The number of detuned oscillators
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {Number}
* @name count
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'count', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.Fat) {
return this._oscillator.count;
}
},
set: function (count) {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.Fat) {
this._oscillator.count = count;
}
}
});
/**
* The detune spread between the oscillators. If "count" is
* set to 3 oscillators and the "spread" is set to 40,
* the three oscillators would be detuned like this: [-20, 0, 20]
* for a total detune spread of 40 cents. See Tone.FatOscillator
* for more info.
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {Cents}
* @name spread
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'spread', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.Fat) {
return this._oscillator.spread;
}
},
set: function (spread) {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.Fat) {
this._oscillator.spread = spread;
}
}
});
/**
* The type of the modulator oscillator. Only if the oscillator
* is set to "am" or "fm" types. see. Tone.AMOscillator or Tone.FMOscillator
* for more info.
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {String}
* @name modulationType
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'modulationType', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.FM || this._sourceType === OmniOscType.AM) {
return this._oscillator.modulationType;
}
},
set: function (mType) {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.FM || this._sourceType === OmniOscType.AM) {
this._oscillator.modulationType = mType;
}
}
});
/**
* The modulation index which is in essence the depth or amount of the modulation. In other terms it is the
* ratio of the frequency of the modulating signal (mf) to the amplitude of the
* modulating signal (ma) -- as in ma/mf.
* See Tone.FMOscillator for more info.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @name modulationIndex
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'modulationIndex', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.FM) {
return this._oscillator.modulationIndex;
}
}
});
/**
* Harmonicity is the frequency ratio between the carrier and the modulator oscillators.
* A harmonicity of 1 gives both oscillators the same frequency.
* Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave. See Tone.AMOscillator or Tone.FMOscillator
* for more info.
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @signal
* @type {Positive}
* @name harmonicity
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'harmonicity', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.FM || this._sourceType === OmniOscType.AM) {
return this._oscillator.harmonicity;
}
}
});
/**
* The modulationFrequency Signal of the oscillator
* (only if the oscillator type is set to pwm). See
* Tone.PWMOscillator for more info.
* @memberOf Tone.OmniOscillator#
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
* @name modulationFrequency
* @example
* var omniOsc = new Tone.OmniOscillator(440, "pwm");
* //can access the modulationFrequency attribute only if type === "pwm"
* omniOsc.modulationFrequency.value = 0.2;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype, 'modulationFrequency', {
get: function () {
if (this._sourceType === OmniOscType.PWM) {
return this._oscillator.modulationFrequency;
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.OmniOscillator} this
*/
Tone.OmniOscillator.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'detune'
]);
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this._oscillator.dispose();
this._oscillator = null;
this._sourceType = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.OmniOscillator;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Base-class for all instruments
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
*/
Tone.Instrument = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Instrument.defaults);
/**
* The output and volume triming node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume of the output in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
* @example
* source.volume.value = -6;
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Instrument);
/**
* the default attributes
* @type {object}
*/
Tone.Instrument.defaults = {
/** the volume of the output in decibels */
'volume': 0
};
/**
* @abstract
* @param {string|number} note the note to trigger
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time to trigger the ntoe
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity to trigger the note
*/
Tone.Instrument.prototype.triggerAttack = Tone.noOp;
/**
* @abstract
* @param {Time} [time=now] when to trigger the release
*/
Tone.Instrument.prototype.triggerRelease = Tone.noOp;
/**
* Trigger the attack and then the release after the duration.
* @param {Frequency} note The note to trigger.
* @param {Time} duration How long the note should be held for before
* triggering the release.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the note should be triggered.
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] The velocity the note should be triggered at.
* @returns {Tone.Instrument} this
* @example
* //trigger "C4" for the duration of an 8th note
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "8n");
*/
Tone.Instrument.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (note, duration, time, velocity) {
if (this.isUndef(time)) {
time = this.now() + this.blockTime;
} else {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
}
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this.triggerAttack(note, time, velocity);
this.triggerRelease(time + duration);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Instrument} this
*/
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this._writable(['volume']);
this.volume = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Instrument;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class This is an abstract base class for other monophonic instruments to
* extend. IMPORTANT: It does not make any sound on its own and
* shouldn't be directly instantiated.
*
* @constructor
* @abstract
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
*/
Tone.Monophonic = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Monophonic.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The glide time between notes.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.portamento = options.portamento;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Monophonic, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Monophonic.defaults = { 'portamento': 0 };
/**
* Trigger the attack of the note optionally with a given velocity.
*
*
* @param {Frequency} note The note to trigger.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the note should start.
* @param {number} [velocity=1] velocity The velocity scaler
* determines how "loud" the note
* will be triggered.
* @returns {Tone.Monophonic} this
* @example
* synth.triggerAttack("C4");
* @example
* //trigger the note a half second from now at half velocity
* synth.triggerAttack("C4", "+0.5", 0.5);
*/
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.triggerAttack = function (note, time, velocity) {
if (this.isUndef(time)) {
time = this.now() + this.blockTime;
} else {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
}
this._triggerEnvelopeAttack(time, velocity);
this.setNote(note, time);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the release portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] If no time is given, the release happens immediatly
* @returns {Tone.Monophonic} this
* @example
* synth.triggerRelease();
*/
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
if (this.isUndef(time)) {
time = this.now() + this.blockTime;
} else {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
}
this._triggerEnvelopeRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* override this method with the actual method
* @abstract
* @private
*/
Tone.Monophonic.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function () {
};
/**
* override this method with the actual method
* @abstract
* @private
*/
Tone.Monophonic.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function () {
};
/**
* Set the note at the given time. If no time is given, the note
* will set immediately.
* @param {Frequency} note The note to change to.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the note should be set.
* @returns {Tone.Monophonic} this
* @example
* //change to F#6 in one quarter note from now.
* synth.setNote("F#6", "+4n");
* @example
* //change to Bb4 right now
* synth.setNote("Bb4");
*/
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.setNote = function (note, time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
if (this.portamento > 0) {
var currentNote = this.frequency.value;
this.frequency.setValueAtTime(currentNote, time);
var portTime = this.toSeconds(this.portamento);
this.frequency.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(note, time + portTime);
} else {
this.frequency.setValueAtTime(note, time);
}
return this;
};
return Tone.Monophonic;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Synth is composed simply of a Tone.OmniOscillator
* routed through a Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope.
*  *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.Synth().toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "8n");
*/
Tone.Synth = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Synth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The oscillator.
* @type {Tone.OmniOscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = new Tone.OmniOscillator(options.oscillator);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this.oscillator.frequency;
/**
* The detune control.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this.oscillator.detune;
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
//connect the oscillators to the output
this.oscillator.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
//start the oscillators
this.oscillator.start();
this._readOnly([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Synth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Synth.defaults = {
'oscillator': { 'type': 'triangle' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.005,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0.3,
'release': 1
}
};
/**
* start the attack portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.Synth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.Synth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* start the release portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.Synth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.Synth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Synth} this
*/
Tone.Synth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'envelope'
]);
this.oscillator.dispose();
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Synth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class AMSynth uses the output of one Tone.Synth to modulate the
* amplitude of another Tone.Synth. The harmonicity (the ratio between
* the two signals) affects the timbre of the output signal greatly.
* Read more about Amplitude Modulation Synthesis on
* [SoundOnSound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/mar00/articles/synthsecrets.htm).
*
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.Synth().toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "8n");
*/
Tone.Synth = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Synth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The oscillator.
* @type {Tone.OmniOscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = new Tone.OmniOscillator(options.oscillator);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this.oscillator.frequency;
/**
* The detune control.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this.oscillator.detune;
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
//connect the oscillators to the output
this.oscillator.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
//start the oscillators
this.oscillator.start();
this._readOnly([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Synth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Synth.defaults = {
'oscillator': { 'type': 'triangle' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.005,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0.3,
'release': 1
}
};
/**
* start the attack portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.Synth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.Synth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* start the release portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.Synth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.Synth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Synth} this
*/
Tone.Synth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'envelope'
]);
this.oscillator.dispose();
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Synth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class AMSynth uses the output of one Tone.Synth to modulate the
* amplitude of another Tone.Synth. The harmonicity (the ratio between
* the two signals) affects the timbre of the output signal greatly.
* Read more about Amplitude Modulation Synthesis on
* [SoundOnSound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/mar00/articles/synthsecrets.htm).
*  *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.AMSynth().toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "4n");
*/
Tone.AMSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.AMSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The carrier voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._carrier = new Tone.Synth();
this._carrier.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The carrier's oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = this._carrier.oscillator;
/**
* The carrier's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.envelope = this._carrier.envelope.set(options.envelope);
/**
* The modulator voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Synth();
this._modulator.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The modulator's oscillator which is applied
* to the amplitude of the oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulation = this._modulator.oscillator.set(options.modulation);
/**
* The modulator's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulationEnvelope = this._modulator.envelope.set(options.modulationEnvelope);
/**
* The frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(440, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune in cents
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* Harmonicity is the ratio between the two voices. A harmonicity of
* 1 is no change. Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch voice1 an octave below voice0
* synth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* convert the -1,1 output to 0,1
* @type {Tone.AudioToGain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationScale = new Tone.AudioToGain();
/**
* the node where the modulation happens
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationNode = new Tone.Gain();
//control the two voices frequency
this.frequency.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this._modulator.frequency);
this.detune.fan(this._carrier.detune, this._modulator.detune);
this._modulator.chain(this._modulationScale, this._modulationNode.gain);
this._carrier.chain(this._modulationNode, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.AMSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.AMSynth.defaults = {
'harmonicity': 3,
'detune': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0.01,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'modulation': { 'type': 'square' },
'modulationEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.5,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
};
/**
* trigger the attack portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will occur
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note
* @private
* @returns {Tone.AMSynth} this
*/
Tone.AMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the port glide
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* trigger the release portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will release
* @private
* @returns {Tone.AMSynth} this
*/
Tone.AMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.AMSynth} this
*/
Tone.AMSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
this._carrier.dispose();
this._carrier = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this._modulationScale.dispose();
this._modulationScale = null;
this._modulationNode.dispose();
this._modulationNode = null;
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope = null;
this.modulationEnvelope = null;
this.modulation = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AMSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MonoSynth is composed of one oscillator, one filter, and two envelopes.
* The amplitude of the Tone.Oscillator and the cutoff frequency of the
* Tone.Filter are controlled by Tone.Envelopes.
*
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.AMSynth().toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "4n");
*/
Tone.AMSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.AMSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The carrier voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._carrier = new Tone.Synth();
this._carrier.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The carrier's oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = this._carrier.oscillator;
/**
* The carrier's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.envelope = this._carrier.envelope.set(options.envelope);
/**
* The modulator voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Synth();
this._modulator.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The modulator's oscillator which is applied
* to the amplitude of the oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulation = this._modulator.oscillator.set(options.modulation);
/**
* The modulator's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulationEnvelope = this._modulator.envelope.set(options.modulationEnvelope);
/**
* The frequency.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(440, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune in cents
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* Harmonicity is the ratio between the two voices. A harmonicity of
* 1 is no change. Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch voice1 an octave below voice0
* synth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* convert the -1,1 output to 0,1
* @type {Tone.AudioToGain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationScale = new Tone.AudioToGain();
/**
* the node where the modulation happens
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._modulationNode = new Tone.Gain();
//control the two voices frequency
this.frequency.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this._modulator.frequency);
this.detune.fan(this._carrier.detune, this._modulator.detune);
this._modulator.chain(this._modulationScale, this._modulationNode.gain);
this._carrier.chain(this._modulationNode, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.AMSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.AMSynth.defaults = {
'harmonicity': 3,
'detune': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0.01,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'modulation': { 'type': 'square' },
'modulationEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.5,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
};
/**
* trigger the attack portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will occur
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note
* @private
* @returns {Tone.AMSynth} this
*/
Tone.AMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the port glide
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* trigger the release portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will release
* @private
* @returns {Tone.AMSynth} this
*/
Tone.AMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.AMSynth} this
*/
Tone.AMSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
this._carrier.dispose();
this._carrier = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this._modulationScale.dispose();
this._modulationScale = null;
this._modulationNode.dispose();
this._modulationNode = null;
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope = null;
this.modulationEnvelope = null;
this.modulation = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.AMSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MonoSynth is composed of one oscillator, one filter, and two envelopes.
* The amplitude of the Tone.Oscillator and the cutoff frequency of the
* Tone.Filter are controlled by Tone.Envelopes.
*  *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.MonoSynth({
* "oscillator" : {
* "type" : "square"
* },
* "envelope" : {
* "attack" : 0.1
* }
* }).toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "8n");
*/
Tone.MonoSynth = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.MonoSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The oscillator.
* @type {Tone.OmniOscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = new Tone.OmniOscillator(options.oscillator);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this.oscillator.frequency;
/**
* The detune control.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this.oscillator.detune;
/**
* The filter.
* @type {Tone.Filter}
*/
this.filter = new Tone.Filter(options.filter);
/**
* The filter envelope.
* @type {Tone.FrequencyEnvelope}
*/
this.filterEnvelope = new Tone.FrequencyEnvelope(options.filterEnvelope);
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
//connect the oscillators to the output
this.oscillator.chain(this.filter, this.envelope, this.output);
//start the oscillators
this.oscillator.start();
//connect the filter envelope
this.filterEnvelope.connect(this.filter.frequency);
this._readOnly([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'filter',
'filterEnvelope',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MonoSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.defaults = {
'frequency': 'C4',
'detune': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'square' },
'filter': {
'Q': 6,
'type': 'lowpass',
'rolloff': -24
},
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.005,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0.9,
'release': 1
},
'filterEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.06,
'decay': 0.2,
'sustain': 0.5,
'release': 2,
'baseFrequency': 200,
'octaves': 7,
'exponent': 2
}
};
/**
* start the attack portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.MonoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.filterEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
return this;
};
/**
* start the release portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.MonoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.filterEnvelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.MonoSynth} this
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'filter',
'filterEnvelope',
'envelope'
]);
this.oscillator.dispose();
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
this.filterEnvelope.dispose();
this.filterEnvelope = null;
this.filter.dispose();
this.filter = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MonoSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.DuoSynth is a monophonic synth composed of two
* MonoSynths run in parallel with control over the
* frequency ratio between the two voices and vibrato effect.
*
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.MonoSynth({
* "oscillator" : {
* "type" : "square"
* },
* "envelope" : {
* "attack" : 0.1
* }
* }).toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "8n");
*/
Tone.MonoSynth = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.MonoSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The oscillator.
* @type {Tone.OmniOscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = new Tone.OmniOscillator(options.oscillator);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = this.oscillator.frequency;
/**
* The detune control.
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = this.oscillator.detune;
/**
* The filter.
* @type {Tone.Filter}
*/
this.filter = new Tone.Filter(options.filter);
/**
* The filter envelope.
* @type {Tone.FrequencyEnvelope}
*/
this.filterEnvelope = new Tone.FrequencyEnvelope(options.filterEnvelope);
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
//connect the oscillators to the output
this.oscillator.chain(this.filter, this.envelope, this.output);
//start the oscillators
this.oscillator.start();
//connect the filter envelope
this.filterEnvelope.connect(this.filter.frequency);
this._readOnly([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'filter',
'filterEnvelope',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MonoSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.defaults = {
'frequency': 'C4',
'detune': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'square' },
'filter': {
'Q': 6,
'type': 'lowpass',
'rolloff': -24
},
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.005,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0.9,
'release': 1
},
'filterEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.06,
'decay': 0.2,
'sustain': 0.5,
'release': 2,
'baseFrequency': 200,
'octaves': 7,
'exponent': 2
}
};
/**
* start the attack portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.MonoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.filterEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
return this;
};
/**
* start the release portion of the envelope
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.MonoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.filterEnvelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.MonoSynth} this
*/
Tone.MonoSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'oscillator',
'frequency',
'detune',
'filter',
'filterEnvelope',
'envelope'
]);
this.oscillator.dispose();
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
this.filterEnvelope.dispose();
this.filterEnvelope = null;
this.filter.dispose();
this.filter = null;
this.frequency = null;
this.detune = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MonoSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.DuoSynth is a monophonic synth composed of two
* MonoSynths run in parallel with control over the
* frequency ratio between the two voices and vibrato effect.
*  *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var duoSynth = new Tone.DuoSynth().toMaster();
* duoSynth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "2n");
*/
Tone.DuoSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.DuoSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* the first voice
* @type {Tone.MonoSynth}
*/
this.voice0 = new Tone.MonoSynth(options.voice0);
this.voice0.volume.value = -10;
/**
* the second voice
* @type {Tone.MonoSynth}
*/
this.voice1 = new Tone.MonoSynth(options.voice1);
this.voice1.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The vibrato LFO.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._vibrato = new Tone.LFO(options.vibratoRate, -50, 50);
this._vibrato.start();
/**
* the vibrato frequency
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.vibratoRate = this._vibrato.frequency;
/**
* the vibrato gain
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._vibratoGain = new Tone.Gain(options.vibratoAmount, Tone.Type.Positive);
/**
* The amount of vibrato
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.vibratoAmount = this._vibratoGain.gain;
/**
* the frequency control
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(440, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* Harmonicity is the ratio between the two voices. A harmonicity of
* 1 is no change. Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch voice1 an octave below voice0
* duoSynth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
//control the two voices frequency
this.frequency.connect(this.voice0.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this.voice1.frequency);
this._vibrato.connect(this._vibratoGain);
this._vibratoGain.fan(this.voice0.detune, this.voice1.detune);
this.voice0.connect(this.output);
this.voice1.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'voice0',
'voice1',
'frequency',
'vibratoAmount',
'vibratoRate'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.DuoSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.defaults = {
'vibratoAmount': 0.5,
'vibratoRate': 5,
'harmonicity': 1.5,
'voice0': {
'volume': -10,
'portamento': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'filterEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
},
'voice1': {
'volume': -10,
'portamento': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'filterEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
}
};
/**
* start the attack portion of the envelopes
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.DuoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.voice0.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.voice1.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.voice0.filterEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
this.voice1.filterEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
return this;
};
/**
* start the release portion of the envelopes
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.DuoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.voice0.triggerRelease(time);
this.voice1.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.DuoSynth} this
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'voice0',
'voice1',
'frequency',
'vibratoAmount',
'vibratoRate'
]);
this.voice0.dispose();
this.voice0 = null;
this.voice1.dispose();
this.voice1 = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this._vibratoGain.dispose();
this._vibratoGain = null;
this._vibrato = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this.vibratoAmount.dispose();
this.vibratoAmount = null;
this.vibratoRate = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.DuoSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class FMSynth is composed of two Tone.Synths where one Tone.Synth modulates
* the frequency of a second Tone.Synth. A lot of spectral content
* can be explored using the modulationIndex parameter. Read more about
* frequency modulation synthesis on [SoundOnSound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/apr00/articles/synthsecrets.htm).
*
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var duoSynth = new Tone.DuoSynth().toMaster();
* duoSynth.triggerAttackRelease("C4", "2n");
*/
Tone.DuoSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.DuoSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* the first voice
* @type {Tone.MonoSynth}
*/
this.voice0 = new Tone.MonoSynth(options.voice0);
this.voice0.volume.value = -10;
/**
* the second voice
* @type {Tone.MonoSynth}
*/
this.voice1 = new Tone.MonoSynth(options.voice1);
this.voice1.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The vibrato LFO.
* @type {Tone.LFO}
* @private
*/
this._vibrato = new Tone.LFO(options.vibratoRate, -50, 50);
this._vibrato.start();
/**
* the vibrato frequency
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.vibratoRate = this._vibrato.frequency;
/**
* the vibrato gain
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._vibratoGain = new Tone.Gain(options.vibratoAmount, Tone.Type.Positive);
/**
* The amount of vibrato
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.vibratoAmount = this._vibratoGain.gain;
/**
* the frequency control
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(440, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* Harmonicity is the ratio between the two voices. A harmonicity of
* 1 is no change. Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch voice1 an octave below voice0
* duoSynth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
//control the two voices frequency
this.frequency.connect(this.voice0.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this.voice1.frequency);
this._vibrato.connect(this._vibratoGain);
this._vibratoGain.fan(this.voice0.detune, this.voice1.detune);
this.voice0.connect(this.output);
this.voice1.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'voice0',
'voice1',
'frequency',
'vibratoAmount',
'vibratoRate'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.DuoSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.defaults = {
'vibratoAmount': 0.5,
'vibratoRate': 5,
'harmonicity': 1.5,
'voice0': {
'volume': -10,
'portamento': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'filterEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
},
'voice1': {
'volume': -10,
'portamento': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'filterEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
}
};
/**
* start the attack portion of the envelopes
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.DuoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.voice0.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.voice1.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.voice0.filterEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
this.voice1.filterEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
return this;
};
/**
* start the release portion of the envelopes
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.DuoSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
this.voice0.triggerRelease(time);
this.voice1.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.DuoSynth} this
*/
Tone.DuoSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'voice0',
'voice1',
'frequency',
'vibratoAmount',
'vibratoRate'
]);
this.voice0.dispose();
this.voice0 = null;
this.voice1.dispose();
this.voice1 = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this._vibratoGain.dispose();
this._vibratoGain = null;
this._vibrato = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this.vibratoAmount.dispose();
this.vibratoAmount = null;
this.vibratoRate = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.DuoSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class FMSynth is composed of two Tone.Synths where one Tone.Synth modulates
* the frequency of a second Tone.Synth. A lot of spectral content
* can be explored using the modulationIndex parameter. Read more about
* frequency modulation synthesis on [SoundOnSound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/apr00/articles/synthsecrets.htm).
* 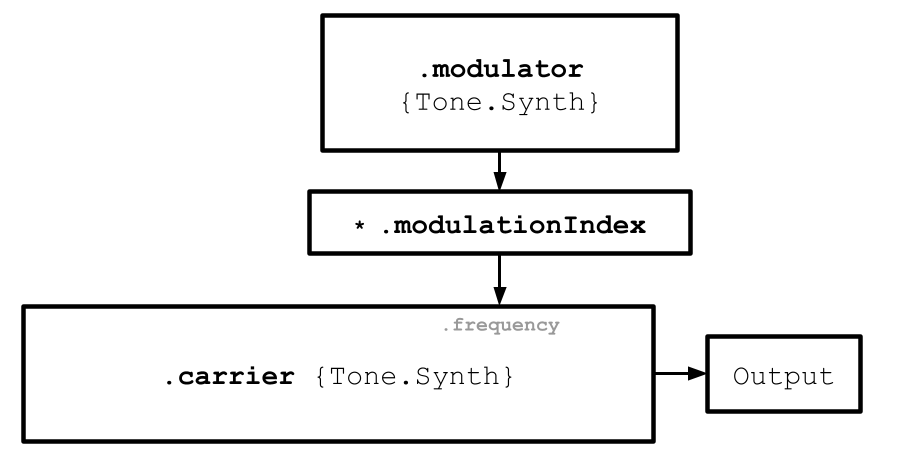 *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var fmSynth = new Tone.FMSynth().toMaster();
* fmSynth.triggerAttackRelease("C5", "4n");
*/
Tone.FMSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.FMSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The carrier voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._carrier = new Tone.Synth(options.carrier);
this._carrier.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The carrier's oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = this._carrier.oscillator;
/**
* The carrier's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.envelope = this._carrier.envelope.set(options.envelope);
/**
* The modulator voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Synth(options.modulator);
this._modulator.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The modulator's oscillator which is applied
* to the amplitude of the oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulation = this._modulator.oscillator.set(options.modulation);
/**
* The modulator's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulationEnvelope = this._modulator.envelope.set(options.modulationEnvelope);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(440, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune in cents
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* Harmonicity is the ratio between the two voices. A harmonicity of
* 1 is no change. Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch voice1 an octave below voice0
* synth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* The modulation index which essentially the depth or amount of the modulation. It is the
* ratio of the frequency of the modulating signal (mf) to the amplitude of the
* modulating signal (ma) -- as in ma/mf.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.modulationIndex = new Tone.Multiply(options.modulationIndex);
this.modulationIndex.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* the node where the modulation happens
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this._modulationNode = new Tone.Gain(0);
//control the two voices frequency
this.frequency.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this._modulator.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.modulationIndex, this._modulationNode);
this.detune.fan(this._carrier.detune, this._modulator.detune);
this._modulator.connect(this._modulationNode.gain);
this._modulationNode.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this._carrier.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'modulationIndex',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FMSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.FMSynth.defaults = {
'harmonicity': 3,
'modulationIndex': 10,
'detune': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0.01,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'modulation': { 'type': 'square' },
'modulationEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.5,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
};
/**
* trigger the attack portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will occur
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note
* @returns {Tone.FMSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.FMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
return this;
};
/**
* trigger the release portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will release
* @returns {Tone.FMSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.FMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.FMSynth} this
*/
Tone.FMSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'modulationIndex',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
this._carrier.dispose();
this._carrier = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.modulationIndex.dispose();
this.modulationIndex = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this._modulationNode.dispose();
this._modulationNode = null;
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope = null;
this.modulationEnvelope = null;
this.modulation = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FMSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MembraneSynth makes kick and tom sounds using a single oscillator
* with an amplitude envelope and frequency ramp. A Tone.OmniOscillator
* is routed through a Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope to the output. The drum
* quality of the sound comes from the frequency envelope applied
* during during Tone.MembraneSynth.triggerAttack(note). The frequency
* envelope starts at
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Monophonic}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var fmSynth = new Tone.FMSynth().toMaster();
* fmSynth.triggerAttackRelease("C5", "4n");
*/
Tone.FMSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.FMSynth.defaults);
Tone.Monophonic.call(this, options);
/**
* The carrier voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._carrier = new Tone.Synth(options.carrier);
this._carrier.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The carrier's oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = this._carrier.oscillator;
/**
* The carrier's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.envelope = this._carrier.envelope.set(options.envelope);
/**
* The modulator voice.
* @type {Tone.Synth}
* @private
*/
this._modulator = new Tone.Synth(options.modulator);
this._modulator.volume.value = -10;
/**
* The modulator's oscillator which is applied
* to the amplitude of the oscillator
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulation = this._modulator.oscillator.set(options.modulation);
/**
* The modulator's envelope
* @type {Tone.Oscillator}
*/
this.modulationEnvelope = this._modulator.envelope.set(options.modulationEnvelope);
/**
* The frequency control.
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(440, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The detune in cents
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
/**
* Harmonicity is the ratio between the two voices. A harmonicity of
* 1 is no change. Harmonicity = 2 means a change of an octave.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
* @example
* //pitch voice1 an octave below voice0
* synth.harmonicity.value = 0.5;
*/
this.harmonicity = new Tone.Multiply(options.harmonicity);
this.harmonicity.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* The modulation index which essentially the depth or amount of the modulation. It is the
* ratio of the frequency of the modulating signal (mf) to the amplitude of the
* modulating signal (ma) -- as in ma/mf.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.modulationIndex = new Tone.Multiply(options.modulationIndex);
this.modulationIndex.units = Tone.Type.Positive;
/**
* the node where the modulation happens
* @type {GainNode}
* @private
*/
this._modulationNode = new Tone.Gain(0);
//control the two voices frequency
this.frequency.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.harmonicity, this._modulator.frequency);
this.frequency.chain(this.modulationIndex, this._modulationNode);
this.detune.fan(this._carrier.detune, this._modulator.detune);
this._modulator.connect(this._modulationNode.gain);
this._modulationNode.connect(this._carrier.frequency);
this._carrier.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'modulationIndex',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.FMSynth, Tone.Monophonic);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.FMSynth.defaults = {
'harmonicity': 3,
'modulationIndex': 10,
'detune': 0,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.01,
'decay': 0.01,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
},
'modulation': { 'type': 'square' },
'modulationEnvelope': {
'attack': 0.5,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.5
}
};
/**
* trigger the attack portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will occur
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note
* @returns {Tone.FMSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.FMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeAttack = function (time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerAttack(time);
return this;
};
/**
* trigger the release portion of the note
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will release
* @returns {Tone.FMSynth} this
* @private
*/
Tone.FMSynth.prototype._triggerEnvelopeRelease = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.modulationEnvelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.FMSynth} this
*/
Tone.FMSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Monophonic.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'frequency',
'harmonicity',
'modulationIndex',
'oscillator',
'envelope',
'modulation',
'modulationEnvelope',
'detune'
]);
this._carrier.dispose();
this._carrier = null;
this._modulator.dispose();
this._modulator = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.modulationIndex.dispose();
this.modulationIndex = null;
this.harmonicity.dispose();
this.harmonicity = null;
this._modulationNode.dispose();
this._modulationNode = null;
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope = null;
this.modulationEnvelope = null;
this.modulation = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.FMSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MembraneSynth makes kick and tom sounds using a single oscillator
* with an amplitude envelope and frequency ramp. A Tone.OmniOscillator
* is routed through a Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope to the output. The drum
* quality of the sound comes from the frequency envelope applied
* during during Tone.MembraneSynth.triggerAttack(note). The frequency
* envelope starts at note * .octaves and ramps to
* note over the duration of .pitchDecay.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var synth = new Tone.MembraneSynth().toMaster();
* synth.triggerAttackRelease("C2", "8n");
*/
Tone.MembraneSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.MembraneSynth.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The oscillator.
* @type {Tone.OmniOscillator}
*/
this.oscillator = new Tone.OmniOscillator(options.oscillator).start();
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
/**
* The number of octaves the pitch envelope ramps.
* @type {Positive}
*/
this.octaves = options.octaves;
/**
* The amount of time the frequency envelope takes.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.pitchDecay = options.pitchDecay;
this.oscillator.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'oscillator',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MembraneSynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MembraneSynth.defaults = {
'pitchDecay': 0.05,
'octaves': 10,
'oscillator': { 'type': 'sine' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.001,
'decay': 0.4,
'sustain': 0.01,
'release': 1.4,
'attackCurve': 'exponential'
}
};
/**
* Trigger the note at the given time with the given velocity.
*
* @param {Frequency} note the note
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time, if not given is now
* @param {number} [velocity=1] velocity defaults to 1
* @returns {Tone.MembraneSynth} this
* @example
* kick.triggerAttack(60);
*/
Tone.MembraneSynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (note, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
note = this.toFrequency(note);
var maxNote = note * this.octaves;
this.oscillator.frequency.setValueAtTime(maxNote, time);
this.oscillator.frequency.exponentialRampToValueAtTime(note, time + this.toSeconds(this.pitchDecay));
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the release portion of the note.
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the note will release
* @returns {Tone.MembraneSynth} this
*/
Tone.MembraneSynth.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.MembraneSynth} this
*/
Tone.MembraneSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'oscillator',
'envelope'
]);
this.oscillator.dispose();
this.oscillator = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MembraneSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* Inharmonic ratio of frequencies based on the Roland TR-808
* Taken from https://ccrma.stanford.edu/papers/tr-808-cymbal-physically-informed-circuit-bendable-digital-model
* @private
* @static
* @type {Array}
*/
var inharmRatios = [
1,
1.483,
1.932,
2.546,
2.63,
3.897
];
/**
* @class A highly inharmonic and spectrally complex source with a highpass filter
* and amplitude envelope which is good for making metalophone sounds. Based
* on CymbalSynth by [@polyrhythmatic](https://github.com/polyrhythmatic).
* Inspiration from [Sound on Sound](http://www.soundonsound.com/sos/jul02/articles/synthsecrets0702.asp).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {Object} [options] The options availble for the synth
* see defaults below
*/
Tone.MetalSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.MetalSynth.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The frequency of the cymbal
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.frequency = new Tone.Signal(options.frequency, Tone.Type.Frequency);
/**
* The array of FMOscillators
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._oscillators = [];
/**
* The frequency multipliers
* @type {Array}
* @private
*/
this._freqMultipliers = [];
/**
* The amplitude for the body
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._amplitue = new Tone.Gain(0).connect(this.output);
/**
* highpass the output
* @type {Tone.Filter}
* @private
*/
this._highpass = new Tone.Filter({
'type': 'highpass',
'Q': -3.0102999566398125
}).connect(this._amplitue);
/**
* The number of octaves the highpass
* filter frequency ramps
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._octaves = options.octaves;
/**
* Scale the body envelope
* for the bandpass
* @type {Tone.Scale}
* @private
*/
this._filterFreqScaler = new Tone.Scale(options.resonance, 7000);
/**
* The envelope which is connected both to the
* amplitude and highpass filter's cutoff frequency
* @type {Tone.Envelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.Envelope({
'attack': options.envelope.attack,
'attackCurve': 'linear',
'decay': options.envelope.decay,
'sustain': 0,
'release': options.envelope.release
}).chain(this._filterFreqScaler, this._highpass.frequency);
this.envelope.connect(this._amplitue.gain);
for (var i = 0; i < inharmRatios.length; i++) {
var osc = new Tone.FMOscillator({
'type': 'square',
'modulationType': 'square',
'harmonicity': options.harmonicity,
'modulationIndex': options.modulationIndex
});
osc.connect(this._highpass).start(0);
this._oscillators[i] = osc;
var mult = new Tone.Multiply(inharmRatios[i]);
this._freqMultipliers[i] = mult;
this.frequency.chain(mult, osc.frequency);
}
//set the octaves
this.octaves = options.octaves;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MetalSynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* default values
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MetalSynth.defaults = {
'frequency': 200,
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.001,
'decay': 1.4,
'release': 0.2
},
'harmonicity': 5.1,
'modulationIndex': 32,
'resonance': 4000,
'octaves': 1.5
};
/**
* Trigger the attack.
* @param {Time} time When the attack should be triggered.
* @param {NormalRange=1} velocity The velocity that the envelope should be triggered at.
* @return {Tone.MetalSynth} this
*/
Tone.MetalSynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (time, vel) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
vel = this.defaultArg(vel, 1);
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, vel);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the release of the envelope.
* @param {Time} time When the release should be triggered.
* @return {Tone.MetalSynth} this
*/
Tone.MetalSynth.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and release of the envelope after the given
* duration.
* @param {Time} duration The duration before triggering the release
* @param {Time} time When the attack should be triggered.
* @param {NormalRange=1} velocity The velocity that the envelope should be triggered at.
* @return {Tone.MetalSynth} this
*/
Tone.MetalSynth.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (duration, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.triggerRelease(time + duration);
return this;
};
/**
* The modulationIndex of the oscillators which make up the source.
* see Tone.FMOscillator.modulationIndex
* @memberOf Tone.MetalSynth#
* @type {Positive}
* @name modulationIndex
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MetalSynth.prototype, 'modulationIndex', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillators[0].modulationIndex.value;
},
set: function (val) {
for (var i = 0; i < this._oscillators.length; i++) {
this._oscillators[i].modulationIndex.value = val;
}
}
});
/**
* The harmonicity of the oscillators which make up the source.
* see Tone.FMOscillator.harmonicity
* @memberOf Tone.MetalSynth#
* @type {Positive}
* @name harmonicity
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MetalSynth.prototype, 'harmonicity', {
get: function () {
return this._oscillators[0].harmonicity.value;
},
set: function (val) {
for (var i = 0; i < this._oscillators.length; i++) {
this._oscillators[i].harmonicity.value = val;
}
}
});
/**
* The frequency of the highpass filter attached to the envelope
* @memberOf Tone.MetalSynth#
* @type {Frequency}
* @name resonance
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MetalSynth.prototype, 'resonance', {
get: function () {
return this._filterFreqScaler.min;
},
set: function (val) {
this._filterFreqScaler.min = val;
this.octaves = this._octaves;
}
});
/**
* The number of octaves above the "resonance" frequency
* that the filter ramps during the attack/decay envelope
* @memberOf Tone.MetalSynth#
* @type {Number}
* @name octaves
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MetalSynth.prototype, 'octaves', {
get: function () {
return this._octaves;
},
set: function (octs) {
this._octaves = octs;
this._filterFreqScaler.max = this._filterFreqScaler.min * Math.pow(2, octs);
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @returns {Tone.MetalSynth} this
*/
Tone.MetalSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
for (var i = 0; i < this._oscillators.length; i++) {
this._oscillators[i].dispose();
this._freqMultipliers[i].dispose();
}
this._oscillators = null;
this._freqMultipliers = null;
this.frequency.dispose();
this.frequency = null;
this._filterFreqScaler.dispose();
this._filterFreqScaler = null;
this._amplitue.dispose();
this._amplitue = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
this._highpass.dispose();
this._highpass = null;
};
return Tone.MetalSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Noise is a noise generator. It uses looped noise buffers to save on performance.
* Tone.Noise supports the noise types: "pink", "white", and "brown". Read more about
* colors of noise on [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colors_of_noise).
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Source}
* @param {string} type the noise type (white|pink|brown)
* @example
* //initialize the noise and start
* var noise = new Tone.Noise("pink").start();
*
* //make an autofilter to shape the noise
* var autoFilter = new Tone.AutoFilter({
* "frequency" : "8m",
* "min" : 800,
* "max" : 15000
* }).connect(Tone.Master);
*
* //connect the noise
* noise.connect(autoFilter);
* //start the autofilter LFO
* autoFilter.start()
*/
Tone.Noise = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['type'], Tone.Noise.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* @private
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
*/
this._source = null;
/**
* the buffer
* @private
* @type {AudioBuffer}
*/
this._buffer = null;
/**
* The playback rate of the noise. Affects
* the "frequency" of the noise.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this._playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
this.type = options.type;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Noise, Tone.Source);
/**
* the default parameters
*
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Noise.defaults = {
'type': 'white',
'playbackRate': 1
};
/**
* The type of the noise. Can be "white", "brown", or "pink".
* @memberOf Tone.Noise#
* @type {string}
* @name type
* @example
* noise.type = "white";
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Noise.prototype, 'type', {
get: function () {
if (this._buffer === _whiteNoise) {
return 'white';
} else if (this._buffer === _brownNoise) {
return 'brown';
} else if (this._buffer === _pinkNoise) {
return 'pink';
}
},
set: function (type) {
if (this.type !== type) {
switch (type) {
case 'white':
this._buffer = _whiteNoise;
break;
case 'pink':
this._buffer = _pinkNoise;
break;
case 'brown':
this._buffer = _brownNoise;
break;
default:
throw new TypeError('Tone.Noise: invalid type: ' + type);
}
//if it's playing, stop and restart it
if (this.state === Tone.State.Started) {
var now = this.now() + this.blockTime;
//remove the listener
this._stop(now);
this._start(now);
}
}
}
});
/**
* The playback rate of the noise. Affects
* the "frequency" of the noise.
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Noise.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
if (this._source) {
this._source.playbackRate.value = rate;
}
}
});
/**
* internal start method
*
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.Noise.prototype._start = function (time) {
this._source = this.context.createBufferSource();
this._source.buffer = this._buffer;
this._source.loop = true;
this._source.playbackRate.value = this._playbackRate;
this._source.connect(this.output);
this._source.start(this.toSeconds(time), Math.random() * (this._buffer.duration - 0.001));
};
/**
* internal stop method
*
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.Noise.prototype._stop = function (time) {
if (this._source) {
this._source.stop(this.toSeconds(time));
}
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Noise} this
*/
Tone.Noise.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
if (this._source !== null) {
this._source.disconnect();
this._source = null;
}
this._buffer = null;
return this;
};
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// THE BUFFERS
// borrowed heavily from http://noisehack.com/generate-noise-web-audio-api/
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/**
* static noise buffers
*
* @static
* @private
* @type {AudioBuffer}
*/
var _pinkNoise = null, _brownNoise = null, _whiteNoise = null;
Tone._initAudioContext(function (audioContext) {
var sampleRate = audioContext.sampleRate;
//four seconds per buffer
var bufferLength = sampleRate * 4;
//fill the buffers
_pinkNoise = function () {
var buffer = audioContext.createBuffer(2, bufferLength, sampleRate);
for (var channelNum = 0; channelNum < buffer.numberOfChannels; channelNum++) {
var channel = buffer.getChannelData(channelNum);
var b0, b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6;
b0 = b1 = b2 = b3 = b4 = b5 = b6 = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
var white = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
b0 = 0.99886 * b0 + white * 0.0555179;
b1 = 0.99332 * b1 + white * 0.0750759;
b2 = 0.969 * b2 + white * 0.153852;
b3 = 0.8665 * b3 + white * 0.3104856;
b4 = 0.55 * b4 + white * 0.5329522;
b5 = -0.7616 * b5 - white * 0.016898;
channel[i] = b0 + b1 + b2 + b3 + b4 + b5 + b6 + white * 0.5362;
channel[i] *= 0.11;
// (roughly) compensate for gain
b6 = white * 0.115926;
}
}
return buffer;
}();
_brownNoise = function () {
var buffer = audioContext.createBuffer(2, bufferLength, sampleRate);
for (var channelNum = 0; channelNum < buffer.numberOfChannels; channelNum++) {
var channel = buffer.getChannelData(channelNum);
var lastOut = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
var white = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
channel[i] = (lastOut + 0.02 * white) / 1.02;
lastOut = channel[i];
channel[i] *= 3.5; // (roughly) compensate for gain
}
}
return buffer;
}();
_whiteNoise = function () {
var buffer = audioContext.createBuffer(2, bufferLength, sampleRate);
for (var channelNum = 0; channelNum < buffer.numberOfChannels; channelNum++) {
var channel = buffer.getChannelData(channelNum);
for (var i = 0; i < bufferLength; i++) {
channel[i] = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
}
}
return buffer;
}();
});
return Tone.Noise;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.NoiseSynth is composed of a noise generator (Tone.Noise), one filter (Tone.Filter),
* and two envelopes (Tone.Envelop). One envelope controls the amplitude
* of the noise and the other is controls the cutoff frequency of the filter.
*  *
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var noiseSynth = new Tone.NoiseSynth().toMaster();
* noiseSynth.triggerAttackRelease("8n");
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.NoiseSynth.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The noise source.
* @type {Tone.Noise}
* @example
* noiseSynth.set("noise.type", "brown");
*/
this.noise = new Tone.Noise();
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
//connect the noise to the output
this.noise.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
//start the noise
this.noise.start();
this._readOnly([
'noise',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.NoiseSynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.defaults = {
'noise': { 'type': 'white' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.005,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0
}
};
/**
* Start the attack portion of the envelopes. Unlike other
* instruments, Tone.NoiseSynth doesn't have a note.
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
* @example
* noiseSynth.triggerAttack();
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* Start the release portion of the envelopes.
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and then the release.
* @param {Time} duration the duration of the note
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time of the attack
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (duration, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.triggerRelease(time + duration);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'noise',
'envelope'
]);
this.noise.dispose();
this.noise = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.NoiseSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Karplus-String string synthesis. Often out of tune.
* Will change when the AudioWorkerNode is available across
* browsers.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {Object} [options] see the defaults
* @example
* var plucky = new Tone.PluckSynth().toMaster();
* plucky.triggerAttack("C4");
*/
Tone.PluckSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.PluckSynth.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* @type {Tone.Noise}
* @private
*/
this._noise = new Tone.Noise('pink');
/**
* The amount of noise at the attack.
* Nominal range of [0.1, 20]
* @type {number}
*/
this.attackNoise = options.attackNoise;
/**
* the LFCF
* @type {Tone.LowpassCombFilter}
* @private
*/
this._lfcf = new Tone.LowpassCombFilter({
'resonance': options.resonance,
'dampening': options.dampening
});
/**
* The resonance control.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.resonance = this._lfcf.resonance;
/**
* The dampening control. i.e. the lowpass filter frequency of the comb filter
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.dampening = this._lfcf.dampening;
//connections
this._noise.connect(this._lfcf);
this._lfcf.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'resonance',
'dampening'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PluckSynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.PluckSynth.defaults = {
'attackNoise': 1,
'dampening': 4000,
'resonance': 0.9
};
/**
* Trigger the note.
* @param {Frequency} note The note to trigger.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the note should be triggered.
* @returns {Tone.PluckSynth} this
*/
Tone.PluckSynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (note, time) {
note = this.toFrequency(note);
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var delayAmount = 1 / note;
this._lfcf.delayTime.setValueAtTime(delayAmount, time);
this._noise.start(time);
this._noise.stop(time + delayAmount * this.attackNoise);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.PluckSynth} this
*/
Tone.PluckSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._noise.dispose();
this._lfcf.dispose();
this._noise = null;
this._lfcf = null;
this._writable([
'resonance',
'dampening'
]);
this.dampening = null;
this.resonance = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PluckSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PolySynth handles voice creation and allocation for any
* instruments passed in as the second paramter. PolySynth is
* not a synthesizer by itself, it merely manages voices of
* one of the other types of synths, allowing any of the
* monophonic synthesizers to be polyphonic.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {number|Object} [polyphony=4] The number of voices to create
* @param {function} [voice=Tone.Synth] The constructor of the voices
* uses Tone.Synth by default.
* @example
* //a polysynth composed of 6 Voices of Synth
* var synth = new Tone.PolySynth(6, Tone.Synth).toMaster();
* //set the attributes using the set interface
* synth.set("detune", -1200);
* //play a chord
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(["C4", "E4", "A4"], "4n");
*/
Tone.PolySynth = function () {
Tone.Instrument.call(this);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'polyphony',
'voice'
], Tone.PolySynth.defaults);
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Instrument.defaults);
//max polyphony
options.polyphony = Math.min(Tone.PolySynth.MAX_POLYPHONY, options.polyphony);
/**
* the array of voices
* @type {Array}
*/
this.voices = new Array(options.polyphony);
/**
* The queue of voices with data about last trigger
* and the triggered note
* @private
* @type {Array}
*/
this._triggers = new Array(options.polyphony);
/**
* The detune in cents
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
this._readOnly('detune');
//create the voices
for (var i = 0; i < options.polyphony; i++) {
var v = new options.voice(arguments[2], arguments[3]);
this.voices[i] = v;
v.connect(this.output);
if (v.hasOwnProperty('detune')) {
this.detune.connect(v.detune);
}
this._triggers[i] = {
release: -1,
note: null,
voice: v
};
}
//set the volume initially
this.volume.value = options.volume;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PolySynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* the defaults
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.PolySynth.defaults = {
'polyphony': 4,
'volume': 0,
'detune': 0,
'voice': Tone.Synth
};
/**
* Trigger the attack portion of the note
* @param {Frequency|Array} notes The notes to play. Accepts a single
* Frequency or an array of frequencies.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The start time of the note.
* @param {number} [velocity=1] The velocity of the note.
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* //trigger a chord immediately with a velocity of 0.2
* poly.triggerAttack(["Ab3", "C4", "F5"], undefined, 0.2);
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (notes, time, velocity) {
if (!Array.isArray(notes)) {
notes = [notes];
}
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var i = 0; i < notes.length; i++) {
var val = notes[i];
//trigger the oldest voice
var oldest = this._triggers[0];
var oldestIndex = 0;
for (var j = 1; j < this._triggers.length; j++) {
if (this._triggers[j].release < oldest.release) {
oldest = this._triggers[j];
oldestIndex = j;
}
}
oldest.release = Infinity;
oldest.note = JSON.stringify(val);
oldest.voice.triggerAttack(val, time, velocity);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and release after the specified duration
*
* @param {Frequency|Array} notes The notes to play. Accepts a single
* Frequency or an array of frequencies.
* @param {Time} duration the duration of the note
* @param {Time} [time=now] if no time is given, defaults to now
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the attack (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* //trigger a chord for a duration of a half note
* poly.triggerAttackRelease(["Eb3", "G4", "C5"], "2n");
* @example
* //can pass in an array of durations as well
* poly.triggerAttackRelease(["Eb3", "G4", "C5"], ["2n", "4n", "4n"]);
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (notes, duration, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.triggerAttack(notes, time, velocity);
if (this.isArray(duration) && this.isArray(notes)) {
for (var i = 0; i < notes.length; i++) {
var d = duration[Math.min(i, duration.length - 1)];
this.triggerRelease(notes[i], time + this.toSeconds(d));
}
} else {
this.triggerRelease(notes, time + this.toSeconds(duration));
}
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the release of the note. Unlike monophonic instruments,
* a note (or array of notes) needs to be passed in as the first argument.
* @param {Frequency|Array} notes The notes to play. Accepts a single
* Frequency or an array of frequencies.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the release will be triggered.
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* poly.triggerRelease(["Ab3", "C4", "F5"], "+2n");
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.triggerRelease = function (notes, time) {
if (!Array.isArray(notes)) {
notes = [notes];
}
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var i = 0; i < notes.length; i++) {
//get the voice
var stringified = JSON.stringify(notes[i]);
for (var v = 0; v < this._triggers.length; v++) {
var desc = this._triggers[v];
if (desc.note === stringified && desc.release > time) {
desc.voice.triggerRelease(time);
desc.release = time;
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Set a member/attribute of the voices.
* @param {Object|string} params
* @param {number=} value
* @param {Time=} rampTime
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* poly.set({
* "filter" : {
* "type" : "highpass"
* },
* "envelope" : {
* "attack" : 0.25
* }
* });
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.set = function (params, value, rampTime) {
for (var i = 0; i < this.voices.length; i++) {
this.voices[i].set(params, value, rampTime);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Get the synth's attributes. Given no arguments get
* will return all available object properties and their corresponding
* values. Pass in a single attribute to retrieve or an array
* of attributes. The attribute strings can also include a "."
* to access deeper properties.
* @param {Array=} params the parameters to get, otherwise will return
* all available.
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.get = function (params) {
return this.voices[0].get(params);
};
/**
* Trigger the release portion of all the currently active voices.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the notes should be released.
* @return {Tone.PolySynth} this
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.releaseAll = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var i = 0; i < this._triggers.length; i++) {
var desc = this._triggers[i];
if (desc.release > time) {
desc.release = time;
desc.voice.triggerRelease(time);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
for (var i = 0; i < this.voices.length; i++) {
this.voices[i].dispose();
this.voices[i] = null;
}
this._writable('detune');
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.voices = null;
this._triggers = null;
return this;
};
/**
* The maximum number of notes that can be allocated
* to a polysynth.
* @type {Number}
* @static
*/
Tone.PolySynth.MAX_POLYPHONY = 20;
return Tone.PolySynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Player is an audio file player with start, loop, and stop functions.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Source}
* @param {string|AudioBuffer} url Either the AudioBuffer or the url from
* which to load the AudioBuffer
* @param {function=} onload The function to invoke when the buffer is loaded.
* Recommended to use Tone.Buffer.on('load') instead.
* @example
* var player = new Tone.Player("./path/to/sample.mp3").toMaster();
* //play as soon as the buffer is loaded
* player.autostart = true;
*/
Tone.Player = function (url) {
var options;
if (url instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
url = url.get();
options = Tone.Player.defaults;
} else {
options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.Player.defaults);
}
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* @private
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
*/
this._source = null;
/**
* If the file should play as soon
* as the buffer is loaded.
* @type {boolean}
* @example
* //will play as soon as it's loaded
* var player = new Tone.Player({
* "url" : "./path/to/sample.mp3",
* "autostart" : true,
* }).toMaster();
*/
this.autostart = options.autostart;
/**
* the buffer
* @private
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
*/
this._buffer = new Tone.Buffer({
'url': options.url,
'onload': this._onload.bind(this, options.onload),
'reverse': options.reverse
});
if (url instanceof AudioBuffer) {
this._buffer.set(url);
}
/**
* if the buffer should loop once it's over
* @type {boolean}
* @private
*/
this._loop = options.loop;
/**
* if 'loop' is true, the loop will start at this position
* @type {Time}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = options.loopStart;
/**
* if 'loop' is true, the loop will end at this position
* @type {Time}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = options.loopEnd;
/**
* the playback rate
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
/**
* Enabling retrigger will allow a player to be restarted
* before the the previous 'start' is done playing. Otherwise,
* successive calls to Tone.Player.start will only start
* the sample if it had played all the way through.
* @type {boolean}
*/
this.retrigger = options.retrigger;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Player, Tone.Source);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Player.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'playbackRate': 1,
'loop': false,
'autostart': false,
'loopStart': 0,
'loopEnd': 0,
'retrigger': false,
'reverse': false
};
/**
* Load the audio file as an audio buffer.
* Decodes the audio asynchronously and invokes
* the callback once the audio buffer loads.
* Note: this does not need to be called if a url
* was passed in to the constructor. Only use this
* if you want to manually load a new url.
* @param {string} url The url of the buffer to load.
* Filetype support depends on the
* browser.
* @param {function=} callback The function to invoke once
* the sample is loaded.
* @returns {Promise}
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.load = function (url, callback) {
return this._buffer.load(url, this._onload.bind(this, callback));
};
/**
* Internal callback when the buffer is loaded.
* @private
*/
Tone.Player.prototype._onload = function (callback) {
callback = this.defaultArg(callback, Tone.noOp);
callback(this);
if (this.autostart) {
this.start();
}
};
/**
* Play the buffer at the given startTime. Optionally add an offset
* and/or duration which will play the buffer from a position
* within the buffer for the given duration.
*
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the player should start.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset from the beginning of the sample
* to start at.
* @param {Time=} duration How long the sample should play. If no duration
* is given, it will default to the full length
* of the sample (minus any offset)
* @returns {Tone.Player} this
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @method start
* @name start
*/
/**
* Internal start method
* @private
*/
Tone.Player.prototype._start = function (startTime, offset, duration) {
if (this._buffer.loaded) {
//if it's a loop the default offset is the loopstart point
if (this._loop) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, this._loopStart);
} else {
//otherwise the default offset is 0
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
}
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
//make sure it has a positive duration
duration = this.defaultArg(duration, Math.max(this._buffer.duration - offset, 0));
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
//the values in seconds
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
//make the source
this._source = this.context.createBufferSource();
this._source.buffer = this._buffer.get();
//set the looping properties
if (this._loop) {
this._source.loop = this._loop;
this._source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(this._loopStart);
this._source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(this._loopEnd);
} else {
//if it's not looping, set the state change at the end of the sample
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, startTime + duration);
}
//and other properties
this._source.playbackRate.value = this._playbackRate;
this._source.connect(this.output);
//start it
if (this._loop) {
//modify the offset if it's greater than the loop time
var loopEnd = this._source.loopEnd || this._buffer.duration;
var loopStart = this._source.loopStart;
var loopDuration = loopEnd - loopStart;
if (offset > loopEnd) {
//move the offset back
while (offset > loopEnd) {
offset -= loopDuration;
}
}
this._source.start(startTime, offset);
} else {
this._source.start(startTime, offset, duration);
}
} else {
throw Error('Tone.Player: tried to start Player before the buffer was loaded');
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop playback.
* @private
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @returns {Tone.Player} this
*/
Tone.Player.prototype._stop = function (time) {
if (this._source) {
this._source.stop(this.toSeconds(time));
this._source = null;
}
return this;
};
/**
* Seek to a specific time in the player's buffer. If the
* source is no longer playing at that time, it will stop.
* If you seek to a time that
* @param {Time} offset The time to seek to.
* @param {Time=} time The time for the seek event to occur.
* @return {Tone.Player} this
* @example
* source.start(0.2);
* source.stop(0.4);
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.seek = function (offset, time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(time) === Tone.State.Started) {
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
// if it's currently playing, stop it
this._stop(time);
//restart it at the given time
this._start(time, offset);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Set the loop start and end. Will only loop if loop is
* set to true.
* @param {Time} loopStart The loop end time
* @param {Time} loopEnd The loop end time
* @returns {Tone.Player} this
* @example
* //loop 0.1 seconds of the file.
* player.setLoopPoints(0.2, 0.3);
* player.loop = true;
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.setLoopPoints = function (loopStart, loopEnd) {
this.loopStart = loopStart;
this.loopEnd = loopEnd;
return this;
};
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will start at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return this._loopStart;
},
set: function (loopStart) {
this._loopStart = loopStart;
if (this._source) {
this._source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(loopStart);
}
}
});
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will end at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return this._loopEnd;
},
set: function (loopEnd) {
this._loopEnd = loopEnd;
if (this._source) {
this._source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(loopEnd);
}
}
});
/**
* The audio buffer belonging to the player.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
return this._buffer;
},
set: function (buffer) {
this._buffer.set(buffer);
}
});
/**
* If the buffer should loop once it's over.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {boolean}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this._loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this._loop = loop;
if (this._source) {
this._source.loop = loop;
}
}
});
/**
* The playback speed. 1 is normal speed. This is not a signal because
* Safari and iOS currently don't support playbackRate as a signal.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {number}
* @name playbackRate
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
if (this._source) {
this._source.playbackRate.value = rate;
}
}
});
/**
* The direction the buffer should play in
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this._buffer.reverse;
},
set: function (rev) {
this._buffer.reverse = rev;
}
});
/**
* Dispose and disconnect.
* @return {Tone.Player} this
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
if (this._source !== null) {
this._source.disconnect();
this._source = null;
}
this._buffer.dispose();
this._buffer = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Player;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Sampler wraps Tone.Player in an AmplitudeEnvelope.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {String} url the url of the audio file
* @param {Function=} onload The callback to invoke when the sample is loaded.
* @example
* var sampler = new Sampler("./audio/casio/A1.mp3", function(){
* //repitch the sample down a half step
* sampler.triggerAttack(-1);
* }).toMaster();
*/
Tone.Sampler = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.Sampler.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The sample player.
* @type {Tone.Player}
*/
this.player = new Tone.Player(options.url, options.onload);
this.player.retrigger = true;
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
this.player.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'player',
'envelope'
]);
this.loop = options.loop;
this.reverse = options.reverse;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Sampler, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
*/
Tone.Sampler.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'loop': false,
'reverse': false,
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.001,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.1
}
};
/**
* Trigger the start of the sample.
* @param {Interval} [pitch=0] The amount the sample should
* be repitched.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the sample should start
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] The velocity of the note
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
* @example
* sampler.triggerAttack(0, "+0.1", 0.5);
*/
Tone.Sampler.prototype.triggerAttack = function (pitch, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
pitch = this.defaultArg(pitch, 0);
this.player.playbackRate = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(pitch);
this.player.start(time);
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* Start the release portion of the sample. Will stop the sample once the
* envelope has fully released.
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the note should release
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
* @example
* sampler.triggerRelease();
*/
Tone.Sampler.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.player.stop(this.toSeconds(this.envelope.release) + time);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and then the release after the duration.
* @param {Interval} interval The interval in half-steps that the
* sample should be pitch shifted.
* @param {Time} duration How long the note should be held for before
* triggering the release.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the note should be triggered.
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] The velocity the note should be triggered at.
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
* @example
* //trigger the unpitched note for the duration of an 8th note
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(0, "8n");
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @name triggerAttackRelease
* @method triggerAttackRelease
*/
/**
* If the output sample should loop or not.
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @type {number|string}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sampler.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this.player.loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this.player.loop = loop;
}
});
/**
* The direction the buffer should play in
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @type {boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sampler.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this.player.reverse;
},
set: function (rev) {
this.player.reverse = rev;
}
});
/**
* The buffer to play.
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sampler.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
return this.player.buffer;
},
set: function (buff) {
this.player.buffer = buff;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
*/
Tone.Sampler.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'player',
'envelope'
]);
this.player.dispose();
this.player = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Sampler;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Maps a NormalRange [0, 1] to an AudioRange [-1, 1].
* See also Tone.AudioToGain.
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @example
* var g2a = new Tone.GainToAudio();
*/
Tone.GainToAudio = function () {
/**
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._norm = this.input = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (x) {
return Math.abs(x) * 2 - 1;
});
};
Tone.extend(Tone.GainToAudio, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.GainToAudio} this
*/
Tone.GainToAudio.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._norm.dispose();
this._norm = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.GainToAudio;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Normalize takes an input min and max and maps it linearly to NormalRange [0,1]
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @param {number} inputMin the min input value
* @param {number} inputMax the max input value
* @example
* var norm = new Tone.Normalize(2, 4);
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(3).connect(norm);
* //output of norm is 0.5.
*/
Tone.Normalize = function (inputMin, inputMax) {
/**
* the min input value
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._inputMin = this.defaultArg(inputMin, 0);
/**
* the max input value
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._inputMax = this.defaultArg(inputMax, 1);
/**
* subtract the min from the input
* @type {Tone.Add}
* @private
*/
this._sub = this.input = new Tone.Add(0);
/**
* divide by the difference between the input and output
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._div = this.output = new Tone.Multiply(1);
this._sub.connect(this._div);
this._setRange();
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Normalize, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* The minimum value the input signal will reach.
* @memberOf Tone.Normalize#
* @type {number}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Normalize.prototype, 'min', {
get: function () {
return this._inputMin;
},
set: function (min) {
this._inputMin = min;
this._setRange();
}
});
/**
* The maximum value the input signal will reach.
* @memberOf Tone.Normalize#
* @type {number}
* @name max
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Normalize.prototype, 'max', {
get: function () {
return this._inputMax;
},
set: function (max) {
this._inputMax = max;
this._setRange();
}
});
/**
* set the values
* @private
*/
Tone.Normalize.prototype._setRange = function () {
this._sub.value = -this._inputMin;
this._div.value = 1 / (this._inputMax - this._inputMin);
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Normalize} this
*/
Tone.Normalize.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._sub.dispose();
this._sub = null;
this._div.dispose();
this._div = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Normalize;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Wrapper around the native BufferSourceNode.
* @param {AudioBuffer|Tone.Buffer} buffer The buffer to play
* @param {Function} onended The callback to invoke when the
* buffer is done playing.
*/
Tone.BufferSource = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'buffer',
'onended'
], Tone.BufferSource.defaults);
/**
* The callback to invoke after the
* buffer source is done playing.
* @type {Function}
*/
this.onended = options.onended;
/**
* The time that the buffer was started.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._startTime = -1;
/**
* The time that the buffer is scheduled to stop.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._stopTime = -1;
/**
* The gain node which envelopes the BufferSource
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._gainNode = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* The buffer source
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
* @private
*/
this._source = this.context.createBufferSource();
this._source.connect(this._gainNode);
/**
* The playbackRate of the buffer
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.playbackRate = new Tone.Param(this._source.playbackRate, Tone.Type.Positive);
/**
* The fadeIn time of the amplitude envelope.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeIn = options.fadeIn;
/**
* The fadeOut time of the amplitude envelope.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeOut = options.fadeOut;
/**
* The value that the buffer ramps to
* @type {Gain}
* @private
*/
this._gain = 1;
/**
* The onended timeout
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._onendedTimeout = -1;
//set the buffer initially
if (!this.isUndef(options.buffer)) {
this.buffer = options.buffer;
}
this.loop = options.loop;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.BufferSource);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.BufferSource.defaults = {
'onended': Tone.noOp,
'fadeIn': 0,
'fadeOut': 0
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, either "started" or "stopped".
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
var now = this.now();
if (this._startTime !== -1 && now >= this._startTime && now < this._stopTime) {
return Tone.State.Started;
} else {
return Tone.State.Stopped;
}
}
});
/**
* Start the buffer
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the player should start.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset from the beginning of the sample
* to start at.
* @param {Time=} duration How long the sample should play. If no duration
* is given, it will default to the full length
* of the sample (minus any offset)
* @param {Gain} [gain=1] The gain to play the buffer back at.
* @param {Time=} fadeInTime The optional fadeIn ramp time.
* @return {Tone.BufferSource} this
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype.start = function (time, offset, duration, gain, fadeInTime) {
if (this._startTime !== -1) {
throw new Error('Tone.BufferSource: can only be started once.');
}
if (this.buffer) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//if it's a loop the default offset is the loopstart point
if (this.loop) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, this.loopStart);
} else {
//otherwise the default offset is 0
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
}
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
//the values in seconds
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._source.start(time, offset);
gain = this.defaultArg(gain, 1);
this._gain = gain;
//the fadeIn time
if (this.isUndef(fadeInTime)) {
fadeInTime = this.toSeconds(this.fadeIn);
} else {
fadeInTime = this.toSeconds(fadeInTime);
}
if (fadeInTime > 0) {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(0, time);
this._gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(this._gain, time + fadeInTime);
} else {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(gain, time);
}
this._startTime = time + fadeInTime;
if (!this.isUndef(duration)) {
duration = this.defaultArg(duration, this.buffer.duration - offset);
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this.stop(time + duration + fadeInTime, fadeInTime);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the buffer. Optionally add a ramp time to fade the
* buffer out.
* @param {Time=} time The time the buffer should stop.
* @param {Time=} fadeOutTime How long the gain should fade out for
* @return {Tone.BufferSource} this
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype.stop = function (time, fadeOutTime) {
if (this.buffer) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//the fadeOut time
if (this.isUndef(fadeOutTime)) {
fadeOutTime = this.toSeconds(this.fadeOut);
} else {
fadeOutTime = this.toSeconds(fadeOutTime);
}
this._stopTime = time + fadeOutTime;
//cancel the end curve
this._gainNode.gain.cancelScheduledValues(this._startTime + this.sampleTime);
//set a new one
if (fadeOutTime > 0) {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(this._gain, time);
this._gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0, time + fadeOutTime);
time += fadeOutTime;
} else {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(0, time);
}
// fix for safari bug and old FF
if (!this.isNumber(this._source.playbackState) || this._source.playbackState === 2) {
this._source.stop(time);
}
clearTimeout(this._onendedTimeout);
this._onendedTimeout = setTimeout(this._onended.bind(this), (this._stopTime - this.now()) * 1000);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Internal callback when the buffer is ended.
* Invokes `onended` and disposes the node.
* @private
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype._onended = function () {
this.onended(this);
this.dispose();
};
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will start at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return this._source.loopStart;
},
set: function (loopStart) {
this._source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(loopStart);
}
});
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will end at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return this._source.loopEnd;
},
set: function (loopEnd) {
this._source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(loopEnd);
}
});
/**
* The audio buffer belonging to the player.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {AudioBuffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
if (this._source) {
return this._source.buffer;
} else {
return null;
}
},
set: function (buffer) {
if (buffer instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
this._source.buffer = buffer.get();
} else {
this._source.buffer = buffer;
}
}
});
/**
* If the buffer should loop once it's over.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {boolean}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this._source.loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this._source.loop = loop;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.BufferSource} this
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.onended = null;
if (this._source) {
this._source.disconnect();
this._source = null;
}
if (this._gainNode) {
this._gainNode.dispose();
this._gainNode = null;
}
this._startTime = -1;
this.playbackRate = null;
this.output = null;
clearTimeout(this._onendedTimeout);
return this;
};
return Tone.BufferSource;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MultiPlayer is well suited for one-shots, multi-sampled instruments
* or any time you need to play a bunch of audio buffers.
* @param {Object|Array|Tone.Buffers} buffers The buffers which are available
* to the MultiPlayer
* @param {Function} onload The callback to invoke when all of the buffers are loaded.
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* var multiPlayer = new MultiPlayer({
* "kick" : "path/to/kick.mp3",
* "snare" : "path/to/snare.mp3",
* }, function(){
* multiPlayer.start("kick");
* });
* @example
* //can also store the values in an array
* var multiPlayer = new MultiPlayer(["path/to/kick.mp3", "path/to/snare.mp3"],
* function(){
* //if an array is passed in, the samples are referenced to by index
* multiPlayer.start(1);
* });
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'urls',
'onload'
], Tone.MultiPlayer.defaults);
if (options.urls instanceof Tone.Buffers) {
/**
* All the buffers belonging to the player.
* @type {Tone.Buffers}
*/
this.buffers = options.urls;
} else {
this.buffers = new Tone.Buffers(options.urls, options.onload);
}
/**
* Keeps track of the currently playing sources.
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
this._activeSources = {};
/**
* The fade in envelope which is applied
* to the beginning of the BufferSource
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeIn = options.fadeIn;
/**
* The fade out envelope which is applied
* to the end of the BufferSource
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeOut = options.fadeOut;
/**
* The output volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume of the output in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
* @example
* source.volume.value = -6;
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
//make the output explicitly stereo
this._volume.output.output.channelCount = 2;
this._volume.output.output.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
//mute initially
this.mute = options.mute;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MultiPlayer, Tone.Source);
/**
* The defaults
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'fadeIn': 0,
'fadeOut': 0
};
/**
* Make the source from the buffername
* @param {String} bufferName
* @return {Tone.BufferSource}
* @private
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype._makeSource = function (bufferName) {
var buffer;
if (this.isString(bufferName) || this.isNumber(bufferName)) {
buffer = this.buffers.get(bufferName).get();
} else if (bufferName instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
buffer = bufferName.get();
} else if (bufferName instanceof AudioBuffer) {
buffer = bufferName;
}
var source = new Tone.BufferSource(buffer).connect(this.output);
if (!this._activeSources.hasOwnProperty(bufferName)) {
this._activeSources[bufferName] = [];
}
this._activeSources[bufferName].push(source);
return source;
};
/**
* Start a buffer by name. The `start` method allows a number of options
* to be passed in such as offset, interval, and gain. This is good for multi-sampled
* instruments and sound sprites where samples are repitched played back at different velocities.
* @param {String} bufferName The name of the buffer to start.
* @param {Time} time When to start the buffer.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset into the buffer to play from.
* @param {Time=} duration How long to play the buffer for.
* @param {Interval} [pitch=0] The interval to repitch the buffer.
* @param {Gain} [gain=1] The gain to play the sample at.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.start = function (bufferName, time, offset, duration, pitch, gain) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var source = this._makeSource(bufferName);
source.start(time, offset, duration, this.defaultArg(gain, 1), this.fadeIn);
if (duration) {
source.stop(time + this.toSeconds(duration), this.fadeOut);
}
pitch = this.defaultArg(pitch, 0);
source.playbackRate.value = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(pitch);
return this;
};
/**
* Start a looping buffer by name. Similar to `start`, but the buffer
* is looped instead of played straight through. Can still be stopped with `stop`.
* @param {String} bufferName The name of the buffer to start.
* @param {Time} time When to start the buffer.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset into the buffer to play from.
* @param {Time=} loopStart The start of the loop.
* @param {Time=} loopEnd The end of the loop.
* @param {Interval} [pitch=0] The interval to repitch the buffer.
* @param {Gain} [gain=1] The gain to play the sample at.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.startLoop = function (bufferName, time, offset, loopStart, loopEnd, pitch, gain) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var source = this._makeSource(bufferName);
source.loop = true;
source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(this.defaultArg(loopStart, 0));
source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(this.defaultArg(loopEnd, 0));
source.start(time, offset, undefined, this.defaultArg(gain, 1), this.fadeIn);
pitch = this.defaultArg(pitch, 0);
source.playbackRate.value = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(pitch);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the first played instance of the buffer name.
* @param {String} bufferName The buffer to stop.
* @param {Time=} time When to stop the buffer
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.stop = function (bufferName, time) {
if (this._activeSources[bufferName] && this._activeSources[bufferName].length) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._activeSources[bufferName].shift().stop(time, this.fadeOut);
} else {
throw new Error('Tone.MultiPlayer: cannot stop a buffer that hasn\'t been started or is already stopped');
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop all currently playing buffers at the given time.
* @param {Time=} time When to stop the buffers.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.stopAll = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var bufferName in this._activeSources) {
var sources = this._activeSources[bufferName];
for (var i = 0; i < sources.length; i++) {
sources[i].stop(time);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Add another buffer to the available buffers.
* @param {String} name The name to that the buffer is refered
* to in start/stop methods.
* @param {String|Tone.Buffer} url The url of the buffer to load
* or the buffer.
* @param {Function} callback The function to invoke after the buffer is loaded.
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.add = function (name, url, callback) {
this.buffers.add(name, url, callback);
return this;
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source. "started"
* if there are any buffers playing. "stopped" otherwise.
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.MultiPlayer#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._activeSources.length > 0 ? Tone.State.Started : Tone.State.Stopped;
}
});
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.MultiPlayer#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* source.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._volume.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._volume.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this._writable('volume');
this.volume = null;
for (var bufferName in this._activeSources) {
this._activeSources[bufferName].forEach(function (source) {
source.dispose();
});
}
this.buffers.dispose();
this.buffers = null;
this._activeSources = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MultiPlayer;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.GrainPlayer implements [granular synthesis](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granular_synthesis).
* Granular Synthesis enables you to adjust pitch and playback rate independently. The grainSize is the
* amount of time each small chunk of audio is played for and the overlap is the
* amount of crossfading transition time between successive grains.
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {String|Tone.Buffer} url The url to load, or the Tone.Buffer to play.
* @param {Function=} callback The callback to invoke after the url is loaded.
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.GrainPlayer.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this);
/**
* The audio buffer belonging to the player.
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
*/
this.buffer = new Tone.Buffer(options.url, options.onload);
/**
* Plays the buffer with a small envelope
* @type {Tone.MultiPlayer}
* @private
*/
this._player = this.output = new Tone.MultiPlayer();
/**
* Create a repeating tick to schedule
* the grains.
* @type {Tone.Clock}
* @private
*/
this._clock = new Tone.Clock(this._tick.bind(this), 1);
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = 0;
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = 0;
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._grainSize = options.grainSize;
/**
* @private
* @type {Number}
*/
this._overlap = options.overlap;
/**
* Adjust the pitch independently of the playbackRate.
* @type {Cents}
*/
this.detune = options.detune;
/**
* The amount of time randomly added
* or subtracted from the grain's offset
* @type {Time}
*/
this.drift = options.drift;
//setup
this.overlap = options.overlap;
this.loop = options.loop;
this.playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
this.grainSize = options.grainSize;
this.loopStart = options.loopStart;
this.loopEnd = options.loopEnd;
this.reverse = options.reverse;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.GrainPlayer, Tone.Source);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'overlap': 0.1,
'grainSize': 0.2,
'drift': 0,
'playbackRate': 1,
'detune': 0,
'loop': false,
'loopStart': 0,
'loopEnd': 0,
'reverse': false
};
/**
* Play the buffer at the given startTime. Optionally add an offset
* from the start of the buffer to play from.
*
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the player should start.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset from the beginning of the sample
* to start at.
* @return {Tone.GrainPlayer} this
*/
/**
* Internal start method
* @param {Time} time
* @param {Time} offset
* @private
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype._start = function (time, offset) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._offset = offset;
this._clock.start(time);
};
/**
* Internal start method
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype._stop = function (time) {
this._clock.stop(time);
this._player.stop(this.buffer, time);
this._offset = 0;
};
/**
* Invoked on each clock tick. scheduled a new
* grain at this time.
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype._tick = function (time) {
var bufferDuration = this.buffer.duration;
if (this.loop && this._loopEnd > 0) {
bufferDuration = this._loopEnd;
}
var drift = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * this.drift;
var offset = this._offset - this._overlap + drift;
var detune = this.detune / 100;
var originalFadeIn = this._player.fadeIn;
if (this.loop && this._offset > bufferDuration) {
//play the end
var endSegmentDuration = this._offset - bufferDuration;
this._player.start(this.buffer, time, offset, endSegmentDuration + this._overlap, detune);
//and play the beginning
offset = this._offset % bufferDuration;
this._offset = this._loopStart;
this._player.fadeIn = 0;
this._player.start(this.buffer, time + endSegmentDuration, this._offset, offset + this._overlap, detune);
} else if (this._offset > bufferDuration) {
//set the state to stopped.
this.stop(time);
} else {
if (offset < 0) {
this._player.fadeIn = Math.max(this._player.fadeIn + offset, 0);
offset = 0;
}
this._player.start(this.buffer, time, offset, this.grainSize + this._overlap, detune);
}
this._player.fadeIn = originalFadeIn;
//increment the offset
var duration = this._clock._nextTick - time;
this._offset += duration * this._playbackRate;
};
/**
* Jump to a specific time and play it.
* @param {Time} offset The offset to jump to.
* @param {Time=} time When to make the jump.
* @return {[type]} [description]
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype.scrub = function (offset, time) {
this._offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
this._tick(this.toSeconds(time));
return this;
};
/**
* The playback rate of the sample
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Positive}
* @name playbackRate
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
this.grainSize = this._grainSize;
}
});
/**
* The loop start time.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return this._loopStart;
},
set: function (time) {
this._loopStart = this.toSeconds(time);
}
});
/**
* The loop end time.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return this._loopEnd;
},
set: function (time) {
this._loopEnd = this.toSeconds(time);
}
});
/**
* The direction the buffer should play in
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this.buffer.reverse;
},
set: function (rev) {
this.buffer.reverse = rev;
}
});
/**
* The size of each chunk of audio that the
* buffer is chopped into and played back at.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name grainSize
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'grainSize', {
get: function () {
return this._grainSize;
},
set: function (size) {
this._grainSize = this.toSeconds(size);
this._clock.frequency.value = this._playbackRate / this._grainSize;
}
});
/**
* This is the duration of the cross-fade between
* sucessive grains.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name overlap
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'overlap', {
get: function () {
return this._overlap;
},
set: function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._overlap = time;
if (this._overlap < 0) {
this._player.fadeIn = 0.01;
this._player.fadeOut = 0.01;
} else {
this._player.fadeIn = time;
this._player.fadeOut = time;
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.GrainPlayer} this
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.buffer.dispose();
this.buffer = null;
this._player.dispose();
this._player = null;
this._clock.dispose();
this._clock = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.GrainPlayer;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.UserMedia uses MediaDevices.getUserMedia to open up
* and external microphone or audio input. Check
* [MediaDevices API Support](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/MediaDevices/getUserMedia)
* to see which browsers are supported. Access to an external input
* is limited to secure (HTTPS) connections.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Decibels=} volume The level of the input
* @example
* //list the inputs and open the third one
* var motu = new Tone.UserMedia();
*
* //opening the input asks the user to activate their mic
* motu.open().then(function(){
* //opening is activates the microphone
* //starting lets audio through
* motu.start(10);
* });
*/
Tone.UserMedia = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['volume'], Tone.UserMedia.defaults);
/**
* The MediaStreamNode
* @type {MediaStreamAudioSourceNode}
* @private
*/
this._mediaStream = null;
/**
* The media stream created by getUserMedia.
* @type {LocalMediaStream}
* @private
*/
this._stream = null;
/**
* The open device
* @type {MediaDeviceInfo}
* @private
*/
this._device = null;
/**
* The output volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume of the output in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
* @example
* input.volume.value = -6;
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
this.mute = options.mute;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.UserMedia);
/**
* the default parameters
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.UserMedia.defaults = {
'volume': 0,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Open the media stream. If a string is passed in, it is assumed
* to be the label or id of the stream, if a number is passed in,
* it is the input number of the stream.
* @param {String|Number} [labelOrId="default"] The label or id of the audio input media device.
* With no argument, the default stream is opened.
* @return {Promise} The promise is resolved when the stream is open.
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.open = function (labelOrId) {
labelOrId = this.defaultArg(labelOrId, 'default');
return this.enumerateDevices().then(function (devices) {
var device;
if (this.isNumber(labelOrId)) {
device = devices[labelOrId];
} else {
device = devices.find(function (device) {
return device.label === labelOrId || device.deviceId === labelOrId;
});
if (!device) {
//otherwise just take the first one
device = devices[0];
}
}
//didn't find a matching device
if (!device) {
throw new Error('Tone.UserMedia: no matching audio inputs.');
}
this._device = device;
//do getUserMedia
var constraints = {
audio: {
'deviceId': device.deviceId,
'echoCancellation': false,
'sampleRate': this.context.sampleRate
}
};
return navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia(constraints).then(function (stream) {
//start a new source only if the previous one is closed
if (!this._stream) {
this._stream = stream;
//Wrap a MediaStreamSourceNode around the live input stream.
this._mediaStream = this.context.createMediaStreamSource(stream);
//Connect the MediaStreamSourceNode to a gate gain node
this._mediaStream.connect(this.output);
}
return this;
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
};
/**
* Close the media stream
* @return {Tone.UserMedia} this
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.close = function () {
if (this._stream) {
this._stream.getAudioTracks().forEach(function (track) {
track.stop();
});
this._stream = null;
//remove the old media stream
this._mediaStream.disconnect();
this._mediaStream = null;
}
this._device = null;
return this;
};
/**
* Returns a promise which resolves with the list of audio input devices available.
* @return {Promise} The promise that is resolved with the devices
* @example
* extInput.enumerateDevices().then(function(devices){
* console.log(devices)
* })
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.enumerateDevices = function () {
return navigator.mediaDevices.enumerateDevices().then(function (devices) {
return devices.filter(function (device) {
return device.kind === 'audioinput';
});
});
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, "started" when the microphone is open
* and "stopped" when the mic is closed.
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._stream && this._stream.active ? Tone.State.Started : Tone.State.Stopped;
}
});
/**
* Returns an identifier for the represented device that is
* persisted across sessions. It is un-guessable by other applications and
* unique to the origin of the calling application. It is reset when the
* user clears cookies (for Private Browsing, a different identifier is
* used that is not persisted across sessions). Returns undefined when the
* device is not open.
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name deviceId
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'deviceId', {
get: function () {
if (this._device) {
return this._device.deviceId;
}
}
});
/**
* Returns a group identifier. Two devices have the
* same group identifier if they belong to the same physical device.
* Returns undefined when the device is not open.
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name groupId
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'groupId', {
get: function () {
if (this._device) {
return this._device.groupId;
}
}
});
/**
* Returns a label describing this device (for example "Built-in Microphone").
* Returns undefined when the device is not open or label is not available
* because of permissions.
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name groupId
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'label', {
get: function () {
if (this._device) {
return this._device.label;
}
}
});
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* userMedia.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._volume.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._volume.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.UserMedia} this
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.close();
this._writable('volume');
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this.volume = null;
return this;
};
/**
* If getUserMedia is supported by the browser.
* @type {Boolean}
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name supported
* @static
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia, 'supported', {
get: function () {
return !Tone.prototype.isUndef(navigator.mediaDevices) && Tone.prototype.isFunction(navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia);
}
});
return Tone.UserMedia;
});
return Tone;
}));
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {Object} [options] the options available for the synth
* see defaults below
* @example
* var noiseSynth = new Tone.NoiseSynth().toMaster();
* noiseSynth.triggerAttackRelease("8n");
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth = function (options) {
//get the defaults
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.NoiseSynth.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The noise source.
* @type {Tone.Noise}
* @example
* noiseSynth.set("noise.type", "brown");
*/
this.noise = new Tone.Noise();
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
//connect the noise to the output
this.noise.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
//start the noise
this.noise.start();
this._readOnly([
'noise',
'envelope'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.NoiseSynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.defaults = {
'noise': { 'type': 'white' },
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.005,
'decay': 0.1,
'sustain': 0
}
};
/**
* Start the attack portion of the envelopes. Unlike other
* instruments, Tone.NoiseSynth doesn't have a note.
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the attack should start
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the note (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
* @example
* noiseSynth.triggerAttack();
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (time, velocity) {
//the envelopes
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* Start the release portion of the envelopes.
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time the release should start
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and then the release.
* @param {Time} duration the duration of the note
* @param {Time} [time=now] the time of the attack
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (duration, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
this.triggerRelease(time + duration);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.NoiseSynth} this
*/
Tone.NoiseSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'noise',
'envelope'
]);
this.noise.dispose();
this.noise = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.NoiseSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Karplus-String string synthesis. Often out of tune.
* Will change when the AudioWorkerNode is available across
* browsers.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {Object} [options] see the defaults
* @example
* var plucky = new Tone.PluckSynth().toMaster();
* plucky.triggerAttack("C4");
*/
Tone.PluckSynth = function (options) {
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.PluckSynth.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* @type {Tone.Noise}
* @private
*/
this._noise = new Tone.Noise('pink');
/**
* The amount of noise at the attack.
* Nominal range of [0.1, 20]
* @type {number}
*/
this.attackNoise = options.attackNoise;
/**
* the LFCF
* @type {Tone.LowpassCombFilter}
* @private
*/
this._lfcf = new Tone.LowpassCombFilter({
'resonance': options.resonance,
'dampening': options.dampening
});
/**
* The resonance control.
* @type {NormalRange}
* @signal
*/
this.resonance = this._lfcf.resonance;
/**
* The dampening control. i.e. the lowpass filter frequency of the comb filter
* @type {Frequency}
* @signal
*/
this.dampening = this._lfcf.dampening;
//connections
this._noise.connect(this._lfcf);
this._lfcf.connect(this.output);
this._readOnly([
'resonance',
'dampening'
]);
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PluckSynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.PluckSynth.defaults = {
'attackNoise': 1,
'dampening': 4000,
'resonance': 0.9
};
/**
* Trigger the note.
* @param {Frequency} note The note to trigger.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the note should be triggered.
* @returns {Tone.PluckSynth} this
*/
Tone.PluckSynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (note, time) {
note = this.toFrequency(note);
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var delayAmount = 1 / note;
this._lfcf.delayTime.setValueAtTime(delayAmount, time);
this._noise.start(time);
this._noise.stop(time + delayAmount * this.attackNoise);
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.PluckSynth} this
*/
Tone.PluckSynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._noise.dispose();
this._lfcf.dispose();
this._noise = null;
this._lfcf = null;
this._writable([
'resonance',
'dampening'
]);
this.dampening = null;
this.resonance = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.PluckSynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.PolySynth handles voice creation and allocation for any
* instruments passed in as the second paramter. PolySynth is
* not a synthesizer by itself, it merely manages voices of
* one of the other types of synths, allowing any of the
* monophonic synthesizers to be polyphonic.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {number|Object} [polyphony=4] The number of voices to create
* @param {function} [voice=Tone.Synth] The constructor of the voices
* uses Tone.Synth by default.
* @example
* //a polysynth composed of 6 Voices of Synth
* var synth = new Tone.PolySynth(6, Tone.Synth).toMaster();
* //set the attributes using the set interface
* synth.set("detune", -1200);
* //play a chord
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(["C4", "E4", "A4"], "4n");
*/
Tone.PolySynth = function () {
Tone.Instrument.call(this);
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'polyphony',
'voice'
], Tone.PolySynth.defaults);
options = this.defaultArg(options, Tone.Instrument.defaults);
//max polyphony
options.polyphony = Math.min(Tone.PolySynth.MAX_POLYPHONY, options.polyphony);
/**
* the array of voices
* @type {Array}
*/
this.voices = new Array(options.polyphony);
/**
* The queue of voices with data about last trigger
* and the triggered note
* @private
* @type {Array}
*/
this._triggers = new Array(options.polyphony);
/**
* The detune in cents
* @type {Cents}
* @signal
*/
this.detune = new Tone.Signal(options.detune, Tone.Type.Cents);
this._readOnly('detune');
//create the voices
for (var i = 0; i < options.polyphony; i++) {
var v = new options.voice(arguments[2], arguments[3]);
this.voices[i] = v;
v.connect(this.output);
if (v.hasOwnProperty('detune')) {
this.detune.connect(v.detune);
}
this._triggers[i] = {
release: -1,
note: null,
voice: v
};
}
//set the volume initially
this.volume.value = options.volume;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.PolySynth, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* the defaults
* @const
* @static
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.PolySynth.defaults = {
'polyphony': 4,
'volume': 0,
'detune': 0,
'voice': Tone.Synth
};
/**
* Trigger the attack portion of the note
* @param {Frequency|Array} notes The notes to play. Accepts a single
* Frequency or an array of frequencies.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The start time of the note.
* @param {number} [velocity=1] The velocity of the note.
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* //trigger a chord immediately with a velocity of 0.2
* poly.triggerAttack(["Ab3", "C4", "F5"], undefined, 0.2);
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.triggerAttack = function (notes, time, velocity) {
if (!Array.isArray(notes)) {
notes = [notes];
}
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var i = 0; i < notes.length; i++) {
var val = notes[i];
//trigger the oldest voice
var oldest = this._triggers[0];
var oldestIndex = 0;
for (var j = 1; j < this._triggers.length; j++) {
if (this._triggers[j].release < oldest.release) {
oldest = this._triggers[j];
oldestIndex = j;
}
}
oldest.release = Infinity;
oldest.note = JSON.stringify(val);
oldest.voice.triggerAttack(val, time, velocity);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and release after the specified duration
*
* @param {Frequency|Array} notes The notes to play. Accepts a single
* Frequency or an array of frequencies.
* @param {Time} duration the duration of the note
* @param {Time} [time=now] if no time is given, defaults to now
* @param {number} [velocity=1] the velocity of the attack (0-1)
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* //trigger a chord for a duration of a half note
* poly.triggerAttackRelease(["Eb3", "G4", "C5"], "2n");
* @example
* //can pass in an array of durations as well
* poly.triggerAttackRelease(["Eb3", "G4", "C5"], ["2n", "4n", "4n"]);
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.triggerAttackRelease = function (notes, duration, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.triggerAttack(notes, time, velocity);
if (this.isArray(duration) && this.isArray(notes)) {
for (var i = 0; i < notes.length; i++) {
var d = duration[Math.min(i, duration.length - 1)];
this.triggerRelease(notes[i], time + this.toSeconds(d));
}
} else {
this.triggerRelease(notes, time + this.toSeconds(duration));
}
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the release of the note. Unlike monophonic instruments,
* a note (or array of notes) needs to be passed in as the first argument.
* @param {Frequency|Array} notes The notes to play. Accepts a single
* Frequency or an array of frequencies.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the release will be triggered.
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* poly.triggerRelease(["Ab3", "C4", "F5"], "+2n");
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.triggerRelease = function (notes, time) {
if (!Array.isArray(notes)) {
notes = [notes];
}
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var i = 0; i < notes.length; i++) {
//get the voice
var stringified = JSON.stringify(notes[i]);
for (var v = 0; v < this._triggers.length; v++) {
var desc = this._triggers[v];
if (desc.note === stringified && desc.release > time) {
desc.voice.triggerRelease(time);
desc.release = time;
}
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Set a member/attribute of the voices.
* @param {Object|string} params
* @param {number=} value
* @param {Time=} rampTime
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
* @example
* poly.set({
* "filter" : {
* "type" : "highpass"
* },
* "envelope" : {
* "attack" : 0.25
* }
* });
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.set = function (params, value, rampTime) {
for (var i = 0; i < this.voices.length; i++) {
this.voices[i].set(params, value, rampTime);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Get the synth's attributes. Given no arguments get
* will return all available object properties and their corresponding
* values. Pass in a single attribute to retrieve or an array
* of attributes. The attribute strings can also include a "."
* to access deeper properties.
* @param {Array=} params the parameters to get, otherwise will return
* all available.
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.get = function (params) {
return this.voices[0].get(params);
};
/**
* Trigger the release portion of all the currently active voices.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the notes should be released.
* @return {Tone.PolySynth} this
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.releaseAll = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var i = 0; i < this._triggers.length; i++) {
var desc = this._triggers[i];
if (desc.release > time) {
desc.release = time;
desc.voice.triggerRelease(time);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.PolySynth} this
*/
Tone.PolySynth.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
for (var i = 0; i < this.voices.length; i++) {
this.voices[i].dispose();
this.voices[i] = null;
}
this._writable('detune');
this.detune.dispose();
this.detune = null;
this.voices = null;
this._triggers = null;
return this;
};
/**
* The maximum number of notes that can be allocated
* to a polysynth.
* @type {Number}
* @static
*/
Tone.PolySynth.MAX_POLYPHONY = 20;
return Tone.PolySynth;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.Player is an audio file player with start, loop, and stop functions.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Source}
* @param {string|AudioBuffer} url Either the AudioBuffer or the url from
* which to load the AudioBuffer
* @param {function=} onload The function to invoke when the buffer is loaded.
* Recommended to use Tone.Buffer.on('load') instead.
* @example
* var player = new Tone.Player("./path/to/sample.mp3").toMaster();
* //play as soon as the buffer is loaded
* player.autostart = true;
*/
Tone.Player = function (url) {
var options;
if (url instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
url = url.get();
options = Tone.Player.defaults;
} else {
options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.Player.defaults);
}
Tone.Source.call(this, options);
/**
* @private
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
*/
this._source = null;
/**
* If the file should play as soon
* as the buffer is loaded.
* @type {boolean}
* @example
* //will play as soon as it's loaded
* var player = new Tone.Player({
* "url" : "./path/to/sample.mp3",
* "autostart" : true,
* }).toMaster();
*/
this.autostart = options.autostart;
/**
* the buffer
* @private
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
*/
this._buffer = new Tone.Buffer({
'url': options.url,
'onload': this._onload.bind(this, options.onload),
'reverse': options.reverse
});
if (url instanceof AudioBuffer) {
this._buffer.set(url);
}
/**
* if the buffer should loop once it's over
* @type {boolean}
* @private
*/
this._loop = options.loop;
/**
* if 'loop' is true, the loop will start at this position
* @type {Time}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = options.loopStart;
/**
* if 'loop' is true, the loop will end at this position
* @type {Time}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = options.loopEnd;
/**
* the playback rate
* @private
* @type {number}
*/
this._playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
/**
* Enabling retrigger will allow a player to be restarted
* before the the previous 'start' is done playing. Otherwise,
* successive calls to Tone.Player.start will only start
* the sample if it had played all the way through.
* @type {boolean}
*/
this.retrigger = options.retrigger;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Player, Tone.Source);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.Player.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'playbackRate': 1,
'loop': false,
'autostart': false,
'loopStart': 0,
'loopEnd': 0,
'retrigger': false,
'reverse': false
};
/**
* Load the audio file as an audio buffer.
* Decodes the audio asynchronously and invokes
* the callback once the audio buffer loads.
* Note: this does not need to be called if a url
* was passed in to the constructor. Only use this
* if you want to manually load a new url.
* @param {string} url The url of the buffer to load.
* Filetype support depends on the
* browser.
* @param {function=} callback The function to invoke once
* the sample is loaded.
* @returns {Promise}
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.load = function (url, callback) {
return this._buffer.load(url, this._onload.bind(this, callback));
};
/**
* Internal callback when the buffer is loaded.
* @private
*/
Tone.Player.prototype._onload = function (callback) {
callback = this.defaultArg(callback, Tone.noOp);
callback(this);
if (this.autostart) {
this.start();
}
};
/**
* Play the buffer at the given startTime. Optionally add an offset
* and/or duration which will play the buffer from a position
* within the buffer for the given duration.
*
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the player should start.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset from the beginning of the sample
* to start at.
* @param {Time=} duration How long the sample should play. If no duration
* is given, it will default to the full length
* of the sample (minus any offset)
* @returns {Tone.Player} this
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @method start
* @name start
*/
/**
* Internal start method
* @private
*/
Tone.Player.prototype._start = function (startTime, offset, duration) {
if (this._buffer.loaded) {
//if it's a loop the default offset is the loopstart point
if (this._loop) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, this._loopStart);
} else {
//otherwise the default offset is 0
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
}
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
//make sure it has a positive duration
duration = this.defaultArg(duration, Math.max(this._buffer.duration - offset, 0));
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
//the values in seconds
startTime = this.toSeconds(startTime);
//make the source
this._source = this.context.createBufferSource();
this._source.buffer = this._buffer.get();
//set the looping properties
if (this._loop) {
this._source.loop = this._loop;
this._source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(this._loopStart);
this._source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(this._loopEnd);
} else {
//if it's not looping, set the state change at the end of the sample
this._state.setStateAtTime(Tone.State.Stopped, startTime + duration);
}
//and other properties
this._source.playbackRate.value = this._playbackRate;
this._source.connect(this.output);
//start it
if (this._loop) {
//modify the offset if it's greater than the loop time
var loopEnd = this._source.loopEnd || this._buffer.duration;
var loopStart = this._source.loopStart;
var loopDuration = loopEnd - loopStart;
if (offset > loopEnd) {
//move the offset back
while (offset > loopEnd) {
offset -= loopDuration;
}
}
this._source.start(startTime, offset);
} else {
this._source.start(startTime, offset, duration);
}
} else {
throw Error('Tone.Player: tried to start Player before the buffer was loaded');
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop playback.
* @private
* @param {Time} [time=now]
* @returns {Tone.Player} this
*/
Tone.Player.prototype._stop = function (time) {
if (this._source) {
this._source.stop(this.toSeconds(time));
this._source = null;
}
return this;
};
/**
* Seek to a specific time in the player's buffer. If the
* source is no longer playing at that time, it will stop.
* If you seek to a time that
* @param {Time} offset The time to seek to.
* @param {Time=} time The time for the seek event to occur.
* @return {Tone.Player} this
* @example
* source.start(0.2);
* source.stop(0.4);
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.seek = function (offset, time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
if (this._state.getValueAtTime(time) === Tone.State.Started) {
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
// if it's currently playing, stop it
this._stop(time);
//restart it at the given time
this._start(time, offset);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Set the loop start and end. Will only loop if loop is
* set to true.
* @param {Time} loopStart The loop end time
* @param {Time} loopEnd The loop end time
* @returns {Tone.Player} this
* @example
* //loop 0.1 seconds of the file.
* player.setLoopPoints(0.2, 0.3);
* player.loop = true;
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.setLoopPoints = function (loopStart, loopEnd) {
this.loopStart = loopStart;
this.loopEnd = loopEnd;
return this;
};
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will start at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return this._loopStart;
},
set: function (loopStart) {
this._loopStart = loopStart;
if (this._source) {
this._source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(loopStart);
}
}
});
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will end at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return this._loopEnd;
},
set: function (loopEnd) {
this._loopEnd = loopEnd;
if (this._source) {
this._source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(loopEnd);
}
}
});
/**
* The audio buffer belonging to the player.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
return this._buffer;
},
set: function (buffer) {
this._buffer.set(buffer);
}
});
/**
* If the buffer should loop once it's over.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {boolean}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this._loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this._loop = loop;
if (this._source) {
this._source.loop = loop;
}
}
});
/**
* The playback speed. 1 is normal speed. This is not a signal because
* Safari and iOS currently don't support playbackRate as a signal.
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {number}
* @name playbackRate
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
if (this._source) {
this._source.playbackRate.value = rate;
}
}
});
/**
* The direction the buffer should play in
* @memberOf Tone.Player#
* @type {boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Player.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this._buffer.reverse;
},
set: function (rev) {
this._buffer.reverse = rev;
}
});
/**
* Dispose and disconnect.
* @return {Tone.Player} this
*/
Tone.Player.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
if (this._source !== null) {
this._source.disconnect();
this._source = null;
}
this._buffer.dispose();
this._buffer = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Player;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Sampler wraps Tone.Player in an AmplitudeEnvelope.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone.Instrument}
* @param {String} url the url of the audio file
* @param {Function=} onload The callback to invoke when the sample is loaded.
* @example
* var sampler = new Sampler("./audio/casio/A1.mp3", function(){
* //repitch the sample down a half step
* sampler.triggerAttack(-1);
* }).toMaster();
*/
Tone.Sampler = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.Sampler.defaults);
Tone.Instrument.call(this, options);
/**
* The sample player.
* @type {Tone.Player}
*/
this.player = new Tone.Player(options.url, options.onload);
this.player.retrigger = true;
/**
* The amplitude envelope.
* @type {Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope}
*/
this.envelope = new Tone.AmplitudeEnvelope(options.envelope);
this.player.chain(this.envelope, this.output);
this._readOnly([
'player',
'envelope'
]);
this.loop = options.loop;
this.reverse = options.reverse;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Sampler, Tone.Instrument);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
*/
Tone.Sampler.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'loop': false,
'reverse': false,
'envelope': {
'attack': 0.001,
'decay': 0,
'sustain': 1,
'release': 0.1
}
};
/**
* Trigger the start of the sample.
* @param {Interval} [pitch=0] The amount the sample should
* be repitched.
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the sample should start
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] The velocity of the note
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
* @example
* sampler.triggerAttack(0, "+0.1", 0.5);
*/
Tone.Sampler.prototype.triggerAttack = function (pitch, time, velocity) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
pitch = this.defaultArg(pitch, 0);
this.player.playbackRate = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(pitch);
this.player.start(time);
this.envelope.triggerAttack(time, velocity);
return this;
};
/**
* Start the release portion of the sample. Will stop the sample once the
* envelope has fully released.
*
* @param {Time} [time=now] The time when the note should release
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
* @example
* sampler.triggerRelease();
*/
Tone.Sampler.prototype.triggerRelease = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this.envelope.triggerRelease(time);
this.player.stop(this.toSeconds(this.envelope.release) + time);
return this;
};
/**
* Trigger the attack and then the release after the duration.
* @param {Interval} interval The interval in half-steps that the
* sample should be pitch shifted.
* @param {Time} duration How long the note should be held for before
* triggering the release.
* @param {Time} [time=now] When the note should be triggered.
* @param {NormalRange} [velocity=1] The velocity the note should be triggered at.
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
* @example
* //trigger the unpitched note for the duration of an 8th note
* synth.triggerAttackRelease(0, "8n");
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @name triggerAttackRelease
* @method triggerAttackRelease
*/
/**
* If the output sample should loop or not.
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @type {number|string}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sampler.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this.player.loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this.player.loop = loop;
}
});
/**
* The direction the buffer should play in
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @type {boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sampler.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this.player.reverse;
},
set: function (rev) {
this.player.reverse = rev;
}
});
/**
* The buffer to play.
* @memberOf Tone.Sampler#
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Sampler.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
return this.player.buffer;
},
set: function (buff) {
this.player.buffer = buff;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @returns {Tone.Sampler} this
*/
Tone.Sampler.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Instrument.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._writable([
'player',
'envelope'
]);
this.player.dispose();
this.player = null;
this.envelope.dispose();
this.envelope = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Sampler;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Maps a NormalRange [0, 1] to an AudioRange [-1, 1].
* See also Tone.AudioToGain.
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @example
* var g2a = new Tone.GainToAudio();
*/
Tone.GainToAudio = function () {
/**
* @type {WaveShaperNode}
* @private
*/
this._norm = this.input = this.output = new Tone.WaveShaper(function (x) {
return Math.abs(x) * 2 - 1;
});
};
Tone.extend(Tone.GainToAudio, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.GainToAudio} this
*/
Tone.GainToAudio.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._norm.dispose();
this._norm = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.GainToAudio;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Normalize takes an input min and max and maps it linearly to NormalRange [0,1]
*
* @extends {Tone.SignalBase}
* @constructor
* @param {number} inputMin the min input value
* @param {number} inputMax the max input value
* @example
* var norm = new Tone.Normalize(2, 4);
* var sig = new Tone.Signal(3).connect(norm);
* //output of norm is 0.5.
*/
Tone.Normalize = function (inputMin, inputMax) {
/**
* the min input value
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._inputMin = this.defaultArg(inputMin, 0);
/**
* the max input value
* @type {number}
* @private
*/
this._inputMax = this.defaultArg(inputMax, 1);
/**
* subtract the min from the input
* @type {Tone.Add}
* @private
*/
this._sub = this.input = new Tone.Add(0);
/**
* divide by the difference between the input and output
* @type {Tone.Multiply}
* @private
*/
this._div = this.output = new Tone.Multiply(1);
this._sub.connect(this._div);
this._setRange();
};
Tone.extend(Tone.Normalize, Tone.SignalBase);
/**
* The minimum value the input signal will reach.
* @memberOf Tone.Normalize#
* @type {number}
* @name min
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Normalize.prototype, 'min', {
get: function () {
return this._inputMin;
},
set: function (min) {
this._inputMin = min;
this._setRange();
}
});
/**
* The maximum value the input signal will reach.
* @memberOf Tone.Normalize#
* @type {number}
* @name max
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.Normalize.prototype, 'max', {
get: function () {
return this._inputMax;
},
set: function (max) {
this._inputMax = max;
this._setRange();
}
});
/**
* set the values
* @private
*/
Tone.Normalize.prototype._setRange = function () {
this._sub.value = -this._inputMin;
this._div.value = 1 / (this._inputMax - this._inputMin);
};
/**
* clean up
* @returns {Tone.Normalize} this
*/
Tone.Normalize.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._sub.dispose();
this._sub = null;
this._div.dispose();
this._div = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.Normalize;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Wrapper around the native BufferSourceNode.
* @param {AudioBuffer|Tone.Buffer} buffer The buffer to play
* @param {Function} onended The callback to invoke when the
* buffer is done playing.
*/
Tone.BufferSource = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'buffer',
'onended'
], Tone.BufferSource.defaults);
/**
* The callback to invoke after the
* buffer source is done playing.
* @type {Function}
*/
this.onended = options.onended;
/**
* The time that the buffer was started.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._startTime = -1;
/**
* The time that the buffer is scheduled to stop.
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._stopTime = -1;
/**
* The gain node which envelopes the BufferSource
* @type {Tone.Gain}
* @private
*/
this._gainNode = this.output = new Tone.Gain();
/**
* The buffer source
* @type {AudioBufferSourceNode}
* @private
*/
this._source = this.context.createBufferSource();
this._source.connect(this._gainNode);
/**
* The playbackRate of the buffer
* @type {Positive}
* @signal
*/
this.playbackRate = new Tone.Param(this._source.playbackRate, Tone.Type.Positive);
/**
* The fadeIn time of the amplitude envelope.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeIn = options.fadeIn;
/**
* The fadeOut time of the amplitude envelope.
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeOut = options.fadeOut;
/**
* The value that the buffer ramps to
* @type {Gain}
* @private
*/
this._gain = 1;
/**
* The onended timeout
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._onendedTimeout = -1;
//set the buffer initially
if (!this.isUndef(options.buffer)) {
this.buffer = options.buffer;
}
this.loop = options.loop;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.BufferSource);
/**
* The defaults
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.BufferSource.defaults = {
'onended': Tone.noOp,
'fadeIn': 0,
'fadeOut': 0
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, either "started" or "stopped".
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
var now = this.now();
if (this._startTime !== -1 && now >= this._startTime && now < this._stopTime) {
return Tone.State.Started;
} else {
return Tone.State.Stopped;
}
}
});
/**
* Start the buffer
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the player should start.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset from the beginning of the sample
* to start at.
* @param {Time=} duration How long the sample should play. If no duration
* is given, it will default to the full length
* of the sample (minus any offset)
* @param {Gain} [gain=1] The gain to play the buffer back at.
* @param {Time=} fadeInTime The optional fadeIn ramp time.
* @return {Tone.BufferSource} this
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype.start = function (time, offset, duration, gain, fadeInTime) {
if (this._startTime !== -1) {
throw new Error('Tone.BufferSource: can only be started once.');
}
if (this.buffer) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//if it's a loop the default offset is the loopstart point
if (this.loop) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, this.loopStart);
} else {
//otherwise the default offset is 0
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
}
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
//the values in seconds
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._source.start(time, offset);
gain = this.defaultArg(gain, 1);
this._gain = gain;
//the fadeIn time
if (this.isUndef(fadeInTime)) {
fadeInTime = this.toSeconds(this.fadeIn);
} else {
fadeInTime = this.toSeconds(fadeInTime);
}
if (fadeInTime > 0) {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(0, time);
this._gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(this._gain, time + fadeInTime);
} else {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(gain, time);
}
this._startTime = time + fadeInTime;
if (!this.isUndef(duration)) {
duration = this.defaultArg(duration, this.buffer.duration - offset);
duration = this.toSeconds(duration);
this.stop(time + duration + fadeInTime, fadeInTime);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the buffer. Optionally add a ramp time to fade the
* buffer out.
* @param {Time=} time The time the buffer should stop.
* @param {Time=} fadeOutTime How long the gain should fade out for
* @return {Tone.BufferSource} this
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype.stop = function (time, fadeOutTime) {
if (this.buffer) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
//the fadeOut time
if (this.isUndef(fadeOutTime)) {
fadeOutTime = this.toSeconds(this.fadeOut);
} else {
fadeOutTime = this.toSeconds(fadeOutTime);
}
this._stopTime = time + fadeOutTime;
//cancel the end curve
this._gainNode.gain.cancelScheduledValues(this._startTime + this.sampleTime);
//set a new one
if (fadeOutTime > 0) {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(this._gain, time);
this._gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0, time + fadeOutTime);
time += fadeOutTime;
} else {
this._gainNode.gain.setValueAtTime(0, time);
}
// fix for safari bug and old FF
if (!this.isNumber(this._source.playbackState) || this._source.playbackState === 2) {
this._source.stop(time);
}
clearTimeout(this._onendedTimeout);
this._onendedTimeout = setTimeout(this._onended.bind(this), (this._stopTime - this.now()) * 1000);
}
return this;
};
/**
* Internal callback when the buffer is ended.
* Invokes `onended` and disposes the node.
* @private
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype._onended = function () {
this.onended(this);
this.dispose();
};
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will start at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return this._source.loopStart;
},
set: function (loopStart) {
this._source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(loopStart);
}
});
/**
* If loop is true, the loop will end at this position.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return this._source.loopEnd;
},
set: function (loopEnd) {
this._source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(loopEnd);
}
});
/**
* The audio buffer belonging to the player.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {AudioBuffer}
* @name buffer
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'buffer', {
get: function () {
if (this._source) {
return this._source.buffer;
} else {
return null;
}
},
set: function (buffer) {
if (buffer instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
this._source.buffer = buffer.get();
} else {
this._source.buffer = buffer;
}
}
});
/**
* If the buffer should loop once it's over.
* @memberOf Tone.BufferSource#
* @type {boolean}
* @name loop
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.BufferSource.prototype, 'loop', {
get: function () {
return this._source.loop;
},
set: function (loop) {
this._source.loop = loop;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.BufferSource} this
*/
Tone.BufferSource.prototype.dispose = function () {
this.onended = null;
if (this._source) {
this._source.disconnect();
this._source = null;
}
if (this._gainNode) {
this._gainNode.dispose();
this._gainNode = null;
}
this._startTime = -1;
this.playbackRate = null;
this.output = null;
clearTimeout(this._onendedTimeout);
return this;
};
return Tone.BufferSource;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.MultiPlayer is well suited for one-shots, multi-sampled instruments
* or any time you need to play a bunch of audio buffers.
* @param {Object|Array|Tone.Buffers} buffers The buffers which are available
* to the MultiPlayer
* @param {Function} onload The callback to invoke when all of the buffers are loaded.
* @extends {Tone}
* @example
* var multiPlayer = new MultiPlayer({
* "kick" : "path/to/kick.mp3",
* "snare" : "path/to/snare.mp3",
* }, function(){
* multiPlayer.start("kick");
* });
* @example
* //can also store the values in an array
* var multiPlayer = new MultiPlayer(["path/to/kick.mp3", "path/to/snare.mp3"],
* function(){
* //if an array is passed in, the samples are referenced to by index
* multiPlayer.start(1);
* });
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'urls',
'onload'
], Tone.MultiPlayer.defaults);
if (options.urls instanceof Tone.Buffers) {
/**
* All the buffers belonging to the player.
* @type {Tone.Buffers}
*/
this.buffers = options.urls;
} else {
this.buffers = new Tone.Buffers(options.urls, options.onload);
}
/**
* Keeps track of the currently playing sources.
* @type {Object}
* @private
*/
this._activeSources = {};
/**
* The fade in envelope which is applied
* to the beginning of the BufferSource
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeIn = options.fadeIn;
/**
* The fade out envelope which is applied
* to the end of the BufferSource
* @type {Time}
*/
this.fadeOut = options.fadeOut;
/**
* The output volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume of the output in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
* @example
* source.volume.value = -6;
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
//make the output explicitly stereo
this._volume.output.output.channelCount = 2;
this._volume.output.output.channelCountMode = 'explicit';
//mute initially
this.mute = options.mute;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.MultiPlayer, Tone.Source);
/**
* The defaults
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'fadeIn': 0,
'fadeOut': 0
};
/**
* Make the source from the buffername
* @param {String} bufferName
* @return {Tone.BufferSource}
* @private
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype._makeSource = function (bufferName) {
var buffer;
if (this.isString(bufferName) || this.isNumber(bufferName)) {
buffer = this.buffers.get(bufferName).get();
} else if (bufferName instanceof Tone.Buffer) {
buffer = bufferName.get();
} else if (bufferName instanceof AudioBuffer) {
buffer = bufferName;
}
var source = new Tone.BufferSource(buffer).connect(this.output);
if (!this._activeSources.hasOwnProperty(bufferName)) {
this._activeSources[bufferName] = [];
}
this._activeSources[bufferName].push(source);
return source;
};
/**
* Start a buffer by name. The `start` method allows a number of options
* to be passed in such as offset, interval, and gain. This is good for multi-sampled
* instruments and sound sprites where samples are repitched played back at different velocities.
* @param {String} bufferName The name of the buffer to start.
* @param {Time} time When to start the buffer.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset into the buffer to play from.
* @param {Time=} duration How long to play the buffer for.
* @param {Interval} [pitch=0] The interval to repitch the buffer.
* @param {Gain} [gain=1] The gain to play the sample at.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.start = function (bufferName, time, offset, duration, pitch, gain) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var source = this._makeSource(bufferName);
source.start(time, offset, duration, this.defaultArg(gain, 1), this.fadeIn);
if (duration) {
source.stop(time + this.toSeconds(duration), this.fadeOut);
}
pitch = this.defaultArg(pitch, 0);
source.playbackRate.value = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(pitch);
return this;
};
/**
* Start a looping buffer by name. Similar to `start`, but the buffer
* is looped instead of played straight through. Can still be stopped with `stop`.
* @param {String} bufferName The name of the buffer to start.
* @param {Time} time When to start the buffer.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset into the buffer to play from.
* @param {Time=} loopStart The start of the loop.
* @param {Time=} loopEnd The end of the loop.
* @param {Interval} [pitch=0] The interval to repitch the buffer.
* @param {Gain} [gain=1] The gain to play the sample at.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.startLoop = function (bufferName, time, offset, loopStart, loopEnd, pitch, gain) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
var source = this._makeSource(bufferName);
source.loop = true;
source.loopStart = this.toSeconds(this.defaultArg(loopStart, 0));
source.loopEnd = this.toSeconds(this.defaultArg(loopEnd, 0));
source.start(time, offset, undefined, this.defaultArg(gain, 1), this.fadeIn);
pitch = this.defaultArg(pitch, 0);
source.playbackRate.value = this.intervalToFrequencyRatio(pitch);
return this;
};
/**
* Stop the first played instance of the buffer name.
* @param {String} bufferName The buffer to stop.
* @param {Time=} time When to stop the buffer
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.stop = function (bufferName, time) {
if (this._activeSources[bufferName] && this._activeSources[bufferName].length) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._activeSources[bufferName].shift().stop(time, this.fadeOut);
} else {
throw new Error('Tone.MultiPlayer: cannot stop a buffer that hasn\'t been started or is already stopped');
}
return this;
};
/**
* Stop all currently playing buffers at the given time.
* @param {Time=} time When to stop the buffers.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.stopAll = function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
for (var bufferName in this._activeSources) {
var sources = this._activeSources[bufferName];
for (var i = 0; i < sources.length; i++) {
sources[i].stop(time);
}
}
return this;
};
/**
* Add another buffer to the available buffers.
* @param {String} name The name to that the buffer is refered
* to in start/stop methods.
* @param {String|Tone.Buffer} url The url of the buffer to load
* or the buffer.
* @param {Function} callback The function to invoke after the buffer is loaded.
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.add = function (name, url, callback) {
this.buffers.add(name, url, callback);
return this;
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source. "started"
* if there are any buffers playing. "stopped" otherwise.
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.MultiPlayer#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._activeSources.length > 0 ? Tone.State.Started : Tone.State.Stopped;
}
});
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.MultiPlayer#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* source.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._volume.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._volume.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.MultiPlayer} this
*/
Tone.MultiPlayer.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this._writable('volume');
this.volume = null;
for (var bufferName in this._activeSources) {
this._activeSources[bufferName].forEach(function (source) {
source.dispose();
});
}
this.buffers.dispose();
this.buffers = null;
this._activeSources = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.MultiPlayer;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.GrainPlayer implements [granular synthesis](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Granular_synthesis).
* Granular Synthesis enables you to adjust pitch and playback rate independently. The grainSize is the
* amount of time each small chunk of audio is played for and the overlap is the
* amount of crossfading transition time between successive grains.
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {String|Tone.Buffer} url The url to load, or the Tone.Buffer to play.
* @param {Function=} callback The callback to invoke after the url is loaded.
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, [
'url',
'onload'
], Tone.GrainPlayer.defaults);
Tone.Source.call(this);
/**
* The audio buffer belonging to the player.
* @type {Tone.Buffer}
*/
this.buffer = new Tone.Buffer(options.url, options.onload);
/**
* Plays the buffer with a small envelope
* @type {Tone.MultiPlayer}
* @private
*/
this._player = this.output = new Tone.MultiPlayer();
/**
* Create a repeating tick to schedule
* the grains.
* @type {Tone.Clock}
* @private
*/
this._clock = new Tone.Clock(this._tick.bind(this), 1);
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._loopStart = 0;
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._loopEnd = 0;
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
/**
* @type {Number}
* @private
*/
this._grainSize = options.grainSize;
/**
* @private
* @type {Number}
*/
this._overlap = options.overlap;
/**
* Adjust the pitch independently of the playbackRate.
* @type {Cents}
*/
this.detune = options.detune;
/**
* The amount of time randomly added
* or subtracted from the grain's offset
* @type {Time}
*/
this.drift = options.drift;
//setup
this.overlap = options.overlap;
this.loop = options.loop;
this.playbackRate = options.playbackRate;
this.grainSize = options.grainSize;
this.loopStart = options.loopStart;
this.loopEnd = options.loopEnd;
this.reverse = options.reverse;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.GrainPlayer, Tone.Source);
/**
* the default parameters
* @static
* @const
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.defaults = {
'onload': Tone.noOp,
'overlap': 0.1,
'grainSize': 0.2,
'drift': 0,
'playbackRate': 1,
'detune': 0,
'loop': false,
'loopStart': 0,
'loopEnd': 0,
'reverse': false
};
/**
* Play the buffer at the given startTime. Optionally add an offset
* from the start of the buffer to play from.
*
* @param {Time} [startTime=now] When the player should start.
* @param {Time} [offset=0] The offset from the beginning of the sample
* to start at.
* @return {Tone.GrainPlayer} this
*/
/**
* Internal start method
* @param {Time} time
* @param {Time} offset
* @private
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype._start = function (time, offset) {
offset = this.defaultArg(offset, 0);
offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._offset = offset;
this._clock.start(time);
};
/**
* Internal start method
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype._stop = function (time) {
this._clock.stop(time);
this._player.stop(this.buffer, time);
this._offset = 0;
};
/**
* Invoked on each clock tick. scheduled a new
* grain at this time.
* @param {Time} time
* @private
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype._tick = function (time) {
var bufferDuration = this.buffer.duration;
if (this.loop && this._loopEnd > 0) {
bufferDuration = this._loopEnd;
}
var drift = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * this.drift;
var offset = this._offset - this._overlap + drift;
var detune = this.detune / 100;
var originalFadeIn = this._player.fadeIn;
if (this.loop && this._offset > bufferDuration) {
//play the end
var endSegmentDuration = this._offset - bufferDuration;
this._player.start(this.buffer, time, offset, endSegmentDuration + this._overlap, detune);
//and play the beginning
offset = this._offset % bufferDuration;
this._offset = this._loopStart;
this._player.fadeIn = 0;
this._player.start(this.buffer, time + endSegmentDuration, this._offset, offset + this._overlap, detune);
} else if (this._offset > bufferDuration) {
//set the state to stopped.
this.stop(time);
} else {
if (offset < 0) {
this._player.fadeIn = Math.max(this._player.fadeIn + offset, 0);
offset = 0;
}
this._player.start(this.buffer, time, offset, this.grainSize + this._overlap, detune);
}
this._player.fadeIn = originalFadeIn;
//increment the offset
var duration = this._clock._nextTick - time;
this._offset += duration * this._playbackRate;
};
/**
* Jump to a specific time and play it.
* @param {Time} offset The offset to jump to.
* @param {Time=} time When to make the jump.
* @return {[type]} [description]
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype.scrub = function (offset, time) {
this._offset = this.toSeconds(offset);
this._tick(this.toSeconds(time));
return this;
};
/**
* The playback rate of the sample
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Positive}
* @name playbackRate
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'playbackRate', {
get: function () {
return this._playbackRate;
},
set: function (rate) {
this._playbackRate = rate;
this.grainSize = this._grainSize;
}
});
/**
* The loop start time.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopStart
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'loopStart', {
get: function () {
return this._loopStart;
},
set: function (time) {
this._loopStart = this.toSeconds(time);
}
});
/**
* The loop end time.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name loopEnd
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'loopEnd', {
get: function () {
return this._loopEnd;
},
set: function (time) {
this._loopEnd = this.toSeconds(time);
}
});
/**
* The direction the buffer should play in
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {boolean}
* @name reverse
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'reverse', {
get: function () {
return this.buffer.reverse;
},
set: function (rev) {
this.buffer.reverse = rev;
}
});
/**
* The size of each chunk of audio that the
* buffer is chopped into and played back at.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name grainSize
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'grainSize', {
get: function () {
return this._grainSize;
},
set: function (size) {
this._grainSize = this.toSeconds(size);
this._clock.frequency.value = this._playbackRate / this._grainSize;
}
});
/**
* This is the duration of the cross-fade between
* sucessive grains.
* @memberOf Tone.GrainPlayer#
* @type {Time}
* @name overlap
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype, 'overlap', {
get: function () {
return this._overlap;
},
set: function (time) {
time = this.toSeconds(time);
this._overlap = time;
if (this._overlap < 0) {
this._player.fadeIn = 0.01;
this._player.fadeOut = 0.01;
} else {
this._player.fadeIn = time;
this._player.fadeOut = time;
}
}
});
/**
* Clean up
* @return {Tone.GrainPlayer} this
*/
Tone.GrainPlayer.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.Source.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.buffer.dispose();
this.buffer = null;
this._player.dispose();
this._player = null;
this._clock.dispose();
this._clock = null;
return this;
};
return Tone.GrainPlayer;
});
Module(function (Tone) {
/**
* @class Tone.UserMedia uses MediaDevices.getUserMedia to open up
* and external microphone or audio input. Check
* [MediaDevices API Support](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/MediaDevices/getUserMedia)
* to see which browsers are supported. Access to an external input
* is limited to secure (HTTPS) connections.
*
* @constructor
* @extends {Tone}
* @param {Decibels=} volume The level of the input
* @example
* //list the inputs and open the third one
* var motu = new Tone.UserMedia();
*
* //opening the input asks the user to activate their mic
* motu.open().then(function(){
* //opening is activates the microphone
* //starting lets audio through
* motu.start(10);
* });
*/
Tone.UserMedia = function () {
var options = this.optionsObject(arguments, ['volume'], Tone.UserMedia.defaults);
/**
* The MediaStreamNode
* @type {MediaStreamAudioSourceNode}
* @private
*/
this._mediaStream = null;
/**
* The media stream created by getUserMedia.
* @type {LocalMediaStream}
* @private
*/
this._stream = null;
/**
* The open device
* @type {MediaDeviceInfo}
* @private
*/
this._device = null;
/**
* The output volume node
* @type {Tone.Volume}
* @private
*/
this._volume = this.output = new Tone.Volume(options.volume);
/**
* The volume of the output in decibels.
* @type {Decibels}
* @signal
* @example
* input.volume.value = -6;
*/
this.volume = this._volume.volume;
this._readOnly('volume');
this.mute = options.mute;
};
Tone.extend(Tone.UserMedia);
/**
* the default parameters
* @type {Object}
*/
Tone.UserMedia.defaults = {
'volume': 0,
'mute': false
};
/**
* Open the media stream. If a string is passed in, it is assumed
* to be the label or id of the stream, if a number is passed in,
* it is the input number of the stream.
* @param {String|Number} [labelOrId="default"] The label or id of the audio input media device.
* With no argument, the default stream is opened.
* @return {Promise} The promise is resolved when the stream is open.
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.open = function (labelOrId) {
labelOrId = this.defaultArg(labelOrId, 'default');
return this.enumerateDevices().then(function (devices) {
var device;
if (this.isNumber(labelOrId)) {
device = devices[labelOrId];
} else {
device = devices.find(function (device) {
return device.label === labelOrId || device.deviceId === labelOrId;
});
if (!device) {
//otherwise just take the first one
device = devices[0];
}
}
//didn't find a matching device
if (!device) {
throw new Error('Tone.UserMedia: no matching audio inputs.');
}
this._device = device;
//do getUserMedia
var constraints = {
audio: {
'deviceId': device.deviceId,
'echoCancellation': false,
'sampleRate': this.context.sampleRate
}
};
return navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia(constraints).then(function (stream) {
//start a new source only if the previous one is closed
if (!this._stream) {
this._stream = stream;
//Wrap a MediaStreamSourceNode around the live input stream.
this._mediaStream = this.context.createMediaStreamSource(stream);
//Connect the MediaStreamSourceNode to a gate gain node
this._mediaStream.connect(this.output);
}
return this;
}.bind(this));
}.bind(this));
};
/**
* Close the media stream
* @return {Tone.UserMedia} this
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.close = function () {
if (this._stream) {
this._stream.getAudioTracks().forEach(function (track) {
track.stop();
});
this._stream = null;
//remove the old media stream
this._mediaStream.disconnect();
this._mediaStream = null;
}
this._device = null;
return this;
};
/**
* Returns a promise which resolves with the list of audio input devices available.
* @return {Promise} The promise that is resolved with the devices
* @example
* extInput.enumerateDevices().then(function(devices){
* console.log(devices)
* })
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.enumerateDevices = function () {
return navigator.mediaDevices.enumerateDevices().then(function (devices) {
return devices.filter(function (device) {
return device.kind === 'audioinput';
});
});
};
/**
* Returns the playback state of the source, "started" when the microphone is open
* and "stopped" when the mic is closed.
* @type {Tone.State}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name state
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'state', {
get: function () {
return this._stream && this._stream.active ? Tone.State.Started : Tone.State.Stopped;
}
});
/**
* Returns an identifier for the represented device that is
* persisted across sessions. It is un-guessable by other applications and
* unique to the origin of the calling application. It is reset when the
* user clears cookies (for Private Browsing, a different identifier is
* used that is not persisted across sessions). Returns undefined when the
* device is not open.
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name deviceId
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'deviceId', {
get: function () {
if (this._device) {
return this._device.deviceId;
}
}
});
/**
* Returns a group identifier. Two devices have the
* same group identifier if they belong to the same physical device.
* Returns undefined when the device is not open.
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name groupId
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'groupId', {
get: function () {
if (this._device) {
return this._device.groupId;
}
}
});
/**
* Returns a label describing this device (for example "Built-in Microphone").
* Returns undefined when the device is not open or label is not available
* because of permissions.
* @type {String}
* @readOnly
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name groupId
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'label', {
get: function () {
if (this._device) {
return this._device.label;
}
}
});
/**
* Mute the output.
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @type {boolean}
* @name mute
* @example
* //mute the output
* userMedia.mute = true;
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia.prototype, 'mute', {
get: function () {
return this._volume.mute;
},
set: function (mute) {
this._volume.mute = mute;
}
});
/**
* Clean up.
* @return {Tone.UserMedia} this
*/
Tone.UserMedia.prototype.dispose = function () {
Tone.prototype.dispose.call(this);
this.close();
this._writable('volume');
this._volume.dispose();
this._volume = null;
this.volume = null;
return this;
};
/**
* If getUserMedia is supported by the browser.
* @type {Boolean}
* @memberOf Tone.UserMedia#
* @name supported
* @static
* @readOnly
*/
Object.defineProperty(Tone.UserMedia, 'supported', {
get: function () {
return !Tone.prototype.isUndef(navigator.mediaDevices) && Tone.prototype.isFunction(navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia);
}
});
return Tone.UserMedia;
});
return Tone;
}));